News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Research Highlight |
 Lab-grown fat with texture like the real thing could enrich cultured meat
Lab-grown fat with texture like the real thing could enrich cultured meat
Approach could make it easier to scale up production of cultivated meat.
-
Nature Video |
 ‘Touch-taste’: how the octopus repurposed its nervous system to hunt
‘Touch-taste’: how the octopus repurposed its nervous system to hunt
Researchers identify the structural basis for octopuses chemo-tactile sense.
- Dan Fox
-
Article |
 Chromosomal fragile site breakage by EBV-encoded EBNA1 at clustered repeats
Chromosomal fragile site breakage by EBV-encoded EBNA1 at clustered repeats
Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 1 is shown to induce breakage of a fragile site on chromosome 11 by binding to a cluster of EBV-like imperfect palindromic repeats.
- Julia Su Zhou Li
- , Ammal Abbasi
- & Don W. Cleveland
-
News |
 Stem-cell-derived ‘embryos’ implanted in monkeys
Stem-cell-derived ‘embryos’ implanted in monkeys
An embryo-like ball of cells offers a way to study pregnancy and its complications without the typical ethical dilemmas.
- Gemma Conroy
-
Research Briefing |
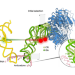 Mechanism of messenger-RNA decoding in humans illuminated
Mechanism of messenger-RNA decoding in humans illuminated
Intracellular machines called ribosomes use messenger-RNA sequences to synthesize proteins. Investigations using single-molecule imaging and cryo-electron microscopy techniques reveal structural and kinetic differences in how human ribosomes function compared with those of bacteria. These differences explain why ribosomes in cell-nucleus-bearing species are slower and more accurate than their bacterial counterparts.
-
Article |
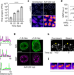 A viral biomolecular condensate coordinates assembly of progeny particles
A viral biomolecular condensate coordinates assembly of progeny particles
Phase separation of the human adenovirus 52-kDa protein has an essential role in the formation of biomolecular condensates, regulating the coordinated assembly of viral progeny particles.
- Matthew Charman
- , Nicholas Grams
- & Matthew D. Weitzman
-
News & Views |
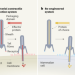 Mix-and-match tools for protein injection into cells
Mix-and-match tools for protein injection into cells
An injection system from bacteria has been re-engineered in an effort to develop a programmable system for protein delivery into cells. Its customizability opens the door to a multitude of biomedical applications.
- Charles F. Ericson
- & Martin Pilhofer
-
Article |
 Norovirus MLKL-like protein initiates cell death to induce viral egress
Norovirus MLKL-like protein initiates cell death to induce viral egress
The murine norovirus NTPase NS3 induces mitochondrial disruption, resulting in cell death, which is required for viral egress.
- Guoxun Wang
- , Di Zhang
- & Tiffany A. Reese
-
Article |
 Formin-mediated nuclear actin at androgen receptors promotes transcription
Formin-mediated nuclear actin at androgen receptors promotes transcription
Functional mutations identified in patients with androgen insensitivity syndrome, in the formin and actin nucleator DAAM2, uncover signal-regulated nuclear actin assembly at a steroid hormone receptor necessary for transcription.
- Julian Knerr
- , Ralf Werner
- & Nadine C. Hornig
-
News & Views |
 From the archive: the cell cycle and Antarctic exploration
From the archive: the cell cycle and Antarctic exploration
Snippets from Nature’s past.
-
Research Briefing |
 Genome doubling perturbs DNA packing and promotes cancer development
Genome doubling perturbs DNA packing and promotes cancer development
Cells in which the whole genome has been doubled do not upscale protein synthesis to cope with the increase in DNA. Instead, a shortage of proteins that regulate the packing of DNA in the nucleus leads to poor segregation of DNA structures, which eventually contributes to the development of cancer.
-
Research Briefing |
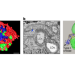 Diversity of mitochondrial networks in lung cancer imaged
Diversity of mitochondrial networks in lung cancer imaged
The structure and function of mitochondrial networks were analysed using a combination of approaches to generate detailed maps of these cellular organelles. This analysis revealed that the mitochondria in different subtypes of lung cancer show distinct functional and structural signatures.
-
Article |
 Lactate regulates cell cycle by remodelling the anaphase promoting complex
Lactate regulates cell cycle by remodelling the anaphase promoting complex
Discovery of a biochemical mechanism through which lactate binds and inhibits the SUMO protease SENP1, stimulating timed degradation of cell cycle proteins, and resulting in mitotic exit.
- Weihai Liu
- , Yun Wang
- & Edward T. Chouchani
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial mapping of mitochondrial networks and bioenergetics in lung cancer
Spatial mapping of mitochondrial networks and bioenergetics in lung cancer
A study describing an approach that combines imaging and profiling techniques to structurally and functionally analyse lung cancer in vivo, revealing heterogeneous mitochondrial networks and an association between bioenergetic phenotypes and mitochondrial organization and function.
