Featured
Advertisement
-
-

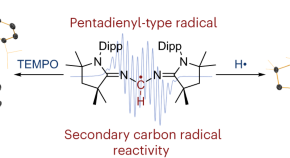
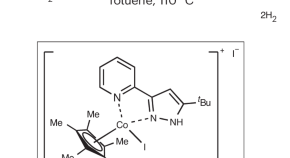
Characterization of a secondary carbon-centred radical
A diazapentadienyl radical featuring a disubstituted carbon centre is discovered allowing the isolation and structural characterization of a stable secondary carbon radical.
-
-
Trending - Altmetric
-
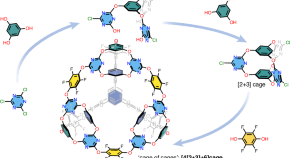
Computationally guided synthesis of a hierarchical [4[2+3]+6] porous organic ‘cage of cages’
-
Synthesis of goldene comprising single-atom layer gold
-
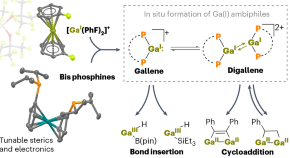
In situ formation of reactive (di)gallenes for bond activation
-
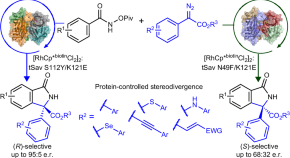
Enantiodivergent synthesis of isoindolones catalysed by a Rh(III)-based artificial metalloenzyme