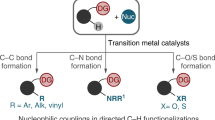
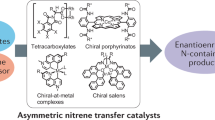
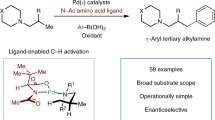
Abstract
C–H activation is a ‘simple-to-complex’ transformation that nature has perfected over millions of years of evolution. Transition-metal-catalysed C–H activation has emerged as an expeditious means to expand the chemical space by introducing diverse functionalities. Notably, among the strategies to selectively cleave a particular C–H bond, the catalytic use of a small molecule as co-catalyst to generate a transient directing group, which provides a balance between step economy and chemical productivity, has gained immense attention in recent years. This allows one to convert a desired C–H bond irrespective of its geometrical or stereochemical configuration. This Review describes the various transient directing groups used in C–H activation and explains their mechanistic significance.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crabtree, R. H. & Lei, A. Introduction: CH activation. Chem. Rev. 117, 8481–8482 (2017).
Kapdi, A. R. & Maiti, D. (eds) Strategies for Palladium-Catalyzed Non-Directed and Directed C–H Bond Functionalization (Elsevier, 2017).
Dey, A., Sinha, S. K., Achar, T. K. & Maiti, D. Accessing remote meta- and para-C(sp2)–H bonds with covalently attached directing groups. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 10820–10843 (2019).
Meng, G. et al. Achieving site-selectivity for C–H activation processes based on distance and geometry: a carpenter’s approach. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 10571–10591 (2020).
Dutta, U., Maiti, S., Bhattacharya, T. & Maiti, D. Arene diversification through distal C(sp2)–H functionalization. Science 372, eabd5992 (2021).
Goswami, N. & Maiti, D. An update on distal C(sp3)–H functionalization involving 1,5-HAT emerging from nitrogen radicals. Isr. J. Chem. 60, 303–312 (2020).
Dutta, U. et al. Para-selective arylation of arenes: a direct route to biaryls by norbornene relay palladation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 132, 21017–21022 (2020).
Davis, H. J. & Phipps, R. J. Harnessing non-covalent interactions to exert control over regioselectivity and site-selectivity in catalytic reactions. Chem. Sci. 8, 864–877 (2017).
Gandeepan, P. & Ackermann, L. Transient directing groups for transformative C–H activation by synergistic metal catalysis. Chem 4, 199–222 (2018).
St John Campbell, S. & Bull, J. A. Transient imines as ‘next generation’ directing groups for the catalytic functionalisation of C–H bonds in a single operation. Org. Biomol. Chem. 16, 4582–4595 (2018).
Bhattacharya, T., Pimparkar, S. & Maiti, D. Combining transition metals and transient directing groups for C–H functionalizations. RSC Adv. 8, 19456–19464 (2018).
Niu, B. et al. Transient ligand-enabled transition metal-catalyzed C–H functionalization. ChemSusChem 12, 2955–2969 (2019).
Higham, J. I. et al. Transient imine directing groups for the C–H functionalisation of aldehydes, ketones and amines: an update 2018–2020. Org. Biomol. Chem. 18, 7291–7315 (2020).
Liao, G. et al. Transition metal-catalyzed enantioselective C–H functionalization via chiral transient directing group strategies. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 19773–19786 (2020).
Liang, Y.-F. et al. Ligand-promoted Pd-catalyzed oxime ether directed C–H hydroxylation of arenes. ACS Catal. 5, 6148–6152 (2015).
Xu, L.-L. et al. Copper mediated C–H amination with oximes: en route to primary anilines. Chem. Sci. 9, 5160–5164 (2018).
Engle, K. M., Mei, T.-S., Wasa, M. & Yu, J.-Q. Weak coordination as a powerful means for developing broadly useful C–H functionalization reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 45, 788–802 (2012).
Jun, C. H., Lee, H. & Hong, J.-B. Hydroacylation of 1-alkene with heteroaromatic aldehyde by Rh(i) and additives. J. Org. Chem. 62, 1200–1201 (1997).
Jun, C. H., Lee, D.-Y., Lee, H. & Hong, J.-B. A highly active catalyst system for intermolecular hydroacylation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 39, 3070–3072 (2000).
