Measure for Measure |
Featured
-
-
World View |
 Why even specialists struggle with black hole proofs
Why even specialists struggle with black hole proofs
Mathematical proofs of black hole physics are becoming too complex even for specialists.
- Alejandro Penuela Diaz
-
Article
| Open Access False vacuum decay via bubble formation in ferromagnetic superfluids
False vacuum decay via bubble formation in ferromagnetic superfluids
The transition from a metastable state to the ground state in classical many-body systems is mediated by bubble nucleation. This transition has now been experimentally observed in a quantum setting using coupled atomic superfluids.
- A. Zenesini
- , A. Berti
- & G. Ferrari
-
-
Comment |
 The microscopic structure of quantum space-time and matter from a renormalization group perspective
The microscopic structure of quantum space-time and matter from a renormalization group perspective
The correct microscopic theory of quantum gravity may be an interacting, scale-invariant, ‘asymptotically safe’ model. This Comment discusses the renormalization group’s role in defining asymptotic safety and understanding its consequences.
- Astrid Eichhorn
-
-
-
World View |
 Space exploration is a team sport, not the preserve of a few powerful men
Space exploration is a team sport, not the preserve of a few powerful men
The lone genius narrative is harmful to science and will not help humans settle in space.
- Erika Nesvold
-
-
News & Views |
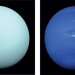 Ammonia and the ice giants
Ammonia and the ice giants
Determining the melting temperature and electrical conductivity of ammonia under the internal conditions of the ice giants Uranus and Neptune is helping us to understand the structure and magnetic field formation of these planets.
- Kenji Ohta
-
Article |
 Melting curve of superionic ammonia at planetary interior conditions
Melting curve of superionic ammonia at planetary interior conditions
Laser-driven shock compression experiments yield the melting curve of the superionic phase of ammonia at conditions relevant to the interiors of Uranus and Neptune.
- J.-A. Hernandez
- , M. Bethkenhagen
- & A. Ravasio
-
Article
| Open Access Mass measurements show slowdown of rapid proton capture process at waiting-point nucleus 64Ge
Mass measurements show slowdown of rapid proton capture process at waiting-point nucleus 64Ge
Rapid proton capture nucleosynthesis stalls at waiting-point nuclides, including 64Ge. Precision mass measurements in the vicinity of this nuclide influence state-of-the-art calculations of X-ray bursts from accreting neutron stars.
- X. Zhou
- , M. Wang
- & S. Zhang
-
-
News & Views |
 Power to the particles
Power to the particles
Particles in space can be accelerated to high energy, the distribution of which follows a power law. This has now been reproduced in laboratory experiments mimicking astrophysical scenarios, which helps to understand the underlying mechanisms.
- Giovanni Lapenta
-
Article |
 Turbulent magnetic reconnection generated by intense lasers
Turbulent magnetic reconnection generated by intense lasers
Laboratory experiments reveal the underlying mechanism of turbulent reconnection, including electron acceleration. These findings are directly relevant for studies of flares in the solar corona.
- Yongli Ping
- , Jiayong Zhong
- & Jie Zhang
-
Article |
 Non-thermal electron acceleration from magnetically driven reconnection in a laboratory plasma
Non-thermal electron acceleration from magnetically driven reconnection in a laboratory plasma
Laboratory experiments demonstrate that electrons are accelerated to high energies by the reconnection electric field in magnetically driven reconnection. This mechanism is expected to be relevant for many astrophysical environments.
- Abraham Chien
- , Lan Gao
- & Ryunosuke Takizawa
-
News & Views |
 The study of the journey of cosmic antimatter
The study of the journey of cosmic antimatter
A potential observation of low-energy antihelium-3 nuclei would have profound impacts on our understanding of the Galaxy. Experiments at particle colliders help us understand how cosmic antimatter travels over long distances before reaching Earth.
- Aihong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Measurement of anti-3He nuclei absorption in matter and impact on their propagation in the Galaxy
Measurement of anti-3He nuclei absorption in matter and impact on their propagation in the Galaxy
Measurements of the inelastic cross section of anti-3He allow the estimation of the transparency of the Milky Way to the propagation of these light antinuclei produced in either cosmic-ray collisions or annihilation of dark-matter particles.
- S. Acharya
- , D. Adamová
- & N. Zurlo
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Lorentz invariance beyond the Planck scale
Lorentz invariance beyond the Planck scale
Lorentz symmetry violations might produce anomalies in the propagation of particles travelling through the Universe. The IceCube Collaboration performed the most precise search for such an effect with neutrinos, finding no sign of anomalous behaviour.
