Perspective
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Discovering conservation laws using optimal transport and manifold learning
Discovering conservation laws using optimal transport and manifold learning
Conservation laws are crucial for analyzing and modeling nonlinear dynamical systems; however, identification of conserved quantities is often quite challenging. The authors propose here a geometric approach to discovering conservation laws directly from trajectory data that does not require an explicit dynamical model of the system or detailed time information.
- Peter Y. Lu
- , Rumen Dangovski
- & Marin Soljačić
-
Article
| Open Access Neural network-based Bluetooth synchronization of multiple wearable devices
Neural network-based Bluetooth synchronization of multiple wearable devices
Synchronization of e-wearables can be challenging due to device performance variations. Here, the authors develop a general neural network-based solution that analyses and correct disparities between multiple virtual clocks and demonstrate it for a Bluetooth synchronized motion capture system at high frequency.
- Karthikeyan Kalyanasundaram Balasubramanian
- , Andrea Merello
- & Marco Crepaldi
-
Article
| Open Access Detecting shortcut learning for fair medical AI using shortcut testing
Detecting shortcut learning for fair medical AI using shortcut testing
Diagnosing shortcut learning in clinical models is difficult, as sensitive attributes may be causally linked with disease. Using multitask learning, the authors propose a method to directly test for the presence of shortcut learning in clinical ML systems.
- Alexander Brown
- , Nenad Tomasev
- & Jessica Schrouff
-
Article
| Open Access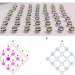 Coherent movement of error-prone individuals through mechanical coupling
Coherent movement of error-prone individuals through mechanical coupling
In biology, individuals are known to achieve higher navigation accuracy when moving in a group compared to single animals. The authors show that simple self-propelled robotic modules that are incapable of accurate motion as individuals can achieve accurate group navigation once coupled via deformable elastic links.
- Federico Pratissoli
- , Andreagiovanni Reina
- & Roderich Groß
-
Article
| Open Access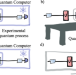 Out-of-distribution generalization for learning quantum dynamics
Out-of-distribution generalization for learning quantum dynamics
Generalization - that is, the ability to extrapolate from training data to unseen data - is fundamental in machine learning, and thus also for quantum ML. Here, the authors show that QML algorithms are able to generalise the training they had on a specific distribution and learn over different distributions.
- Matthias C. Caro
- , Hsin-Yuan Huang
- & Zoë Holmes
-
Article
| Open Access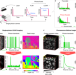 CASPI: collaborative photon processing for active single-photon imaging
CASPI: collaborative photon processing for active single-photon imaging
The sparse, noisy, and distorted raw photon data captured by single-photon cameras make it difficult to estimate scene properties under challenging illumination conditions. Here, the authors present Collaborative photon processing for Active Single-Photon Imaging (CASPI), a technology-agnostic, application-agnostic, and training-free photon processing pipeline for high-resolution single-photon cameras.
- Jongho Lee
- , Atul Ingle
- & Mohit Gupta
-
Article
| Open Access Data-driven direct diagnosis of Li-ion batteries connected to photovoltaics
Data-driven direct diagnosis of Li-ion batteries connected to photovoltaics
Li-ion batteries are used to store energy harvested from photovoltaics. However, battery use is sporadic and standard diagnostic methods cannot be applied. Here, the authors propose a methodology for diagnosing photovoltaics-connected Li-ion batteries that use trained machine learning algorithms.
- Matthieu Dubarry
- , Nahuel Costa
- & Dax Matthews
-
Article
| Open Access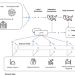 Evidence-driven spatiotemporal COVID-19 hospitalization prediction with Ising dynamics
Evidence-driven spatiotemporal COVID-19 hospitalization prediction with Ising dynamics
Amid the COVID-19 pandemic, accurate hospitalization predictions are vital. Here, the authors show that a deep learning model based on statistical mechanics is able to forecast hospitalizations, supporting targeted vaccination efforts.
- Junyi Gao
- , Joerg Heintz
- & Jimeng Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Decentralized federated learning through proxy model sharing
Decentralized federated learning through proxy model sharing
Federated learning enables multi-institutional collaborations on decentralized data with improved privacy protection. Here, authors propose a new scheme for decentralized federated learning with much less communication overhead and stronger privacy.
- Shivam Kalra
- , Junfeng Wen
- & H. R. Tizhoosh
-
Article
| Open Access General framework for E(3)-equivariant neural network representation of density functional theory Hamiltonian
General framework for E(3)-equivariant neural network representation of density functional theory Hamiltonian
Fundamental symmetries are crucial to the deep-learning modeling of physical systems. Here the authors use equivariant neural networks preserving the Euclidean symmetries to accelerate electronic structure calculations by orders of magnitude keeping sub-meV accuracy.