Vautravers, N. R., Regent, D. D. & Breit, B. Inter- and intramolecular hydroacylation of alkenes employing a bifunctional catalyst system. Chem. Commun. 47, 6635–6637 (2011).
Beletskiy, E. V., Sudheer, C. & Douglas, C. J. Cooperative catalysis approach to intramolecular hydroacylation. J. Org. Chem. 77, 5884–5893 (2012).
Jun, C.-H. & Hwang, D.-C. Simultaneous hydrogenation and hydroacylation of vinyl groups in polybutadiene by use of a rhodium catalyst. Polymer 39, 7143–7147 (1998).
Tan, P. W., Juwaini, N. A. B. & Seayad, J. Rhodium(iii)-amine dual catalysis for the oxidative coupling of aldehydes by directed C–H activation: synthesis of phthalides. Org. Lett. 15, 5166–5169 (2013).
Hu, W., Zheng, Q., Sun, S. & Cheng, J. Rh(iii)-catalyzed bilateral cyclization of aldehydes with nitrosos toward unsymmetrical acridines proceeding with C–H functionalization enabled by a transient directing group. Chem. Commun. 53, 6263–6266 (2017).
Liu, X., Wang, Z., Chen, Q., He, M.-Y. & Wang, L. Rhodium-catalyzed ortho-C–H olefination of aromatic aldehydes employing transient directing strategy. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 32, e4039 (2018).
Wang, X., Song, S. & Jiao, N. Rh-catalyzed transient directing group promoted C–H amidation of benzaldehydes utilizing dioxazolones. Chin. J. Chem. 36, 213–216 (2018).
Hande, A. K., Ramesh, V. B. & Prabhu, K. R. Rh(iii)-catalyzed ortho-C-(sp2)–H amidation of ketones and aldehydes under synergistic ligand-accelerated catalysis. Chem. Commun. 54, 12113–12116 (2018).
Shen, J., Liu, X., Wang, L., Chen, Q. & He, M. Rh(iii)-catalyzed synthesis of unsymmetrical acridines from aldehydes and azides using transient directing strategy in biomass-derived γ-valerolactone. Synth. Commun. 48, 1354–1362 (2018).
Kim, S. et al. Dual role of anthranils as amination and transient directing group sources: synthesis of 2-acyl acridines. Org. Lett. 20, 4010–4014 (2018).
Liu, X.-H. et al. Diverse ortho-C(sp2)–H functionalization of benzaldehydes using transient directing groups. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 888–896 (2017). This paper describes a series of benzaldehyde ortho-functionalization reactions.
Mu, D., Wang, X., Chen, G. & He, G. Iridium-catalyzed ortho-C(sp2)–H amidation of benzaldehydes with organic azides. J. Org. Chem. 82, 4497–4503 (2017).
Li, F. et al. Assembly of diverse spirocyclic pyrrolidines via transient directing group enabled ortho-C(sp2)–H alkylation of benzaldehydes. Org. Lett. 20, 146–149 (2018).
Zheng, Y., Tice, C. M. & Singh, S. B. The use of spirocyclic scaffolds in drug discovery. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 24, 3673–3682 (2014).
Rasheed, O. & Zhang, F.-L. Ruthenium-catalyzed ortho-C(sp2)–H amidation of benzaldehydes with organic azides. Synlett 29, 1033–1036 (2018).
Chen, X.-Y., Ozturk, S. & Sorensen, E. J. Synthesis of fluorenones from benzaldehydes and aryl iodides: dual C–H functionalizations using a transient directing group. Org. Lett. 19, 1140–1143 (2017).
Chen, X.-Y., Ozturk, S. & Sorensen, E. J. Pd-catalyzed ortho C–H hydroxylation of benzaldehydes using a transient directing group. Org. Lett. 19, 6280–6283 (2017).
Chen, X.-Y. & Sorensen, E. J. Pd-catalyzed, ortho-C–H methylation and fluorination of benzaldehydes using orthanilic acids as transient directing groups. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 2789–2792 (2018).
