Review Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Population-scale dietary interests during the COVID-19 pandemic
Population-scale dietary interests during the COVID-19 pandemic
The SARS-CoV-2 virus has altered people’s lives around the world, not only through the disease it causes, but also through unprecedented restrictions. Here the authors document population-wide shifts in dietary interests in 18 countries in 2020, as revealed through time series of Google search volumes.
- Kristina Gligorić
- , Arnaud Chiolero
- & Robert West
-
Perspective
| Open Access Embodied neuromorphic intelligence
Embodied neuromorphic intelligence
A grand challenge in robotics is realising intelligent agents capable of autonomous interaction with the environment. In this Perspective, the authors discuss the potential, challenges and future direction of research aimed at demonstrating embodied intelligent robotics via neuromorphic technology.
- Chiara Bartolozzi
- , Giacomo Indiveri
- & Elisa Donati
-
Article
| Open Access Inverse design of 3d molecular structures with conditional generative neural networks
Inverse design of 3d molecular structures with conditional generative neural networks
The targeted discovery of molecules with specific structural and chemical properties is an open challenge in computational chemistry. Here, the authors propose a conditional generative neural network for the inverse design of 3d molecular structures.
- Niklas W. A. Gebauer
- , Michael Gastegger
- & Kristof T. Schütt
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide functional screens enable the prediction of high activity CRISPR-Cas9 and -Cas12a guides in Yarrowia lipolytica
Genome-wide functional screens enable the prediction of high activity CRISPR-Cas9 and -Cas12a guides in Yarrowia lipolytica
The successful use of CRISPR-based mutagenesis in non-conventional microorganisms requires high activity sgRNAs. Here, the authors present DeepGuide, a neural network-based architecture, that learns from genome-wide CRISPR activity profiles to accurately design Cas9 and Cas12a sgRNAs with high activity in the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica.
- Dipankar Baisya
- , Adithya Ramesh
- & Ian Wheeldon
-
Article
| Open Access Density of states prediction for materials discovery via contrastive learning from probabilistic embeddings
Density of states prediction for materials discovery via contrastive learning from probabilistic embeddings
Electrons and phonons give rise to important properties of materials. The machine learning framework Mat2Spec vastly accelerates their computational characterization, enabling discovery of materials for thermoelectrics and solar energy technologies.
- Shufeng Kong
- , Francesco Ricci
- & John M. Gregoire
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum algorithmic measurement
Quantum algorithmic measurement
Applying the language of computational complexity to study real-world experiments requires a rigorous framework. Here, the authors provide such a framework and establish that there can be an exponential savings in resources if an experimentalist can entangle apparatuses with experimental samples.
- Dorit Aharonov
- , Jordan Cotler
- & Xiao-Liang Qi
-
Perspective
| Open Access Perspectives in machine learning for wildlife conservation
Perspectives in machine learning for wildlife conservation
Animal ecologists are increasingly limited by constraints in data processing. Here, Tuia and colleagues discuss how collaboration between ecologists and data scientists can harness machine learning to capitalize on the data generated from technological advances and lead to novel modeling approaches.
- Devis Tuia
- , Benjamin Kellenberger
- & Tanya Berger-Wolf
-
Article
| Open Access Representing individual electronic states for machine learning GW band structures of 2D materials
Representing individual electronic states for machine learning GW band structures of 2D materials
The study introduces novel methods for representing electronic states as input to machine learning models, which is used to learn high-fidelity band structures of two-dimensional materials from low- fidelity input.
- Nikolaj Rørbæk Knøsgaard
- & Kristian Sommer Thygesen
-
Article
| Open Access Brain-inspired global-local learning incorporated with neuromorphic computing
Brain-inspired global-local learning incorporated with neuromorphic computing
Global and local learning represent two distinct approaches to artificial intelligence. In this manuscript, Wu et al present a hybrid learning strategy, drawing from elements of both approaches, and implement it on a co-designed neuromorphic platform.
- Yujie Wu
- , Rong Zhao
- & Luping Shi
-
Article
| Open Access A deep learning framework identifies dimensional representations of Alzheimer’s Disease from brain structure
A deep learning framework identifies dimensional representations of Alzheimer’s Disease from brain structure
Alzheimer’s disease is heterogeneous in its neuroimaging and clinical phenotypes. Here the authors present a semi-supervised deep learning method, Smile-GAN, to show four neurodegenerative patterns and two progression pathways providing prognostic and clinical information.