- Xiaoxun Gong
- , He Li
- & Yong Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Optical neural network via loose neuron array and functional learning
Optical neural network via loose neuron array and functional learning
Here the authors have realized a programmable incoherent optical neural network that delivers light-speed, high-bandwidth, and power-efficient neural network inference via processing parallel visible light signals in the free space.
- Yuchi Huo
- , Hujun Bao
- & Sung-Eui Yoon
-
Article
| Open Access Cross-modal autoencoder framework learns holistic representations of cardiovascular state
Cross-modal autoencoder framework learns holistic representations of cardiovascular state
A challenge in diagnostics is integrating different data modalities to characterize physiological state. Here, the authors show, using the heart as a model system, that cross-modal autoencoders can integrate and translate modalities to improve diagnostics and identify associated genetic variants.
- Adityanarayanan Radhakrishnan
- , Sam F. Friedman
- & Caroline Uhler
-
Article
| Open Access Complex computation from developmental priors
Complex computation from developmental priors
Neuroscience has long inspired AI, however the neuroevolutionary search that produces sophisticated behaviors has not been systematized. This paper defines neurodevelopmental ML as a discovery process for structures that promote complex computations.
- Dániel L. Barabási
- , Taliesin Beynon
- & Nicolas Perez-Nieves
-
Article
| Open Access Random fractal-enabled physical unclonable functions with dynamic AI authentication
Random fractal-enabled physical unclonable functions with dynamic AI authentication
In order to be used on a large scale, unclonable tags for anti-counterfeiting should allow mass production at low cost, as well as fast and easy authentication. Here, the authors show how to use one-step annealing of gold films to quickly realize robust tags with high capacity, allowing fast deep-learning based authentication via smartphone readout.
- Ningfei Sun
- , Ziyu Chen
- & Qian Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Combining data and theory for derivable scientific discovery with AI-Descartes
Combining data and theory for derivable scientific discovery with AI-Descartes
Automatic extraction of consistent governing laws from data is a challenging problem. The authors propose a method that takes as input experimental data and background theory and combines symbolic regression with logical reasoning to obtain scientifically meaningful symbolic formulas.
- Cristina Cornelio
- , Sanjeeb Dash
- & Lior Horesh
-
Article
| Open Access Lacking mechanistic disease definitions and corresponding association data hamper progress in network medicine and beyond
Lacking mechanistic disease definitions and corresponding association data hamper progress in network medicine and beyond
Large-scale disease-association data are widely used for pathomechanism mining, even if disease definitions used for annotation are mostly phenotype-based. Here, the authors show that this bias can lead to a blurred view on disease mechanisms, highlighting the need for close-up studies based on molecular data for well-characterized patient cohorts.
- Sepideh Sadegh
- , James Skelton
- & David B. Blumenthal
-
Perspective
| Open Access Catalyzing next-generation Artificial Intelligence through NeuroAI
Catalyzing next-generation Artificial Intelligence through NeuroAI
One of the ambitions of computational neuroscience is that we will continue to make improvements in the field of artificial intelligence that will be informed by advances in our understanding of how the brains of various species evolved to process information. To that end, here the authors propose an expanded version of the Turing test that involves embodied sensorimotor interactions with the world as a new framework for accelerating progress in artificial intelligence.
- Anthony Zador
- , Sean Escola
- & Doris Tsao
-
Article
| Open Access A spectral method for assessing and combining multiple data visualizations
A spectral method for assessing and combining multiple data visualizations
Dimension reduction is an indispensable part of modern data science, and many algorithms have been developed. Here, the authors develop a theoretically justified, simple to use and reliable spectral method to assess and combine multiple dimension reduction visualizations of a given dataset from diverse algorithms.
- Rong Ma
- , Eric D. Sun
- & James Zou
-
Article
| Open Access Universal expressiveness of variational quantum classifiers and quantum kernels for support vector machines
Universal expressiveness of variational quantum classifiers and quantum kernels for support vector machines
Rigorous results about the real computational advantages of quantum machine learning are few. Here, the authors prove that a PROMISEBQP-complete problem can be expressed by variational quantum classifiers and quantum support vector machines, meaning that a quantum advantage can be achieved for all ML classification problems that cannot be classically solved in polynomial time.