Mu, D., He, G. & Chen, G. Palladium-catalyzed ortho-C–H arylation of benzaldehydes using ortho-sulfinyl aniline as transient auxiliary. Chem. Asian J. 13, 2423–2426 (2018).
Ichikawa, Y. et al. Selective ablation of β-galactosidase-expressing cells with a rationally designed activatable photosensitizer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 6772–6775 (2014).
Qiao, H. et al. Palladium-catalyzed direct ortho-C–H selenylation of benzaldehydes using benzidine as a transient directing group. Org. Lett. 21, 6914–6918 (2019).
Li, F. et al. Monodentate transient directing group enabled Pd-catalyzed ortho-C–H methoxylation and chlorination of benzaldehydes. Org. Lett. 21, 3692–3695 (2019).
Yong, Q., Suna, B. & Zhang, F.-L. Palladium-catalyzed ortho-C(sp2)–H bromination of benzaldehydes via a monodentate transient directing group strategy. Tetrahedron Lett. 60, 151263–151266 (2019).
Khan, B., Dwivedi, V. & Sundararaju, B. Cp*Co(III)-catalyzed o-amidation of benzaldehydes with dioxazolones using transient directing group strategy. Adv. Synth. Catal. 362, 1195–1200 (2020).
Huang, J. et al. Cobalt-catalyzed ortho-C(sp2)–H amidation of benzaldehydes with dioxazolones using transient directing groups. Org. Lett. 21, 7342–7345 (2019).
Ma, F., Lei, M. & Hu, L. Acetohydrazone: a transient directing group for arylation of unactivated C(sp3)–H bonds. Org. Lett. 18, 2708–2711 (2016).
Wen, F. & Li, Z. Semicarbazide: a transient directing group for C(sp3)–H arylation of 2-methylbenzaldehydes. Adv. Synth. Catal. 362, 133–138 (2020).
Huple, D. B., Chen, C. H., Das, A. & Liu, R. S. Silver-catalyzed exo-dig-azacyclization/[3+2] cycloaddition cascades on 1-tosylhydrazon-4-oxy-5-yne substrates: applicability to diverse alkenes. Adv. Synth. Catal. 353, 1877–1882 (2011).
Paradkar, M. V., Kulkarni, S. A., Joseph, A. R. & Ranade, A. An efficient synthesis of dimethoxyphthalides. J. Chem. Res. 8, 364–366 (2000).
Nicolaou, K. C., Montagnon, T., Vassilikogiannakis, G. & Mathison, C. J. N. The total synthesis of coleophomones B, C, and D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 8872–8888 (2005).
Chen, J., Bai, C., Tong, X., Liu, D. & Bao, Y.-S. A dual role for acetohydrazide in Pd-catalyzed controlled C(sp3)–H acetoxylation of aldehydes. RSC Adv. 10, 12192–12196 (2020).
St John-Campbell, S., White, A. J. P. & Bull, J. A. Single operation palladium catalysed C(sp3)–H functionalisation of tertiary aldehydes: investigations into transient imine directing groups. Chem. Sci. 8, 4840–4847 (2017).
St John Campbell, S. & Bull, J. A. Intramolecular palladium(ii)/(iv) catalysed C(sp3)–H arylation of tertiary aldehydes using a transient imine directing group. Chem. Commun. 55, 9172–9175 (2019).
Wang, J. et al. Palladium-catalyzed β-C–H arylation of ketones using amino amide as a transient directing group: applications to synthesis of phenanthridinone alkaloids. Adv. Synth. Catal. 360, 3709–3715 (2018).
St John-Campbell, S., White, A. J. P. & Bull, J. A. Methylene C(sp3)–H β,β′-diarylation of cyclohexanecarbaldehydes promoted by a transient directing group and pyridone ligand. Org. Lett. 22, 1807–1812 (2020).
Shao, Q., Wu, K., Zhuang, Z., Qian, S. & Yu, J.-Q. From Pd(OAc)2 to chiral catalysts: the discovery and development of bifunctional mono-N-protected amino acid ligands for diverse C–H functionalization reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 53, 833–851 (2020).
Zhang, F.-L., Hong, K., Li, T.-J., Park, H. & Yu, J.-Q. Functionalization of C(sp3)–H bonds using a transient directing group. Science 351, 252–256 (2016). This is a pioneering work on C(sp3)–H functionalization using a TDG.