- Zhijian Yang
- , Ilya M. Nasrallah
- & Balebail Ashok Raj
-
Article
| Open Access A Deep Gravity model for mobility flows generation
A Deep Gravity model for mobility flows generation
The movements of individuals within and among cities influence critical aspects of our society, such as well-being, the spreading of epidemics, and the quality of the environment. Here, the authors use deep neural networks to discover non-linear relationships between geographical variables and mobility flows.
- Filippo Simini
- , Gianni Barlacchi
- & Luca Pappalardo
-
Article
| Open Access Autonomous extraction of millimeter-scale deformation in InSAR time series using deep learning
Autonomous extraction of millimeter-scale deformation in InSAR time series using deep learning
A deep neural network is developed to automatically extract ground deformation from Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar time series. Applied to data over the North Anatolian Fault, the method can detect 2 mm deformation transients and reveals a slow earthquake twice as extensive as previously recognized.
- Bertrand Rouet-Leduc
- , Romain Jolivet
- & Claudia Hulbert
-
Article
| Open Access Spatiotemporal prediction of COVID-19 cases using inter- and intra-county proxies of human interactions
Spatiotemporal prediction of COVID-19 cases using inter- and intra-county proxies of human interactions
Measurements of human interaction through proxies such as social connectedness or movement patterns have proved useful for predictive modeling of COVID-19. In this study, the authors develop a spatiotemporal machine learning model to predict county level new cases in the US using a variety of predictive features.
- Behzad Vahedi
- , Morteza Karimzadeh
- & Hamidreza Zoraghein
-
Article
| Open Access Computational design and optimization of electro-physiological sensors
Computational design and optimization of electro-physiological sensors
Though skin-conformable electro-physiological sensors are attractive for epidermal electronics, their optimal design remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a computational design approach for realizing multi-modal electro-physiological sensors that optimizes electrode layout design.
- Aditya Shekhar Nittala
- , Andreas Karrenbauer
- & Jürgen Steimle
-
Article
| Open Access Nationwide rollout reveals efficacy of epidemic control through digital contact tracing
Nationwide rollout reveals efficacy of epidemic control through digital contact tracing
The effectiveness of digital contact tracing for COVID-19 control remains uncertain. Here, the authors use data from the Smittestopp app, used in Norway in spring 2020, and estimate that 80% of nearby devices were detected by the app, and at least 11% of close contacts were not visible to manual contact tracing.
- Ahmed Elmokashfi
- , Joakim Sundnes
- & Olav Lysne
-
Article
| Open Access Embodied intelligence via learning and evolution
Embodied intelligence via learning and evolution
The authors propose a new framework, deep evolutionary reinforcement learning, evolves agents with diverse morphologies to learn hard locomotion and manipulation tasks in complex environments, and reveals insights into relations between environmental physics, embodied intelligence, and the evolution of rapid learning.
- Agrim Gupta
- , Silvio Savarese
- & Li Fei-Fei
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial intelligence system reduces false-positive findings in the interpretation of breast ultrasound exams
Artificial intelligence system reduces false-positive findings in the interpretation of breast ultrasound exams
Ultrasound is an important imaging modality for the detection and characterization of breast cancer, but it has been noted to have high false-positive rates. Here, the authors present an artificial intelligence system that achieves radiologist-level accuracy in identifying breast cancer in ultrasound imaging.
- Yiqiu Shen
- , Farah E. Shamout
- & Krzysztof J. Geras
-
Article
| Open Access Peering into lunar permanently shadowed regions with deep learning
Peering into lunar permanently shadowed regions with deep learning
Some regions on the Moon are permanently covered in shadow and are therefore extremely difficult to see into. We develop a deep learning driven algorithm which enhances images of these regions, allowing us to see inside them with high resolution for the first time.
- V. T. Bickel
- , B. Moseley
- & M. Shirley
-
Article
| Open Access Epistatic Net allows the sparse spectral regularization of deep neural networks for inferring fitness functions
Epistatic Net allows the sparse spectral regularization of deep neural networks for inferring fitness functions
Finding a biologically-relevant inductive bias for training DNNs on large fitness landscapes is challenging. Here, the authors propose a method called Epistatic Net that improves DNN prediction accuracy and interpretation speed by integrating the knowledge that higher-order epistatic interactions are usually sparse.
- Amirali Aghazadeh
- , Hunter Nisonoff
- & Kannan Ramchandran
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning dismantling and early-warning signals of disintegration in complex systems
Machine learning dismantling and early-warning signals of disintegration in complex systems
Network dismantling allows to find minimum set of units attacking which leads to system’s break down. Grassia et al. propose a deep-learning framework for dismantling of large networks which can be used to quantify the vulnerability of networks and detect early-warning signals of their collapse.
