Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Extracellular Ca2+ is a danger signal activating the NLRP3 inflammasome through G protein-coupled calcium sensing receptors
Extracellular Ca2+ is a danger signal activating the NLRP3 inflammasome through G protein-coupled calcium sensing receptors
Levels of extracellular calcium can increase at sites of infection and inflammation; however, the physiological significance of this has been unclear. This work shows that extracellular calcium acts as a danger signal, triggering the NLRP3 inflammasome via two G protein-coupled receptors.
- Manuela Rossol
- , Matthias Pierer
- & Ulf Wagner
-
Article |
 Phospho-dependent ubiquitination and degradation of PAR-1 regulates synaptic morphology and tau-mediated Aβ toxicity in Drosophila
Phospho-dependent ubiquitination and degradation of PAR-1 regulates synaptic morphology and tau-mediated Aβ toxicity in Drosophila
PAR-1 inDrosophilahas been identified as a key physiological tau kinase. Lee and colleagues perform genetic screens for regulators of PAR-1 and find that it is targeted for ubiquitination and degradation by the ubiquitin ligase complex SCF(Slimb), and that this pathway modulates synaptic morphology.
- Seongsoo Lee
- , Ji-Wu Wang
- & Bingwei Lu
-
Article
| Open Access The genome of Prunus mume
The genome of Prunus mume
The Prunus mume was domesticated in China over 3,000 years ago and is an important ornamental plant and fruit. Here Qixiang Zhang et al.obtain the first assembly of its genome with a combination of next-generation sequencing, whole-genome mapping and restriction-site-associated DNA.
- Qixiang Zhang
- , Wenbin Chen
- & Jun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Alba shapes the archaeal genome using a delicate balance of bridging and stiffening the DNA
Alba shapes the archaeal genome using a delicate balance of bridging and stiffening the DNA
How the genome is physically organized is less understood in archaea than in eubacteria or eukaryotes. Laurens et al. measure DNA binding by the Sulfolobus solfataricusproteins Alba1 and Alba2 using single-molecule techniques and conclude that the presence of Alba2 leads to more bridging between DNA.
- Niels Laurens
- , Rosalie P.C. Driessen
- & Gijs J.L. Wuite
-
Article |
 Fluid flow and interlinked feedback loops establish left–right asymmetric decay of Cerl2 mRNA
Fluid flow and interlinked feedback loops establish left–right asymmetric decay of Cerl2 mRNA
During embryonic development, midline fluid flow results in asymmetric nodal gene expression. Using genetic manipulations and mathematical modelling, Nakamura et al. find that expression of the nodal antagonist Cerl2 is regulated post-transcriptionally, and that asymmetry is maintained by Wnt-Cerl2 feedback loops.
- Tetsuya Nakamura
- , Daisuke Saito
- & Hiroshi Hamada
-
Article |
 Structured patterns in geographic variability of metabolic phenotypes in Arabidopsis thaliana
Structured patterns in geographic variability of metabolic phenotypes in Arabidopsis thaliana
Plants such asArabidopsishave evolved genetic adaptations to their geographic location. Here, a network-based approach is applied to study the link between geographic location and heterogeneous molecular phenotypes, revealing a pattern of isolation by distance in genotypic variability, flowering and metabolic phenotypes.
- Sabrina Kleessen
- , Carla Antonio
- & Zoran Nikoloski
-
Article
| Open Access Pioneer glutamatergic cells develop into a morpho-functionally distinct population in the juvenile CA3 hippocampus
Pioneer glutamatergic cells develop into a morpho-functionally distinct population in the juvenile CA3 hippocampus
The heterogeneity of cortical interneurons results from spatio-temporal differences in embryonic origin. Marissal et al. show that early-generated glutamatergic neurons display distinct morpho-functional features, suggesting that temporal factors are also important in determining glutamatergic function.
- Thomas Marissal
- , Paolo Bonifazi
- & Rosa Cossart
-
Article |
 Fossil pollen records reveal a late rise of open-habitat ecosystems in Patagonia
Fossil pollen records reveal a late rise of open-habitat ecosystems in Patagonia
The rise of open-habitat ecosystems in southern South America is thought to have occurred with the spread of hypsodont mammals 26 million years ago. In this study, the fossil record of plants preserved in Patagonia suggests that open-habitat ecosystems emerged 15 million years later than previously assumed.