- Jonas Jäger
- & Roman V. Krems
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum machine learning beyond kernel methods
Quantum machine learning beyond kernel methods
Comparing the capabilities of different quantum machine learning protocols is difficult. Here, the authors show that different learning models based on parametrized quantum circuits can all be seen as quantum linear models, thus driving general conclusions on their resource requirements and capabilities.
- Sofiene Jerbi
- , Lukas J. Fiderer
- & Vedran Dunjko
-
Article
| Open Access Digital circuits and neural networks based on acid-base chemistry implemented by robotic fluid handling
Digital circuits and neural networks based on acid-base chemistry implemented by robotic fluid handling
The complementarity of acids and bases is a fundamental chemical concept. Here, the authors use simple acid-base chemistry to encode binary information and perform information processing including digital circuits and neural networks using robotic fluid handling.
- Ahmed A. Agiza
- , Kady Oakley
- & Sherief Reda
-
Article
| Open Access High-order tensor flow processing using integrated photonic circuits
High-order tensor flow processing using integrated photonic circuits
Convolutional operation is a very efficient way to handle tensor analytics, but it consumes a large quantity of additional memory. Here, the authors demonstrate an integrated photonic tensor processor which directly handles high-order tensors without tensor-matrix transformation.
- Shaofu Xu
- , Jing Wang
- & Weiwen Zou
-
Article
| Open Access Sleep-like unsupervised replay reduces catastrophic forgetting in artificial neural networks
Sleep-like unsupervised replay reduces catastrophic forgetting in artificial neural networks
Artificial neural networks are known to perform well on recently learned tasks, at the same time forgetting previously learned ones. The authors propose an unsupervised sleep replay algorithm to recover old tasks synaptic connectivity that may have been damaged after new task training.
- Timothy Tadros
- , Giri P. Krishnan
- & Maxim Bazhenov
-
Article
| Open Access A Multifaceted benchmarking of synthetic electronic health record generation models
A Multifaceted benchmarking of synthetic electronic health record generation models
Synthetic health data have the potential to mitigate privacy concerns when sharing data to support biomedical research and the development of innovative healthcare applications. In this work, the authors introduce a use case oriented benchmarking framework to evaluate data synthesis models through a set of utility and privacy metrics.
- Chao Yan
- , Yao Yan
- & Bradley A. Malin
-
Article
| Open Access Negotiation and honesty in artificial intelligence methods for the board game of Diplomacy
Negotiation and honesty in artificial intelligence methods for the board game of Diplomacy
Artificial Intelligence has achieved success in a variety of single-player or competitive two-player games with no communication between players. Here, the authors propose an approach where Artificial Intelligence agents have ability to negotiate and form agreements, playing the board game Diplomacy.
- János Kramár
- , Tom Eccles
- & Yoram Bachrach
-
Article
| Open Access Federated learning enables big data for rare cancer boundary detection
Federated learning enables big data for rare cancer boundary detection
Federated ML (FL) provides an alternative to train accurate and generalizable ML models, by only sharing numerical model updates. Here, the authors present the largest FL study to-date to generate an automatic tumor boundary detector for glioblastoma.
- Sarthak Pati
- , Ujjwal Baid
- & Spyridon Bakas
-
Article
| Open Access Visual motion perception as online hierarchical inference
Visual motion perception as online hierarchical inference
How the human visual system leverages the rich structure in object motion for perception remains unclear. Here, Bill et al. propose a theory of how the brain could infer motion relations in real time and offer a unifying explanation for various perceptual phenomena.
- Johannes Bill
- , Samuel J. Gershman
- & Jan Drugowitsch
-
Article
| Open Access Imperceptible, designable, and scalable braided electronic cord
Imperceptible, designable, and scalable braided electronic cord
Inspired by the characteristics of textile-based flexible electronic sensors, the authors report a braided electronic cord with a low-cost, and automated fabrication to realize imperceptible, designable, and scalable user interfaces with the features of user-friendliness, excellent durability and rich interaction mode.
- Min Chen
- , Jingyu Ouyang
- & Guangming Tao
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping global dynamics of benchmark creation and saturation in artificial intelligence
Mapping global dynamics of benchmark creation and saturation in artificial intelligence
Recent studies raised concerns over the state of AI benchmarking, reporting issues such as benchmark overfitting, benchmark saturation and increasing centralization of benchmark dataset creation. To facilitate monitoring of the health of the AI benchmarking ecosystem, the authors introduce methodologies for creating condensed maps of the global dynamics of benchmark.