- Marco Grassia
- , Manlio De Domenico
- & Giuseppe Mangioni
-
Article
| Open Access Seasonal Arctic sea ice forecasting with probabilistic deep learning
Seasonal Arctic sea ice forecasting with probabilistic deep learning
Accurate seasonal forecasts of sea ice are highly valuable, particularly in the context of sea ice loss due to global warming. A new machine learning tool for sea ice forecasting offers a substantial increase in accuracy over current physics-based dynamical model predictions.
- Tom R. Andersson
- , J. Scott Hosking
- & Emily Shuckburgh
-
Article
| Open Access A generalizable and accessible approach to machine learning with global satellite imagery
A generalizable and accessible approach to machine learning with global satellite imagery
This paper presents MOSAIKS, a system for planet-scale prediction of multiple outcomes using satellite imagery and machine learning (SIML). MOSAIKS generalizes across prediction domains and has the potential to enhance accessibility of SIML across research disciplines.
- Esther Rolf
- , Jonathan Proctor
- & Solomon Hsiang
-
Article
| Open Access Empirical assessment and comparison of neuro-evolutionary methods for the automatic off-line design of robot swarms
Empirical assessment and comparison of neuro-evolutionary methods for the automatic off-line design of robot swarms
Off-line neuro-evolution produces robot swarms whose good performance in simulation does not often transfer to the real word. With an extensive empirical study, Hasselmann et al. substantiate overfitting as the dominant cause.
- Ken Hasselmann
- , Antoine Ligot
- & Mauro Birattari
-
Article
| Open Access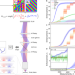 Fast holographic scattering compensation for deep tissue biological imaging
Fast holographic scattering compensation for deep tissue biological imaging
Wavefront shaping is used to overcome scattering in biological tissues during imaging, but determining the compensation is slow. Here, the authors use holographic phase stepping interferometry, where new phase information is updated after each measurement, enabling fast improvement of the wavefront correction.
- Molly A. May
- , Nicolas Barré
- & Alexander Jesacher
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting trends in the quality of state-of-the-art neural networks without access to training or testing data
Predicting trends in the quality of state-of-the-art neural networks without access to training or testing data
In many machine learning applications, one uses pre-trained neural networks, having limited access to training and test data. Martin et al. show how to predict trends in the quality of such neural networks without access to this information, relevant for reproducibility, diagnostics, and validation.
- Charles H. Martin
- , Tongsu (Serena) Peng
- & Michael W. Mahoney
-
Article
| Open Access Correlator convolutional neural networks as an interpretable architecture for image-like quantum matter data
Correlator convolutional neural networks as an interpretable architecture for image-like quantum matter data
Physical principles underlying machine learning analysis of quantum gas microscopy data are not well understood. Here the authors develop a neural network based approach to classify image data in terms of multi-site correlation functions and reveal the role of fourth-order correlations in the Fermi-Hubbard model.
- Cole Miles
- , Annabelle Bohrdt
- & Eun-Ah Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Principled approach to the selection of the embedding dimension of networks
Principled approach to the selection of the embedding dimension of networks
Network embedding is a machine learning technique for construction of low-dimensional representations of large networks. Gu et al. propose a method for the identification of an optimal embedding dimension for the encoding of network structural information inspired by natural language processing.
- Weiwei Gu
- , Aditya Tandon
- & Filippo Radicchi
-
Article
| Open Access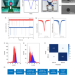 Combining machine learning and nanopore construction creates an artificial intelligence nanopore for coronavirus detection
Combining machine learning and nanopore construction creates an artificial intelligence nanopore for coronavirus detection
Rapid, accurate and specific point-of-care diagnostics can help manage and contain fast-spreading infections. Here, the authors present a nanopore-based system that uses artificial intelligence to discriminate between four coronaviruses in saliva, with little need for sample pre-processing.
- Masateru Taniguchi
- , Shohei Minami
- & Kazunori Tomono
-
Article
| Open Access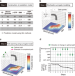 Health improvement framework for actionable treatment planning using a surrogate Bayesian model
Health improvement framework for actionable treatment planning using a surrogate Bayesian model
Clinical decision-making regarding treatments based on personal characteristics leads to effective health improvements. Here, the authors introduce a modeling framework to evaluate the actionability of treatment pathways.