- Luis Palazzesi
- & Viviana Barreda
-
Article
| Open Access Rapamycin reverses impaired social interaction in mouse models of tuberous sclerosis complex
Rapamycin reverses impaired social interaction in mouse models of tuberous sclerosis complex
Tuberous sclerosis complex is an autosomal dominant cognitive disorder caused by mutations affecting TSCgenes. Sato and colleagues examine tuberous sclerosis complex mutant mice and find that the behavioural and anatomical abnormalities can be reversed by inhibiting rapamycin-sensitive signalling pathways, even in adulthood.
- Atsushi Sato
- , Shinya Kasai
- & Masashi Mizuguchi
-
Article
| Open Access Virus-like glycodendrinanoparticles displaying quasi-equivalent nested polyvalency upon glycoprotein platforms potently block viral infection
Virus-like glycodendrinanoparticles displaying quasi-equivalent nested polyvalency upon glycoprotein platforms potently block viral infection
Host–pathogen relationships can be mediated by polyvalent glycan ligand–protein interactions. Here well-defined highly valent glycodendrimeric constructs are synthesized that can mimic pathogens, and can inhibit a model of infection by the Ebola virus.
- Renato Ribeiro-Viana
- , Macarena Sánchez-Navarro
- & Benjamin G. Davis
-
Article |
 DJ-1 promotes angiogenesis and osteogenesis by activating FGF receptor-1 signaling
DJ-1 promotes angiogenesis and osteogenesis by activating FGF receptor-1 signaling
Osteoblasts and endothelial cells have important roles in bone regeneration. Kim and colleagues identify the protein DJ-1 as an angiogenic and osteogenic signalling molecule involved in the cross-talk between these cells and show that DJ-1 promotes bone regeneration and fracture healing in mice.
- Jung-Min Kim
- , Hong-In Shin
- & Pann-Ghill Suh
-
Article |
 Predator richness increases the effect of prey diversity on prey yield
Predator richness increases the effect of prey diversity on prey yield
The functioning of bacterial communities is affected by selection, but the role of predation by single or multiple predators is unclear. In a study of 465 bacterial microcosms, Saleem et al.find that multiple predation causes positive bacterial diversity effects due to increased evenness among bacterial species.
- Muhammad Saleem
- , Ingo Fetzer
- & Antonis Chatzinotas
-
Article |
 PPARγ is an E3 ligase that induces the degradation of NFκB/p65
PPARγ is an E3 ligase that induces the degradation of NFκB/p65
NFκB/p65 and PPARγ are both transcription factors that perform distinct but overlapping roles in cellular regulation. Hou et al. report that PPARγ acts as an E3 ubiquitin ligase and promotes Lys48-linked ubiquitination and degradation of p65, terminating NFκB-mediated inflammation and tumorigenesis.
- Yongzhong Hou
- , France Moreau
- & Kris Chadee
-
Article |
 Plasmodium falciparum heat shock protein 110 stabilizes the asparagine repeat-rich parasite proteome during malarial fevers
Plasmodium falciparum heat shock protein 110 stabilizes the asparagine repeat-rich parasite proteome during malarial fevers
The proteome of the malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum has an overabundance of aggregation-prone asparagine repeat-containing proteins. Muralidharan et al. show that PlasmodiumHsp110 protein potently prevents aggregation of asparagine-rich proteins, thereby allowing the parasite to survive febrile episodes.
- Vasant Muralidharan
- , Anna Oksman
- & Daniel E. Goldberg
-
Article |
 Elevated oncofoetal miR-17-5p expression regulates colorectal cancer progression by repressing its target gene P130
Elevated oncofoetal miR-17-5p expression regulates colorectal cancer progression by repressing its target gene P130
Tumorigenesis has been likened to a form of cellular reversion to the embryonic state. Ma et al.identify a foetal miRNA as an oncogenic activator of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in colorectal cancer, whose expression is negatively correlated with survival but is positively correlated with response to adjuvant chemotherapy.
- Yanlei Ma
- , Peng Zhang
- & Huanlong Qin
-
Article |
 Delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs in tumour cell-derived microparticles
Delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs in tumour cell-derived microparticles
Microparticles are small vesicular structures that are shed from cellular plasma membranes. Tang and colleagues show that cells treated with chemotherapeutic drugs produce drug-containing microparticles, which can be used as anticancer agents in mice.