- Mingqi Han
- , Eric A. Bushong
- & David B. Shackelford
-
News |
 Gigantic map of fly brain is a first for a complex animal
Gigantic map of fly brain is a first for a complex animal
Fruit fly ‘connectome’ will help researchers to study how the brain works, and could further understanding of neurological diseases.
- Miryam Naddaf
-
News |
 The mice with two dads: scientists create eggs from male cells
The mice with two dads: scientists create eggs from male cells
Proof-of-concept mouse experiment will have a long road before use in humans is possible.
- Heidi Ledford
- & Max Kozlov
-
News & Views |
 Mitochondrial molecule controls inflammation
Mitochondrial molecule controls inflammation
Cellular organelles called mitochondria contain their own DNA and RNA. The molecule fumarate has now been found to trigger the release of these nucleic acids into the cytosol, aberrantly activating inflammation.
- Taylor A. Poor
- & Navdeep S. Chandel
-
Article
| Open Access Fumarate induces vesicular release of mtDNA to drive innate immunity
Fumarate induces vesicular release of mtDNA to drive innate immunity
Fumarate metabolism regulates the innate immune response through a mechanism in which high levels of fumarate result in the generation of mitochondrial-derived vesicles and the release of mitochondrial DNA into the cytosol, which activates inflammatory pathways.
- Vincent Zecchini
- , Vincent Paupe
- & Christian Frezza
-
Article |
 Macrophage fumarate hydratase restrains mtRNA-mediated interferon production
Macrophage fumarate hydratase restrains mtRNA-mediated interferon production
Inhibition of the tricarboxylic acid cycle enzyme fumarate hydratase leads to deregulation of cytokine production in macrophages, which has implications in human diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Alexander Hooftman
- , Christian G. Peace
- & Luke A. J. O’Neill
-
Article
| Open Access Autoregulation of GPCR signalling through the third intracellular loop
Autoregulation of GPCR signalling through the third intracellular loop
Biochemical and molecular dynamics studies show that the third intracellular loop of G protein-coupled receptors autoregulates the receptor activity and tunes the signalling specificity by controlling access to the G protein-binding site.
- Fredrik Sadler
- , Ning Ma
- & Sivaraj Sivaramakrishnan
-
Article |
 Co-opting signalling molecules enables logic-gated control of CAR T cells
Co-opting signalling molecules enables logic-gated control of CAR T cells
Logic gating is used to develop a CAR T cell platform that is highly specific and allows the activity of T cells to be restricted to the encounter of two antigens, thus reducing on-target, off-tumour toxicity.
- Aidan M. Tousley
- , Maria Caterina Rotiroti
- & Robbie G. Majzner
-
Article |
 Nucleolar URB1 ensures 3′ ETS rRNA removal to prevent exosome surveillance
Nucleolar URB1 ensures 3′ ETS rRNA removal to prevent exosome surveillance
A high-resolution microscopy screen of candidate nucleolar proteins identifies URB1 as a protein that is confined to the periphery of the dense fibrillar component, with key roles in pre-ribosomal RNA folding and processing.
- Lin Shan
- , Guang Xu
- & Ling-Ling Chen
-
Article |
 Molecular sensing of mechano- and ligand-dependent adhesion GPCR dissociation
Molecular sensing of mechano- and ligand-dependent adhesion GPCR dissociation
A technique to detect the release of N-terminal fragments of Drosophila adhesion G-protein-coupled receptors (aGPCRs) provides insight into the dissociation of aGPCRs, and shows that receptor autoproteolysis enables non-cell-autonomous activity of aGPCRs in the brain.
- Nicole Scholz
- , Anne-Kristin Dahse
- & Tobias Langenhan
-
News & Views |
 Bleb protrusions help cancer cells to cheat death
Bleb protrusions help cancer cells to cheat death
Processes that regulate cell death can rid the body of cancer cells. However, some of these cells have ways to thwart such processes, and one such death-defying mechanism has been found to rely on cellular protrusions called blebs.
- Michal Reichman-Fried
- & Erez Raz
-
Article |
 Blebs promote cell survival by assembling oncogenic signalling hubs
Blebs promote cell survival by assembling oncogenic signalling hubs
A study demonstrates that sustained membrane blebs in cancer cells recruit curvature-sensing septins that form plasma membrane-proximal signalling hubs that promote cancer cell survival.
- Andrew D. Weems
- , Erik S. Welf
- & Gaudenz Danuser
-
News & Views |
 Path unveiled for protein entry into chloroplasts
Path unveiled for protein entry into chloroplasts
Structures of the machinery for importing proteins into chloroplast organelles of algae, determined using cryo-electron microscopy, have opened a new chapter in efforts to understand how chloroplasts are built.