Yang, K., Li, Q., Liu, Y., Li, G. & Ge, H. Catalytic C–H arylation of aliphatic aldehydes enabled by a transient ligand. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 12775–12778 (2016). This work highlights C(sp3)–H arylation of aliphatic aldehydes using a TDG.
Pan, L., Yang, K., Li, G. & Ge, H. Palladium-catalyzed site-selective arylation of aliphatic ketones enabled by a transient ligand. Chem. Commun. 54, 2759–2762 (2018).
Hong, K., Park, H. & Yu, J.-Q. Methylene C(sp3)–H arylation of aliphatic ketones using a transient directing group. ACS Catal. 7, 6938–6941 (2017).
Wu, Y.-J., Yao, Q.-J., Chen, H.-M., Liao, G. & Shi, B.-F. Palladium-catalyzed ortho-C–H silylation of biaryl aldehydes using a transient directing group. Sci. China Chem. 63, 875–880 (2020).
Zhang, X.-L. et al. Dehydrogenative β-arylation of saturated aldehydes using transient directing groups. Org. Lett. 21, 2731–2735 (2019).
Guan, Z., Chen, S., Huang, Y. & Yao, H. Rhodium(iii)-catalyzed intramolecular olefin hydroarylation of aromatic aldehydes using a transient directing group. Org. Lett. 21, 3959–3962 (2019).
Thrimurtulu, N. et al. Palladium catalyzed regioselective C4-arylation and olefination of indoles and azaindoles. Adv. Synth. Catal. 361, 1441–1446 (2019).
Xu, J. et al. Pd-catalyzed direct ortho-C–H arylation of aromatic ketones enabled by a transient directing group. Org. Lett. 19, 1562–1565 (2017).
Li, B. et al. Transient ligand enabled ortho-arylation of five-membered heterocyclic carbonyl compounds: facile build-up of mechanochromic materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 3401–3405 (2018).
Wang, D.-Y. et al. Direct dehydrogenative arylation of benzaldehydes with arenes using transient directing groups. Org. Lett. 20, 1794–1797 (2018).
Gou, B.-B., Liu, H.-F., Chen, J. & Zhou, L. Palladium-catalyzed site-selective C(sp3)–H arylation of phenylacetaldehydes. Org. Lett. 21, 7084–7088 (2019).
Wang, Z., Dong, W., Sun, B., Yu, Q. & Zhang, F.-L. Cascade reaction for the synthesis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons via transient directing group strategy. Tetrahedron 75, 4031–4041 (2019).
Park, H., Yoo, K., Jung, B. & Kim, M. Direct synthesis of anthracenes from o-tolualdehydes and aryl iodides through Pd(ii)-catalyzed sp3 C–H arylation and electrophilic aromatic cyclization. Tetrahedron. 74, 2048–2055 (2018).
Smyth, J. E., Butler, N. M. & Keller, P. A. A twist of nature–the significance of atropisomers in biological systems. Nat. Prod. Rep. 32, 1562–1583 (2015).
Gustafson, J., Lim, D. & Miller, S. J. Dynamic kinetic resolution of biaryl atropisomers via peptide-catalyzed asymmetric bromination. Science 328, 1251–1255 (2010).
Newton, C. G., Wang, S.-G., Oliveira, C. C. & Cramer, N. Catalytic enantioselective transformations involving C–H bond cleavage by transition-metal complexes. Chem. Rev. 117, 8908–8976 (2017).
Yao, Q.-J., Zhang, S., Zhan, B.-B. & Shi, B.-F. Atroposelective synthesis of axially chiral biaryls by palladium-catalyzed asymmetric C–H olefination enabled by a transient chiral auxiliary. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 6617–6621 (2017). This is the first atroposelective functionalization using a TDG.
Fan, J. et al. Asymmetric total synthesis of TAN-1085 facilitated by Pd-catalyzed atroposelective C–H olefination. Org. Lett. 21, 3352–3356 (2019).
Ohmori, K. et al. Concise total synthesis and structure assignment of TAN-1085. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 43, 3167–3171 (2004).