- Ke Tang
- , Yi Zhang
- & Bo Huang
-
Article |
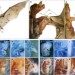 The developmental basis of bat wing muscle
The developmental basis of bat wing muscle
Phylogenetic bat studies suggest that powered flight is evolutionarily conserved. Tokita et al.find that bat wing muscles are derived from multiple myogenic sources with different embryonic origins, and that spatiotemporal correlations exist between outgrowth of wing membranes and expansion of wing muscles.
- Masayoshi Tokita
- , Takaaki Abe
- & Kazuo Suzuki
-
Article
| Open Access Proteome-wide selected reaction monitoring assays for the human pathogen Streptococcus pyogenes
Proteome-wide selected reaction monitoring assays for the human pathogen Streptococcus pyogenes
Selected reaction monitoring mass spectrometry (SRM-MS) can quantify dynamic changes in protein expression with high sensitivity. Karlsson et al. define optimal detection parameters for 10,412 distinct group A Streptococcus pyogenespeptides, which facilitates proteome-wide SRM-MS studies in this bacterium.
- Christofer Karlsson
- , Lars Malmström
- & Johan Malmström
-
Article |
 Catalytic site remodelling of the DOT1L methyltransferase by selective inhibitors
Catalytic site remodelling of the DOT1L methyltransferase by selective inhibitors
Selective inhibitors of protein methyltransferases are anticancer drug candidates. Yu et al. report the structural changes that occur when selective inhibitors bind to the protein methyltransferase DOT1L.
- Wenyu Yu
- , Emma J. Chory
- & Matthieu Schapira
-
Article
| Open Access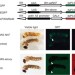 A visible dominant marker for insect transgenesis
A visible dominant marker for insect transgenesis
Genetic modification in insects mostly involves the use of fluorescent markers to identify successful transformation. Here Osanai-Futahashi et al.report a marker system based on changes in melanin pigmentation that allows the identification of genetically modified insects with the naked eye.
- Mizuko Osanai-Futahashi
- , Takahiro Ohde
- & Hideki Sezutsu
-
Article
| Open Access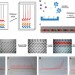 Multiplexed volumetric bar-chart chip for point-of-care diagnostics
Multiplexed volumetric bar-chart chip for point-of-care diagnostics
Diagnostic microfluidic devices often require complicated optical systems and computers to quantify results. Here, Qin and colleagues link enzymatic biomarker detection with the displacement of ink, resulting in a device that displays quantitative results as bar graphs directly on the device.
- Yujun Song
- , Yuanqing Zhang
- & Lidong Qin
-
Article |
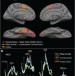 Sequential then interactive processing of letters and words in the left fusiform gyrus
Sequential then interactive processing of letters and words in the left fusiform gyrus
Reading requires accurate and rapid distinction between similar visual stimuli. Thesen and colleagues use human intracranial electrophysiology and brain imaging to show that letter-selective responses, in an area of the brain immediately posterior to the visual word-form area, occur before word selection.
- Thomas Thesen
- , Carrie R. McDonald
- & Eric Halgren
-
Article |
 Spread of white-nose syndrome on a network regulated by geography and climate
Spread of white-nose syndrome on a network regulated by geography and climate
Knowledge of how a disease spreads can lead to useful predictions to help manage and contain it. Here, Maher et al.model white-nose syndrome spreading in North American bats, and show that concentrated habitat distribution and longer winters can mediate pathogen dispersal, matching the ecological traits of bats.
- Sean P. Maher
- , Andrew M. Kramer
- & John M. Drake
-
Article |
 A role for calpain-dependent cleavage of TDP-43 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis pathology
A role for calpain-dependent cleavage of TDP-43 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis pathology
The mislocalization and downregulation of the proteins TDP-43 and ADAR2, respectively, are implicated in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis pathology. Yamashita et al. find that downregulation of ADAR2 results in calcium-permeable AMPA receptor-mediated calpain activation and subsequent aberrant cleavage of TDP-43.
- Takenari Yamashita
- , Takuto Hideyama
- & Shin Kwak
-
Article |
 ASK3 responds to osmotic stress and regulates blood pressure by suppressing WNK1-SPAK/OSR1 signaling in the kidney
ASK3 responds to osmotic stress and regulates blood pressure by suppressing WNK1-SPAK/OSR1 signaling in the kidney
Cells must be able to sense and respond to changes in osmotic pressure, which can be lethal. Here, Naguro and colleagues reveal a role for the protein kinase ASK3 in sensing osmotic stress in the mouse kidney and show that ASK3 contributes to the regulation of blood pressure.