- Takashi Hirashima
- & Toshiya Endo
-
Research Briefing |
 Structural insights into how a blood-pressure drug inhibits an ion transporter
Structural insights into how a blood-pressure drug inhibits an ion transporter
The sodium–chloride cotransporter (NCC) is a protein dimer central to sodium handling by the kidney and is the target of an important class of drug for high blood pressure called thiazide diuretics. Structures of human NCC with and without a bound thiazide diuretic provide insights into NCC transport function and drug inhibition.
-
Article
| Open Access Telomere-to-mitochondria signalling by ZBP1 mediates replicative crisis
Telomere-to-mitochondria signalling by ZBP1 mediates replicative crisis
Dysfunctional telomeres activate innate immune responses through mitochondrial TERRA–ZBP1 complexes to eliminate cells that are destined for neoplastic transformation.
- Joe Nassour
- , Lucia Gutierrez Aguiar
- & Jan Karlseder
-
Obituary |
 C. David Allis (1951–2023)
C. David Allis (1951–2023)
Biologist who revolutionized the chromatin and gene-expression field.
- Sharon Dent
- & Shiv Grewal
-
News |
 Dogma-defying bacteria package DNA in unusual ways
Dogma-defying bacteria package DNA in unusual ways
Some bacteria appear to encase their genomes in proteins called histones — which weren’t thought to exist in bacterial cells.
- Heidi Ledford
-
Article |
 Architecture of chloroplast TOC–TIC translocon supercomplex
Architecture of chloroplast TOC–TIC translocon supercomplex
A cryo-electron microscopy analysis of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii TOC–TIC supercomplex reveals that Tic214 traverses the chloroplast inner membrane, the intermembrane space and the outer membrane, connecting the TOC complex with the TIC proteins.
- Hao Liu
- , Anjie Li
- & Zhenfeng Liu
-
Research Briefing |
 A census of complexes formed by mitochondrial proteins
A census of complexes formed by mitochondrial proteins
Mitochondria are intracellular organelles that contain a large set of proteins to help them produce energy, among other functions. A systematic analysis reveals how mitochondrial proteins are organized into complexes and assemblies, facilitating the identification of the molecular mechanisms and pathways that underlie the organelle’s many functions.
-
Research Briefing |
 A transient protein megacomplex that controls degradation of cell components
A transient protein megacomplex that controls degradation of cell components
Whether to self-degrade is a crucial cellular decision. When nutrients are abundant, degradation of cell components is reduced through inactivation of a protein called TFEB by the enzyme complex mTORC1. The structure of a megacomplex consisting of 36 polypeptide chains, which presents TFEB to mTORC1, has been resolved.
-
Article
| Open Access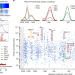 Mitochondrial complexome reveals quality-control pathways of protein import
Mitochondrial complexome reveals quality-control pathways of protein import
An analysis of MitCOM—a comprehensive resource for the identification, organization and interaction of mitochondrial machineries and pathways in yeast—identifies a constitutive pathway for the removal of preproteins.
- Uwe Schulte
- , Fabian den Brave
- & Thomas Becker
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the lysosomal mTORC1–TFEB–Rag–Ragulator megacomplex
Structure of the lysosomal mTORC1–TFEB–Rag–Ragulator megacomplex
Cryogenic-electron microscopy is used to determine the structure of TFEB as presented to mTORC1 for phosphorylation and an explanation is found for the strong dependence of TFEB phosphorylation on FLCN and the RagC GDP state.
- Zhicheng Cui
- , Gennaro Napolitano
- & James H. Hurley
-
Research Briefing |
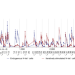 Immune cells’ ability to persist and replicate long outlives species lifespan
Immune cells’ ability to persist and replicate long outlives species lifespan
Immune cells called T cells were activated in mice and transferred to new mice; the process was repeated several times. The T-cell population derived from the original mice continued to respond to the same immune trigger after ten years — which is about four times the lifespan of a mouse.
-
Article |
 Functional T cells are capable of supernumerary cell division and longevity
Functional T cells are capable of supernumerary cell division and longevity
Through iterative cycles of viral challenge and rechallenge over ten years, mouse T cells are demonstrated to have essentially infinite potential for population expansion and longevity without malignant transformation or loss of functional competence.
- Andrew G. Soerens
- , Marco Künzli
- & David Masopust
-
News & Views |
 Targets mapped for almost all human kinase enzymes
Targets mapped for almost all human kinase enzymes
A computational resource can identify candidate protein targets for almost all members of a major class of kinase enzyme in humans, with implications for understanding cell signalling in health and disease.