Liao, G. et al. Pd-catalyzed atroposelective C–H allylation through β-O elimination: diverse synthesis of axially chiral biaryls. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 17151–17155 (2018).
Liao, G. et al. Scalable, stereocontrolled formal syntheses of (+)-isoschizandrin and (+)-steganone: development and applications of palladium(ii)-catalyzed atroposelective C–H alkynylation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 3661–3665 (2018).
Liao, G. et al. Synthesis of chiral aldehyde catalysts by Pd-catalyzed atroposelective C–H naphthylation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 11464–11468 (2019).
Zhang, S. et al. Enantioselective synthesis of atropisomers featuring pentatomic heteroaromatics by Pd-catalyzed C–H alkynylation. ACS Catal. 9, 1956–1961 (2019).
Chen, H.-M. et al. Pd-catalyzed atroposelective C–H allylation and alkenylation: access to enantioenriched atropisomers featuring pentatomic heteroaromatics. Organometallics 38, 4022–4028 (2019).
Zhang, J., Xu, Q., Wu, J., Fan, J. & Xie, M. Construction of N–C axial chirality through atroposelective C–H olefination of N-arylindoles by palladium/amino acid cooperative catalysis. Org. Lett. 21, 6361–6365 (2019).
Song, H. et al. Synthesis of axially chiral styrenes via Pd-catalyzed asymmetric C–H olefination enabled by an amino amide transient directing group. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 6576–6580 (2020).
Xu, J., Liu, Y., Zhang, J., Xua, X. & Jin, Z. Palladium-catalyzed enantioselective C(sp2)–H arylation of ferrocenyl ketones enabled by a chiral transient directing group. Chem. Commun. 54, 689–692 (2018).
Rueda-Becerril, M. et al. Fluorine transfer to alkyl radicals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 4026–4029 (2012).
Bloom, S. et al. A polycomponent metal-catalyzed aliphatic, allylic, and benzylic fluorination. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51, 10580–10583 (2012).
Liu, W. et al. Oxidative aliphatic C–H fluorination with fluoride ion catalyzed by a manganese porphyrin. Science 337, 1322–1325 (2012).
Kalow, J. A. & Doyle, A. G. Enantioselective ring opening of epoxides by fluoride anion promoted by a cooperative dual-catalyst system. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 3268–3269 (2010).
Katcher, M. H. & Doyle, A. G. Palladium-catalyzed asymmetric synthesis of allylic fluorides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 17402–17404 (2010).
Park, H., Verma, P., Hong, K. & Yu, J.-Q. Controlling Pd(iv) reductive elimination pathways enables Pd(ii)-catalysed enantioselective C(sp3)–H fluorination. Nat. Chem. 10, 755–762 (2018). This work highlights Pd(ii)-catalysed enantioselective C(sp3)–H fluorination using a TDG.
Xiao, L.-J. et al. Pd(ii)-catalyzed enantioselective C(sp3)–H arylation of cyclobutyl ketones using a chiral transient directing group. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 9594–9600 (2020).
Song, G., Wang, F. & Li, X. C–C, C–O and C–N bond formation via rhodium(iii)-catalyzed oxidative C–H activation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 3651–3678 (2012).
Ye, B. & Cramer, N. Chiral cyclopentadienyl ligands as stereocontrolling element in asymmetric C–H functionalization. Science 338, 504–506 (2012).
Audic, B., Wodrich, M. D. & Cramer, N. Mild complexation protocol for chiral CpxRh and Ir complexes suitable for in situ catalysis. Chem. Sci. 10, 781–787 (2019).
Li, G., Jiang, J., Xie, H. & Wang, J. Introducing the chiral transient directing group strategy to rhodium(iii)-catalyzed asymmetric C–H activation. Chem. Eur. J. 25, 4688–4694 (2019).
Li, Z.-Y. et al. Ruthenium-catalyzed enantioselective C–H functionalization: a practical access to optically active indoline derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 15730–15736 (2019).
Li, G., Liu, Q., Vasamsetty, L., Guo, W. & Wang, J. A rare ruthenium(ii)-catalyzed inert C–H bond activation assisted by a chiral transient directing group. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 3475–3479 (2020).
Oxtoby, L. J. et al. A transient-directing-group strategy enables enantioselective reductive Heck hydroarylation of alkenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 8885–8890 (2020).