- Isao Naguro
- , Tsuyoshi Umeda
- & Hidenori Ichijo
-
Article
| Open Access Transmembrane insertion of twin-arginine signal peptides is driven by TatC and regulated by TatB
Transmembrane insertion of twin-arginine signal peptides is driven by TatC and regulated by TatB
TatA, B and C act together to translocate folded proteins across bacterial and chloroplast membranes, however the precise mechanism remains unclear. Fröbel and colleagues discover that TatC has unforeseen membrane insertase activity, while TatB prevents premature cleavage before translocation.
- Julia Fröbel
- , Patrick Rose
- & Matthias Müller
-
Article |
 Recent patterns of crop yield growth and stagnation
Recent patterns of crop yield growth and stagnation
Demand for crops is increasing, but it is not clear whether the yields can meet this demand. Using crop yield observations, this study analyses global trends and finds that while yields continue to increase in some areas, across 24–39% of crop-growing regions, yields have stagnated or declined over the past 50 years.
- Deepak K. Ray
- , Navin Ramankutty
- & Jonathan A. Foley
-
Article |
 CRT1 is a nuclear-translocated MORC endonuclease that participates in multiple levels of plant immunity
CRT1 is a nuclear-translocated MORC endonuclease that participates in multiple levels of plant immunity
The CRT1 gene in Arabidopsis confers effector-triggered immunity. Here Kang et al.show that CRT1 has a broader endonuclease role in plant innate immunity, including basal, non-host and systemic acquired resistance, and becomes partially localized to the nucleus upon immune receptor activation.
- Hong-Gu Kang
- , Hyong Woo Choi
- & Daniel F. Klessig
-
Article |
 Preotic neural crest cells contribute to coronary artery smooth muscle involving endothelin signalling
Preotic neural crest cells contribute to coronary artery smooth muscle involving endothelin signalling
Endothelin-1 regulates cardiovascular development by acting on neural crest cells. Here endothelin-1-deficient mice are studied, revealing that preotic neural crest cells differentiate into coronary artery smooth muscle cells through endothelin-1-dependent mechanisms.
- Yuichiro Arima
- , Sachiko Miyagawa-Tomita
- & Hiroki Kurihara
-
Article
| Open Access MPIase is a glycolipozyme essential for membrane protein integration
MPIase is a glycolipozyme essential for membrane protein integration
Proteins are integrated into cellular membranes either co-translationally through Sec/SRP or post-translationally by chaperones. These authors show that an integration-dedicated chaperone inE. coli, MPIase, is a glycolipid and facilitates protein insertion into the inner membrane of the bacterium.
- Ken-ichi Nishiyama
- , Masahide Maeda
- & Keiko Shimamoto
-
Article |
 Receptor tyrosine kinase ErbB2 translocates into mitochondria and regulates cellular metabolism
Receptor tyrosine kinase ErbB2 translocates into mitochondria and regulates cellular metabolism
ErbB2 is a receptor tyrosine kinase that localizes to the plasma membrane. Dinget al. now show that ErbB2 also localizes to mitochondria, where it regulates mitochondrial respiratory function and resistance to cancer chemotherapy.
- Yan Ding
- , Zixing Liu
- & Ming Tan
-
Article |
 Repeated evolution in overlapping mimicry rings among North American velvet ants
Repeated evolution in overlapping mimicry rings among North American velvet ants
In Müllerian mimicry two or more harmful species share a similar appearance for mutual benefit. This study identifies a large Müllerian mimicry complex in North American velvet ants, where 65 species mimic each other through shared colour patterns gained as the result of independent evolution.
- Joseph S. Wilson
- , Kevin A. Williams
- & James P. Pitts
-
Article
| Open Access T-bet and GATA3 orchestrate Th1 and Th2 differentiation through lineage-specific targeting of distal regulatory elements
T-bet and GATA3 orchestrate Th1 and Th2 differentiation through lineage-specific targeting of distal regulatory elements
T-bet and GATA3 regulate differentiation of T cells into Th1 or Th2 cell fates, but little is known about their functional interaction outside of the IFNγ and Il4 /Il5/Il13 loci. Kanhere et al. map these factors across the genome in human T cells, revealing unappreciated breadth of function and interplay between them.