- Kazuki Nakamura
- , Ryosuke Kojima
- & Yasushi Okuno
-
Article
| Open Access Spectral bias and task-model alignment explain generalization in kernel regression and infinitely wide neural networks
Spectral bias and task-model alignment explain generalization in kernel regression and infinitely wide neural networks
Canatar et al. propose a predictive theory of generalization in kernel regression applicable to real data. This theory explains various generalization phenomena observed in wide neural networks, which admit a kernel limit and generalize well despite being overparameterized.
- Abdulkadir Canatar
- , Blake Bordelon
- & Cengiz Pehlevan
-
Article
| Open Access Power of data in quantum machine learning
Power of data in quantum machine learning
Expectations for quantum machine learning are high, but there is currently a lack of rigorous results on which scenarios would actually exhibit a quantum advantage. Here, the authors show how to tell, for a given dataset, whether a quantum model would give any prediction advantage over a classical one.
- Hsin-Yuan Huang
- , Michael Broughton
- & Jarrod R. McClean
-
Article
| Open Access Synaptic metaplasticity in binarized neural networks
Synaptic metaplasticity in binarized neural networks
Deep neural networks usually rapidly forget the previously learned tasks while training new ones. Laborieux et al. propose a method for training binarized neural networks inspired by neuronal metaplasticity that allows to avoid catastrophic forgetting and is relevant for neuromorphic applications.
- Axel Laborieux
- , Maxence Ernoult
- & Damien Querlioz
-
Article
| Open Access Robust high-dimensional memory-augmented neural networks
Robust high-dimensional memory-augmented neural networks
The implementation of memory-augmented neural networks using conventional computer architectures is challenging due to a large number of read and write operations. Here, Karunaratne, Schmuck et al. propose an architecture that enables analog in-memory computing on high-dimensional vectors at accuracy matching 32-bit software equivalent.
- Geethan Karunaratne
- , Manuel Schmuck
- & Abbas Rahimi
-
Article
| Open Access Learned adaptive multiphoton illumination microscopy for large-scale immune response imaging
Learned adaptive multiphoton illumination microscopy for large-scale immune response imaging
Multiphoton microscopy requires precise increases in excitation power with imaging depth to generate contrast without damaging the sample. Here the authors show how an adaptive illumination function can be learned from the sample’s shape and used for in vivo imaging of whole lymph nodes.
- Henry Pinkard
- , Hratch Baghdassarian
- & Laura Waller
-
Article
| Open Access Qualitative similarities and differences in visual object representations between brains and deep networks
Qualitative similarities and differences in visual object representations between brains and deep networks
Deep neural networks are widely considered as good models for biological vision. Here, we describe several qualitative similarities and differences in object representations between brains and deep networks that elucidate when deep networks can be considered good models for biological vision and how they can be improved.
- Georgin Jacob
- , R. T. Pramod
- & S. P. Arun
-
Article
| Open Access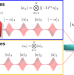 Experimental demonstration of quantum advantage for NP verification with limited information
Experimental demonstration of quantum advantage for NP verification with limited information
Most demonstrations of quantum advantages with optics rely on single photons, and are thus difficult to scale up. Here, the authors use coherent states to demonstrate a quantum advantage for the task of verifying the solution to a NP-complete problem when only partial information on the solution is available.
- Federico Centrone
- , Niraj Kumar
- & Iordanis Kerenidis
-
Article
| Open Access Intelligent driving intelligence test for autonomous vehicles with naturalistic and adversarial environment
Intelligent driving intelligence test for autonomous vehicles with naturalistic and adversarial environment
Tests for autonomous vehicles are usually made in the naturalistic driving environment where safety-critical scenarios are rare. Feng et al. propose a testing approach combining naturalistic and adversarial environment which allows to accelerate testing process and detect dangerous driving events.
- Shuo Feng
- , Xintao Yan
- & Henry X. Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Deep convolutional neural networks to predict cardiovascular risk from computed tomography
Deep convolutional neural networks to predict cardiovascular risk from computed tomography
Coronary artery calcium is an accurate predictor of cardiovascular events but this information is not routinely quantified. Here the authors show a robust and time-efficient deep learning system to automatically quantify coronary calcium on CT scans and predict cardiovascular events in a large, multicentre study.
- Roman Zeleznik
- , Borek Foldyna
- & Hugo J. W. L. Aerts
-
Article
| Open Access A population-based controlled experiment assessing the epidemiological impact of digital contact tracing
A population-based controlled experiment assessing the epidemiological impact of digital contact tracing
While Digital contact tracing (DCT) has been argued to be a valuable complement to manual tracing in the containment of COVID-19, no empirical evidence of its effectiveness is available to date. Here, the authors report the results of a 4-week population-based controlled experiment, where they assessed the impact of the Spanish DCT app.