- Simon Ott
- , Adriano Barbosa-Silva
- & Matthias Samwald
-
Article
| Open Access Single-shot quantum error correction with the three-dimensional subsystem toric code
Single-shot quantum error correction with the three-dimensional subsystem toric code
Topological quantum error correction is a promising approach towards fault-tolerant quantum computing, but suffers from large time overhead. Here, the authors generalise the stabiliser toric code to a single-shot 3D subsystem toric code, featuring good performance and resilience to measurement errors.
- Aleksander Kubica
- & Michael Vasmer
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible learning of quantum states with generative query neural networks
Flexible learning of quantum states with generative query neural networks
The use of machine learning to characterise quantum states has been demonstrated, but usually training the algorithm using data from the same state one wants to characterise. Here, the authors show an algorithm that can learn all states that share structural similarities with the ones used for the training.
- Yan Zhu
- , Ya-Dong Wu
- & Giulio Chiribella
-
Article
| Open Access Detecting the ultra low dimensionality of real networks
Detecting the ultra low dimensionality of real networks
Reducing of dimension is often necessary to detect and analyze patterns in large datasets and complex networks. Here, the authors propose a method for detection of the intrinsic dimensionality of high-dimensional networks to reproduce their complex structure using a reduced tractable geometric representation.
- Pedro Almagro
- , Marián Boguñá
- & M. Ángeles Serrano
-
Article
| Open Access A neural theory for counting memories
A neural theory for counting memories
It is unclear how the brain keeps track of the number of times different events are experienced. Here, a neural circuit is proposed for this problem inspired by a classic solution in computer science, and evidence of this circuit is shown in the fruit fly brain.
- Sanjoy Dasgupta
- , Daisuke Hattori
- & Saket Navlakha
-
Article
| Open Access Noise-injected analog Ising machines enable ultrafast statistical sampling and machine learning
Noise-injected analog Ising machines enable ultrafast statistical sampling and machine learning
Ising machines are accelerators for computing difficult optimization problems. In this work, Böhm et al. demonstrate a method that extends their use to perform statistical sampling and machine learning orders-of-magnitudes faster than digital computers.
- Fabian Böhm
- , Diego Alonso-Urquijo
- & Guy Van der Sande
-
Article
| Open Access Noise-resilient and high-speed deep learning with coherent silicon photonics
Noise-resilient and high-speed deep learning with coherent silicon photonics
The challenge of high-speed and high-accuracy coherent photonic neurons for deep learning applications lies to solve noise related issues. Here, Mourgias-Alexandris et al. address this problem by introducing a noise-resilient hardware architectural and a deep learning training platform.
- G. Mourgias-Alexandris
- , M. Moralis-Pegios
- & N. Pleros
-
Article
| Open Access Clustering by measuring local direction centrality for data with heterogeneous density and weak connectivity
Clustering by measuring local direction centrality for data with heterogeneous density and weak connectivity
Clustering is a powerful machine learning method for discovering similar patterns according to the proximity of elements in feature space. Here the authors propose a local direction centrality clustering algorithm that copes with heterogeneous density and weak connectivity issues.
- Dehua Peng
- , Zhipeng Gui
- & Huayi Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesizing theories of human language with Bayesian program induction
Synthesizing theories of human language with Bayesian program induction
Humans can infer rules for building words in a new language from a handful of examples, and linguists also can infer language patterns across related languages. Here, the authors provide an algorithm which models these grammatical abilities by synthesizing human-understandable programs for building words.
- Kevin Ellis
- , Adam Albright
- & Timothy J. O’Donnell
-
Article
| Open Access Generalization in quantum machine learning from few training data
Generalization in quantum machine learning from few training data
The power of quantum machine learning algorithms based on parametrised quantum circuits are still not fully understood. Here, the authors report rigorous bounds on the generalisation error in variational QML, confirming how known implementable models generalize well from an efficient amount of training data.
- Matthias C. Caro
- , Hsin-Yuan Huang
- & Patrick J. Coles
-
Article
| Open Access Secure human action recognition by encrypted neural network inference
Secure human action recognition by encrypted neural network inference
Advanced computer vision technology can provide near real-time home monitoring to support "aging in place” by detecting falls and symptoms related to seizures and stroke. In this paper, the authors propose a strategy that uses homomorphic encryption, which guarantees information confidentiality while retaining action detection.