- Aditi Kanhere
- , Arnulf Hertweck
- & Richard G. Jenner
-
Article
| Open Access Cambrian lobopodians and extant onychophorans provide new insights into early cephalization in Panarthropoda
Cambrian lobopodians and extant onychophorans provide new insights into early cephalization in Panarthropoda
Lobopodians include stem-group arthropods and panarthropods, and date back to the early Cambrian. Ou et al. describe specimens of the early Cambrian lobopodian Onychodictyon ferox, revealing new head structures such as modified appendages, eyes, a terminal mouth and a sucking pharynx.
- Qiang Ou
- , Degan Shu
- & Georg Mayer
-
Article
| Open Access Luminescent proteins for high-speed single-cell and whole-body imaging
Luminescent proteins for high-speed single-cell and whole-body imaging
Luminescent proteins are important tools for biomedical imaging but tend to emit fairly little light. Saito et al.. describe a brighter version of a bioluminescent protein that can visualize intracellular dynamics of various signalling molecules with high spatial and temporal resolution.
- Kenta Saito
- , Y-F Chang
- & Takeharu Nagai
-
Article |
 Reprogramming to pluripotency is an ancient trait of vertebrate Oct4 and Pou2 proteins
Reprogramming to pluripotency is an ancient trait of vertebrate Oct4 and Pou2 proteins
The mammalian transcription factors Oct4 and Pou2 are implicated in germ cell pluripotency induction and maintenance. Tapia and colleagues find that axolotl Pou2 and Oct4 reprogram mouse and human fibroblasts to a pluripotent state, suggesting ancestral Oct4 and Pou2 gene function is evolutionarily conserved.
- Natalia Tapia
- , Peter Reinhardt
- & Hans R. Schöler
-
Article |
 Distinct modes of DNA accessibility in plant chromatin
Distinct modes of DNA accessibility in plant chromatin
Epigenetic modifications are thought to affect the accessibility of DNA, but it is not clear whether this is a universal effect. These authors map DNA accessibility inArabidopsis thalianaand find that, in contrast to fruitflies, H3K9 dimethylation reduces accessibility in a DNA methylation-dependent manner.
- Huan Shu
- , Thomas Wildhaber
- & Lars Hennig
-
Article
| Open Access Exhaustion of nucleus pulposus progenitor cells with ageing and degeneration of the intervertebral disc
Exhaustion of nucleus pulposus progenitor cells with ageing and degeneration of the intervertebral disc
Back pain and sciatica are often caused by intervertebral disc degeneration. Sakai and colleagues identify a subset of nucleus pulposus progenitor cells from the intervertebral disc and show that loss of these progenitor cells correlates with ageing and intervertebral disc degeneration.
- Daisuke Sakai
- , Yoshihiko Nakamura
- & Joji Mochida
-
Article |
 Single-particle structure determination by correlations of snapshot X-ray diffraction patterns
Single-particle structure determination by correlations of snapshot X-ray diffraction patterns
Free-electron lasers enable diffractive imaging of single nanostructures, but algorithms, such as correlation analyses, are needed to determine their diffraction volume from accumulated data. Starodub et al.present such a method for X-ray diffractive imaging of nanometre-scale polystyrene dimers.
- D. Starodub
- , A. Aquila
- & M.J. Bogan
-
Article |
 Cooperation between different RNA virus genomes produces a new phenotype
Cooperation between different RNA virus genomes produces a new phenotype
RNA viruses are known to rapidly evolve new features through errors in replication and reshuffling of genomic segments. These authors report another strategy used by the measles virus to improve infectivity; the cooperation between wild-type and mutant fusion proteins in the same viral particle.
- Yuta Shirogane
- , Shumpei Watanabe
- & Yusuke Yanagi
-
Article |
 The RB family is required for the self-renewal and survival of human embryonic stem cells
The RB family is required for the self-renewal and survival of human embryonic stem cells
While human embryonic stem cells (ESC) hold great therapeutic promise, many aspects of their basic biology remain poorly understood. Conklin et al.show that too much or too little activation of RB family proteins is detrimental to human ESC populations and identify unique cell cycle regulatory networks in these cells.
- Jamie F. Conklin
- , Julie Baker
- & Julien Sage
-
Article
| Open Access Laminin E8 fragments support efficient adhesion and expansion of dissociated human pluripotent stem cells
Laminin E8 fragments support efficient adhesion and expansion of dissociated human pluripotent stem cells
The use of animal products as culture substrates for human embryonic stem cell and induced pluripotent stem cell culture raises numerous safety concerns in a therapeutic setting. Miyazaki et al.. show that minimal fragments of human laminins provide a more effective support for the culture of these cell types.