- Giulia Gubitosi
-
-
News & Views |
 A historic match for nuclei and neutron stars
A historic match for nuclei and neutron stars
Bayesian history matching is a statistical tool used to calibrate complex numerical models. Now, it has been applied to first-principles simulations of several nuclei, including 208Pb, whose properties are linked to the interior of neutron stars.
- Arnau Rios
-
Letter |
 Experiments with levitated force sensor challenge theories of dark energy
Experiments with levitated force sensor challenge theories of dark energy
In experiments with a levitated force sensor, no signatures of a fifth force are detected. This rules out the basic chameleon model, which is a popular theory providing an explanation for dark energy.
- Peiran Yin
- , Rui Li
- & Jiangfeng Du
-
Article
| Open Access Ab initio predictions link the neutron skin of 208Pb to nuclear forces
Ab initio predictions link the neutron skin of 208Pb to nuclear forces
Predictions of the properties of 208Pb from first principles augmented by statistical learning techniques reproduce those seen in experiments but rule out very thick neutron skins.
- Baishan Hu
- , Weiguang Jiang
- & Ian Vernon
-
News & Views |
 Good vibrations
Good vibrations
Originally suggested for the detection of gravitational waves, resonantly vibrating metal beams have been used in a recent laboratory experiment to measure Newton’s constant of gravitation and to verify Newton’s gravitational law.
- Christian Rothleitner
-
Article |
 Dynamic measurement of gravitational coupling between resonating beams in the hertz regime
Dynamic measurement of gravitational coupling between resonating beams in the hertz regime
Measurements of the gravitational interaction between two parallel beams vibrating in bending motion enable the quantitative investigation of dynamic gravitation in the hertz regime and allow the determination of the gravitational constant.
- Tobias Brack
- , Bernhard Zybach
- & Jürg Dual
-
-
Article |
 Polymeric jets throw light on the origin and nature of the forest of solar spicules
Polymeric jets throw light on the origin and nature of the forest of solar spicules
A combination of numerical simulations and fluid dynamics experiments provides insights into the generation of a forest of solar plasma jets on the Sun.
- Sahel Dey
- , Piyali Chatterjee
- & Robertus Erdélyi
-
News & Views |
 OK Computer
OK Computer
Promising machine learning techniques can deduce the properties of merging black holes from gravitational wave signals a million times faster than current state-of-the-art methods.
- Rory Smith
-
Article |
 Bayesian parameter estimation using conditional variational autoencoders for gravitational-wave astronomy
Bayesian parameter estimation using conditional variational autoencoders for gravitational-wave astronomy
A method for estimating the source properties of gravitational-wave events shows a speed-up of six orders of magnitude over established approaches. This is a promising tool for follow-up observations of electromagnetic counterparts.
- Hunter Gabbard
- , Chris Messenger
- & Roderick Murray-Smith
-
Article
| Open Access Search for topological defect dark matter with a global network of optical magnetometers
Search for topological defect dark matter with a global network of optical magnetometers
A search for transient dark matter in the form of domain walls of axion-like particles finds no statistically significant signal. This places constraints on our theoretical understanding of such scenarios.
- Samer Afach
- , Ben C. Buchler
- & Jianwei Zhang
-
Article |
 Search for axion-like dark matter with spin-based amplifiers
Search for axion-like dark matter with spin-based amplifiers
A search for axion-like dark matter with a quantum sensor that enhances potential signals is reported. This work constrains the parameter space of different interactions between nucleons and axion-like particles and between nucleons and dark photons.
- Min Jiang
- , Haowen Su
- & Dmitry Budker
-
-
Article |
 Laboratory evidence for proton energization by collisionless shock surfing
Laboratory evidence for proton energization by collisionless shock surfing
Proton acceleration by a super-critical collisionless shock is observed in laboratory experiments, and numerical simulations suggest shock surfing as the underlying acceleration mechanism.
- W. Yao
- , A. Fazzini
- & J. Fuchs
-
Measure for Measure |
 One unit to rule them all
One unit to rule them all
Initially used to measure the brightness of radio sources, the jansky has spread to other areas of astronomy, as Natasha Hurley-Walker recounts.
- Natasha Hurley-Walker
-
-
News & Views |
 The life of an analogue black hole
The life of an analogue black hole
Table-top superfluid experiments offer a way of bringing the physics of astrophysical black holes into the lab. But the presence of two event horizons in these superfluid black holes complicates matters — and makes them more interesting.