- Miran Kim
- , Xiaoqian Jiang
- & Shayan Shams
-
Article
| Open Access Explaining a series of models by propagating Shapley values
Explaining a series of models by propagating Shapley values
Series of machine learning models, relevant for tasks in biology, medicine, and finance, usually involve complex feature attribution techniques. The authors introduce a tractable method to compute local feature attributions for a series of machine learning models inspired by connections to the Shapley value.
- Hugh Chen
- , Scott M. Lundberg
- & Su-In Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Lead federated neuromorphic learning for wireless edge artificial intelligence
Lead federated neuromorphic learning for wireless edge artificial intelligence
Designing energy-efficient computing solution for the implementation of AI algorithms in edge devices remains a challenge. Yang et al. proposes a decentralized brain-inspired computing method enabling multiple edge devices to collaboratively train a global model without a fixed central coordinator.
- Helin Yang
- , Kwok-Yan Lam
- & H. Vincent Poor
-
Article
| Open Access Surrogate- and invariance-boosted contrastive learning for data-scarce applications in science
Surrogate- and invariance-boosted contrastive learning for data-scarce applications in science
Deep learning techniques usually require a large quantity of training data and may be challenging for scarce datasets. The authors propose a framework that involves contrastive and transfer learning and reduces data requirements for training while keeping the prediction accuracy.
- Charlotte Loh
- , Thomas Christensen
- & Marin Soljačić
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanical intelligence for learning embodied sensor-object relationships
Mechanical intelligence for learning embodied sensor-object relationships
Information-based search strategies are relevant for the learning of interacting agents dynamics and usually need predefined data. The authors propose a method to collect data for learning a predictive sensor model, without requiring domain knowledge, human input, or previously existing data.
- Ahalya Prabhakar
- & Todd Murphey
-
Article
| Open Access Instant diagnosis of gastroscopic biopsy via deep-learned single-shot femtosecond stimulated Raman histology
Instant diagnosis of gastroscopic biopsy via deep-learned single-shot femtosecond stimulated Raman histology
Diagnosis of gastric cancer currently requires gastroscopic biopsy, which requires time and expertize to perform. Here, the authors demonstrate a femto-SRS imaging method which showed high accuracy in diagnosing gastric cancer without the need for pathologistbased diagnosis.
- Zhijie Liu
- , Wei Su
- & Minbiao Ji
-
Article
| Open Access Towards artificial general intelligence via a multimodal foundation model
Towards artificial general intelligence via a multimodal foundation model
Artificial intelligence approaches inspired by human cognitive function have usually single learned ability. The authors propose a multimodal foundation model that demonstrates the cross-domain learning and adaptation for broad range of downstream cognitive tasks.
- Nanyi Fei
- , Zhiwu Lu
- & Ji-Rong Wen
-
Article
| Open Access E(3)-equivariant graph neural networks for data-efficient and accurate interatomic potentials
E(3)-equivariant graph neural networks for data-efficient and accurate interatomic potentials
An E(3)-equivariant deep learning interatomic potential is introduced for accelerating molecular dynamics simulations. The method obtains state-of-the-art accuracy, can faithfully describe dynamics of complex systems with remarkable sample efficiency.
- Simon Batzner
- , Albert Musaelian
- & Boris Kozinsky
-
Article
| Open Access Automated exploitation of the big configuration space of large adsorbates on transition metals reveals chemistry feasibility
Automated exploitation of the big configuration space of large adsorbates on transition metals reveals chemistry feasibility
The discovery of heterogeneous catalysts for large molecule conversion has been lagging due to the combinatorial inventory of intermediates. Here, the author presents an automated framework to explore the chemical space of reaction intermediates.
- Geun Ho Gu
- , Miriam Lee
- & Dionisios G. Vlachos
-
Article
| Open Access The neural coding framework for learning generative models
The neural coding framework for learning generative models
Brain-inspired neural generative models can be designed to learn complex probability distributions from data. Here the authors propose a neural generative computational framework, inspired by the theory of predictive processing in the brain, that facilitates parallel computing for complex tasks.
- Alexander Ororbia
- & Daniel Kifer
-
Article
| Open Access Accurate auto-labeling of chest X-ray images based on quantitative similarity to an explainable AI model
Accurate auto-labeling of chest X-ray images based on quantitative similarity to an explainable AI model
Here the authors develop a method for accurate auto-labelling of CXR images from large public datasets based on quantitative probability-of similarity to an explainable AI model. The labels can be used to fine-tune the original model through iterative re-training.
- Doyun Kim
- , Joowon Chung
- & Synho Do

 Applied machine learning as a driver for polymeric biomaterials design
Applied machine learning as a driver for polymeric biomaterials design