- Sean J. Humphrey
- & Elise J. Needham
-
Article
| Open Access An atlas of substrate specificities for the human serine/threonine kinome
An atlas of substrate specificities for the human serine/threonine kinome
Analysis of the kinase activity of 300 protein Ser/Thr kinases reveals that the substrate specificity of the kinome is substantially more diverse than expected and is driven extensively by negative selectivity
- Jared L. Johnson
- , Tomer M. Yaron
- & Lewis C. Cantley
-
Research Briefing |
 Structural landscape inside cells mapped in detail
Structural landscape inside cells mapped in detail
More than 200,000 human stem cells were imaged at high resolution and in 3D to make a reference data set that was used to create a generalizable computational framework. This enables cell shapes and the locations of internal structures to be measured and compared using rigorous statistical methods.
-
Article
| Open Access A quantitative map of nuclear pore assembly reveals two distinct mechanisms
A quantitative map of nuclear pore assembly reveals two distinct mechanisms
Single-molecule calibrated live microscopy and computational modelling have revealed that human nuclear pore complex assembly takes different pathways during the exit from mitosis and during nuclear growth in interphase.
- Shotaro Otsuka
- , Jeremy O. B. Tempkin
- & Jan Ellenberg
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated intracellular organization and its variations in human iPS cells
Integrated intracellular organization and its variations in human iPS cells
A dataset of 3D images from more than 200,000 human induced pluripotent stem cells is used to develop a framework to analyse cell shape and the location and organization of major intracellular structures.
- Matheus P. Viana
- , Jianxu Chen
- & Susanne M. Rafelski
-
Article
| Open Access Phenotypic signatures of immune selection in HIV-1 reservoir cells
Phenotypic signatures of immune selection in HIV-1 reservoir cells
A proteogenomic profiling analysis of single cells from the blood and lymph nodes of individuals living with HIV-1 reveals that CD4+ memory T cells harbouring intact provirus show signatures associated with resistance to immune-mediated killing and cell survival.
- Weiwei Sun
- , Ce Gao
- & Mathias Lichterfeld
-
Article
| Open Access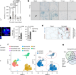 Senescence atlas reveals an aged-like inflamed niche that blunts muscle regeneration
Senescence atlas reveals an aged-like inflamed niche that blunts muscle regeneration
A lifetime cartography of in vivo senescent cells shows that they are heterogeneous. Senescent cells create an aged-like inflamed niche that mirrors inflammation associated with ageing and arrests stem cell proliferation and tissue regeneration.
- Victoria Moiseeva
- , Andrés Cisneros
- & Pura Muñoz-Cánoves
-
Outlook |
 Could CAR-T-cell therapy offer hope to children with cancer?
Could CAR-T-cell therapy offer hope to children with cancer?
The immunotherapy is beginning to show promise in solid tumours, but researchers want more dedicated research in young people.
- Elie Dolgin
-
News & Views |
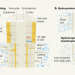 How plant roots go with the flow
How plant roots go with the flow
How do environmental cues steer the branching of plant roots? Insights into how water availability shapes root growth reveal an unexpected mechanism behind the hormone-mediated regulation of this process.
- Christa Testerink
- & Jasper Lamers
-
Article
| Open Access Programming multicellular assembly with synthetic cell adhesion molecules
Programming multicellular assembly with synthetic cell adhesion molecules
Synthetic cell adhesion molecules yield customized cell–cell interactions with adhesion properties that are similar to native interactions, and offer abilities for cell and tissue engineering and for systematically studying multicellular organization.
- Adam J. Stevens
- , Andrew R. Harris
- & Wendell A. Lim
-
Article |
 CLSTN3β enforces adipocyte multilocularity to facilitate lipid utilization
CLSTN3β enforces adipocyte multilocularity to facilitate lipid utilization
An adipocyte-selective product of the Clstn3 locus (CLSTN3β) facilitates the use of stored triglyceride by limiting lipid droplet (LD) expansion, defining a molecular mechanism that regulates LD form and function to facilitate lipid utilization in thermogenic adipocytes.
- Kevin Qian
- , Marcus J. Tol
- & Peter Tontonoz
-
News & Views |
 Swollen axons impair neuronal circuits in Alzheimer’s disease
Swollen axons impair neuronal circuits in Alzheimer’s disease
Abnormal protein aggregates are a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease. It emerges that these plaques cause swellings in neuronal projections called axons that prevent proper circuit function.
- Inma Cobos
- & Jorge J. Palop
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Autophagy
- Cell adhesion
- Cell death
- Cell division
- Cell growth
- Cell migration
- Cell polarity
- Cell signalling
- Cellular imaging
- Chromosomes
- Circadian rhythms
- Cytoskeleton
- Glycobiology
- Mechanisms of disease
- Membrane trafficking
- Nuclear organization
- Nuclear transport
- Organelles
- Post-translational modifications
- Protein folding
- Protein transport
- Proteolysis
- Senescence

 Learning the metabolic language of cancer
Learning the metabolic language of cancer