- Giovanni Modugno
-
Article |
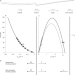 Observation of stationary spontaneous Hawking radiation and the time evolution of an analogue black hole
Observation of stationary spontaneous Hawking radiation and the time evolution of an analogue black hole
In an analogue black hole in an atomic Bose–Einstein condensate, spontaneous Hawking radiation is confirmed to be stationary and the time evolution of Hawking radiation is reported.
- Victor I. Kolobov
- , Katrine Golubkov
- & Jeff Steinhauer
-
Editorial |
 In this galaxy far, far away
In this galaxy far, far away
The Nobel Prize in Physics 2020 has been awarded to Roger Penrose for his work on black hole formation, and to Andrea Ghez and Reinhard Genzel for their observation of a supermassive compact object at the Galactic Centre.
-
Measure for Measure |
 The sound of weights and measures
The sound of weights and measures
In first-century China, emperor Wang Mang standardized weights and measures in his newly established dynasty. Noa Hegesh tells the story of sound as the basis for this standardization.
- Noa Hegesh
-
News & Views |
 Clock comparison using black holes
Clock comparison using black holes
Observing accreting black holes in the early Universe allows precise comparison of clocks over intercontinental distances on Earth. This is achieved with a novel observation strategy using the next generation of very long baseline interferometry systems.
- Rüdiger Haas
-
Article |
 Intercontinental comparison of optical atomic clocks through very long baseline interferometry
Intercontinental comparison of optical atomic clocks through very long baseline interferometry
Very long baseline interferometry is used to compare two optical clocks located in Japan and Italy through the observation of extragalactic radio sources. This approach overcomes limitations of the performance of satellite transfer techniques.
- Marco Pizzocaro
- , Mamoru Sekido
- & Tetsuya Ido
-
-
Article |
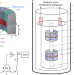 Search for axion-like dark matter with ferromagnets
Search for axion-like dark matter with ferromagnets
The presence of axion-like dark matter candidates is expected to induce an oscillating magnetic field, enhanced by a ferromagnet. Limits on the electromagnetic coupling strength of axion-like particles are reported over a mass range spanning three decades.
- Alexander V. Gramolin
- , Deniz Aybas
- & Alexander O. Sushkov
-
-
News & Views |
 An acoustic black hole
An acoustic black hole
An elegant experiment showing that acoustic waves are amplified after scattering by a rotating body demonstrates an effect predicted in 1971 by Yakov Zel’dovich. This result has implications for the understanding of scattering from black holes.
- Bruce W. Drinkwater
-
News & Views |
 Miniature supernova shock waves
Miniature supernova shock waves
A laser–plasma experiment has recreated shock waves in collisionless, weakly magnetized conditions and evidenced electron acceleration to relativistic energies, offering unprecedented insight into a long-standing problem in astrophysics.
- Laurent Gremillet
- & Martin Lemoine
-
Article |
 Cosmology at the end of the world
Cosmology at the end of the world
Braneworld cosmologies describe our universe as a four-dimensional membrane embedded in a bulk five-dimensional anti-de Sitter spacetime. In a possible holographic realization, observers on the brane experience cosmology, and gravity is localized.
- Stefano Antonini
- & Brian Swingle
-
Letter
| Open Access Evidence for quark-matter cores in massive neutron stars
Evidence for quark-matter cores in massive neutron stars
The cores of neutron stars could be made of hadronic matter or quark matter. By combining first-principles calculations with observational data, evidence for the presence of quark matter in neutron star cores is found.
- Eemeli Annala
- , Tyler Gorda
- & Aleksi Vuorinen
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Astronomical instrumentation
- Astrophysical disks
- Astrophysical dust
- Astrophysical magnetic fields
- Compact astrophysical objects
- Computational astrophysics
- Cosmology
- Dark energy and dark matter
- Early universe
- Exoplanets
- Galaxies and clusters
- General relativity and gravity
- High-energy astrophysics
- Interstellar medium
- Laboratory astrophysics
- Particle astrophysics
- Stars
- Stellar evolution
- Time-domain astronomy
- Transient astrophysical phenomena

 We can see clearly now
We can see clearly now The gravity of quantum thermalization
The gravity of quantum thermalization Background to the fore
Background to the fore Light from dark stars
Light from dark stars How to harvest gravitational energy
How to harvest gravitational energy Nights too bright
Nights too bright A strong field of exotic effects
A strong field of exotic effects The deep end of the magma ocean
The deep end of the magma ocean Atmospheric abundance
Atmospheric abundance A supermassive doughnut
A supermassive doughnut When the dust settles
When the dust settles Unequal equals
Unequal equals