- Takamichi Miyazaki
- , Sugiko Futaki
- & Eihachiro Kawase
-
Article |
 Cardioprotection by Klotho through downregulation of TRPC6 channels in the mouse heart
Cardioprotection by Klotho through downregulation of TRPC6 channels in the mouse heart
Mice that cannot produce the hormone Klotho show various aging-related phenotypes. Here, Xie and colleagues reveal that Klotho protects the heart of mice from stress-induced remodelling by inhibiting exocytosis of the TRPC6 ion channel in cardiomyocytes.
- Jian Xie
- , Seung-Kuy Cha
- & Chou-Long Huang
-
Article |
 Suppression of adult neurogenesis impairs population coding of similar contexts in hippocampal CA3 region
Suppression of adult neurogenesis impairs population coding of similar contexts in hippocampal CA3 region
The dentate gyrus and CA3 of the hippocampus are involved in pattern separation. Niibori and colleagues investigate the role of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in pattern separation and find that suppressing adult neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus impairs coding of similar, but not dissimilar contexts.
- Yosuke Niibori
- , Tzong-Shiue Yu
- & Paul W. Frankland
-
Article |
 Cholesterol modulates cell signaling and protein networking by specifically interacting with PDZ domain-containing scaffold proteins
Cholesterol modulates cell signaling and protein networking by specifically interacting with PDZ domain-containing scaffold proteins
Cholesterol indirectly regulates intracellular signalling by modulating the physical properties of lipid membranes. Sheng et al.now show that many PDZ domains contain a functional cholesterol-binding motif, revealing that cholesterol can also control the localization and function of signalling proteins directly.
- Ren Sheng
- , Yong Chen
- & Wonhwa Cho
-
Article |
 A fast and accurate SNP detection algorithm for next-generation sequencing data
A fast and accurate SNP detection algorithm for next-generation sequencing data
The amount of data supplied by next-generation sequencing technologies presents a challenge for traditional algorithms to detect single-nucleotide polymorphisms. Xu et al.develop an efficient detection program and demonstrate its utility by identifying polymorphisms in cancer genomes and human populations.
- Feng Xu
- , Weixin Wang
- & Junwen Wang
-
Article |
 Competition–colonization dynamics in experimental bacterial metacommunities
Competition–colonization dynamics in experimental bacterial metacommunities
Species coexistence can be explained by the competition–colonization trade-off theory. Here, Livingston et al. illustrate this theory in a metacommunity experiment using two bacterial strains, finding a negative correlation between diversity and productivity when scaled to full metacommunities.
- George Livingston
- , Miguel Matias
- & Nicolas Mouquet
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic blastomere behaviour reflects human embryo ploidy by the four-cell stage
Dynamic blastomere behaviour reflects human embryo ploidy by the four-cell stage
Abnormal human embryo development is implicated in the embryo arrest observed during in vitrofertilization. Chavez and colleagues perform time-lapse imaging on human embryos and find that chromosomally abnormal embryos exhibit diverse cell cycle parameters that may contribute to arrest.
- Shawn L. Chavez
- , Kevin E. Loewke
- & Renee A. Reijo Pera
-
Article |
 Involvement of PGC-1α in the formation and maintenance of neuronal dendritic spines
Involvement of PGC-1α in the formation and maintenance of neuronal dendritic spines
PGC-1α regulates mitochondrial biogenesis and adaptive thermogenesis. Cheng and colleagues alter the expression of PGC-1α in primary neuronal cultures and in the adult mouse brain, and find that it regulates dendritic spine formation and maintenance by mediating the synaptogenic actions of BDNF and CREB.
- Aiwu Cheng
- , Ruiqian Wan
- & Mark P. Mattson
Browse narrower subjects
- Biochemistry
- Biological techniques
- Biophysics
- Biotechnology
- Cancer
- Cell biology
- Chemical biology
- Computational biology and bioinformatics
- Developmental biology
- Drug discovery
- Ecology
- Evolution
- Genetics
- Immunology
- Microbiology
- Molecular biology
- Neuroscience
- Physiology
- Plant sciences
- Psychology
- Stem cells
- Structural biology
- Systems biology
- Zoology

 Activity of the mitochondrial calcium uniporter varies greatly between tissues
Activity of the mitochondrial calcium uniporter varies greatly between tissues