- Pablo Rodríguez
- , Santiago Graña
- & Lucas Lacasa
-
Article
| Open Access A co-design framework of neural networks and quantum circuits towards quantum advantage
A co-design framework of neural networks and quantum circuits towards quantum advantage
The advantages coming from involving quantum systems in machine learning are still not fully clear. Here, the authors propose a software/hardware co-design framework towards quantum-friendly neural networks showing quantum advantage, representing data as either random variables or numbers in unitary matrices.
- Weiwen Jiang
- , Jinjun Xiong
- & Yiyu Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Survey data and human computation for improved flu tracking
Survey data and human computation for improved flu tracking
Digital trace data from search engines lacks information about the experiences of the individuals generating the data. Here the authors link search data and human computation to build a tracking model of influenza-like illness.
- Stefan Wojcik
- , Avleen S. Bijral
- & David Lazer
-
Article
| Open Access Detection of eye contact with deep neural networks is as accurate as human experts
Detection of eye contact with deep neural networks is as accurate as human experts
Eye contact is a key social behavior and its measurement could facilitate the diagnosis and treatment of autism. Here the authors show that a deep neural network model can detect eye contact as accurately has human experts.
- Eunji Chong
- , Elysha Clark-Whitney
- & James M. Rehg
-
Article
| Open Access Training confounder-free deep learning models for medical applications
Training confounder-free deep learning models for medical applications
The presence of confounding effects is one of the most critical challenges in using deep learning to advance discovery in medical imaging studies. Here, the authors introduce an end-to-end approach for deriving features invariant to confounding factors as inputs to prediction models.
- Qingyu Zhao
- , Ehsan Adeli
- & Kilian M. Pohl
-
Article
| Open Access Designing accurate emulators for scientific processes using calibration-driven deep models
Designing accurate emulators for scientific processes using calibration-driven deep models
The success of machine learning for scientific discovery normally depends on how well the inherent assumptions match the problem in hand. Here, Thiagarajan et al. alleviate this constraint by allowing the change of optimization criterion in a data-driven approach to emulate complex scientific processes.
- Jayaraman J. Thiagarajan
- , Bindya Venkatesh
- & Brian Spears
-
Article
| Open Access Navigating the landscape of multiplayer games
Navigating the landscape of multiplayer games
Multiplayer games can be used as testbeds for the development of learning algorithms for artificial intelligence. Omidshafiei et al. show how to characterize and compare such games using a graph-based approach, generating new games that could potentially be interesting for training in a curriculum.
- Shayegan Omidshafiei
- , Karl Tuyls
- & Rémi Munos
-
Article
| Open Access Capturing human categorization of natural images by combining deep networks and cognitive models
Capturing human categorization of natural images by combining deep networks and cognitive models
Theories of human categorization have traditionally been evaluated in the context of simple, low-dimensional stimuli. In this work, the authors use a large dataset of human behavior over 10,000 natural images to re-evaluate these theories, revealing interesting differences from previous results.
- Ruairidh M. Battleday
- , Joshua C. Peterson
- & Thomas L. Griffiths
-
Article
| Open Access Low cost DNA data storage using photolithographic synthesis and advanced information reconstruction and error correction
Low cost DNA data storage using photolithographic synthesis and advanced information reconstruction and error correction
The current bottleneck for DNA data storage systems is the cost and speed of synthesis. Here, the authors use inexpensive, massively parallel light-directed synthesis and correct for a high error rate with a pipeline of encoding and reconstruction algorithms.
- Philipp L. Antkowiak
- , Jory Lietard
- & Robert N. Grass
-
Article
| Open Access Autoreservoir computing for multistep ahead prediction based on the spatiotemporal information transformation
Autoreservoir computing for multistep ahead prediction based on the spatiotemporal information transformation
Predicting future values of a short time series remains a challenge. Here, the authors propose an auto-reservoir computing framework, which achieved accurate and robust multistep ahead prediction by transforming high-dimensional data into temporal dynamics.
- Pei Chen
- , Rui Liu
- & Luonan Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Identifying domains of applicability of machine learning models for materials science
Identifying domains of applicability of machine learning models for materials science
Machine learning models insufficient for certain screening tasks can still provide valuable predictions in specific sub-domains of the considered materials. Here, the authors introduce a diagnostic tool to detect regions of low expected model error as demonstrated for the case of transparent conducting oxides.
- Christopher Sutton
- , Mario Boley
- & Matthias Scheffler

 Current progress and open challenges for applying deep learning across the biosciences
Current progress and open challenges for applying deep learning across the biosciences