Liu, Y. & Ge, H. Site-selective C–H arylation of primary aliphatic amines enabled by a catalytic transient directing group. Nat. Chem. 9, 26–32 (2017).
Wu, Y., Chen, Y.-Q., Liu, T., Eastgate, M. D. & Yu, J.-Q. Pd-catalyzed γ-C(sp3)–H arylation of free amines using a transient directing group. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138, 14554–14557 (2016).
Chen, Y.-Q., Wu, Y., Wang, Z., Qiao, J. X. & Yu, J.-Q. Transient directing group enabled Pd-catalyzed γ-C(sp3)–H oxygenation of alkyl amines. ACS Catal. 10, 5657–5662 (2020).
Hu, X.-X. et al. The stabilizing effect of the transient imine directing group in the Pd(ii)-catalyzed C(sp3)–H arylation of free primary amines. Org. Chem. Front. 5, 1670–1678 (2018).
Lin, H., Wang, C., Bannister, T. D. & Kamenecka, T. M. Site-selective γ-C(sp3)–H and γ-C(sp2)–H arylation of free amino esters promoted by a catalytic transient directing group. Chem. Eur. J. 24, 9535–9541 (2018).
Chen, Y.-Q. et al. Overcoming the limitations of γ- and δ-C–H arylation of amines through ligand development. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 17884–17894 (2018).
St John-Campbell, S., Ou, A. K. & Bull, J. A. Palladium-catalyzed C(sp3)–H arylation of primary amines using a catalytic alkyl acetal to form a transient directing group. Chem. Eur. J. 24, 17838–17843 (2018).
Chen, Y.-Q. et al. Pd-catalyzed γ-C(sp3)–H fluorination of free amines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142, 9966–9974 (2020).
Bedford, R. B., Coles, S. J., Hursthouse, M. B. & Limmert, M. E. The catalytic intermolecular ortho-arylation of phenols. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 42, 112–114 (2003).
Bedford, R. B. & Limmert, M. E. Catalytic intermolecular ortho-arylation of phenols. J. Org. Chem. 68, 8669–8682 (2003).
Bedford, R. B. et al. Simple rhodium–chlorophosphine pre-catalysts for the ortho-arylation of phenols. Chem. Commun. https://doi.org/10.1039/B718128K (2008).
Oi, S., Watanabe, S.-I., Fukita, S. & Inoue, Y. Rhodium-HMPT-catalyzed direct ortho arylation of phenols with aryl bromides. Tetrahedron Lett. 44, 8665–8668 (2003).
Guo, R.-T., Zhang, Y.-L., Tian, J.-J., Zhu, K.-Y. & Wang, X.-C. Rhodium-catalyzed ortho-selective carbene C–H insertion of unprotected phenols directed by a transient oxonium ylide intermediate. Org. Lett. 22, 908–913 (2020).
Yang, J.-F. et al. Ligand-accelerated direct C–H arylation of BINOL: a rapid one-step synthesis of racemic 3,3′-diaryl BINOLs. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 14116–14120 (2016).
Lewis, J. C., Wu, J., Bergman, R. G. & Ellman, J. A. Preagostic Rh–H interactions and C–H bond functionalization: a combined experimental and theoretical investigation of rhodium(i) phosphinite complexes. Organometallics 24, 5737–5746 (2005).
Carrión, M. C. & Cole-Hamilton, D. J. Halide-free ethylation of phenol by multifunctional catalysis using phosphinite ligands. Chem. Commun. https://doi.org/10.1039/B610038D (2006).
Li, D. Y. et al. Cascade reaction of alkynols and 7-oxabenzonorbornadienes involving transient hemiketal group directed C–H activation and synergistic RhIII/ScIII catalysis. Org. Lett. 18, 5134–5137 (2016).
Mohr, Y. et al. Regiospecificity in ligand-free Pd-catalyzed C–H arylation of indoles: LiHMDS as base and transient directing group. ACS Catal. 10, 2713–2719 (2020).
Acknowledgements
Financial support was provided by Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), India (CRG/2018/003951). University Grants Commission of India (UGC India) supported the scholarships to N.G. and T.B.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N.G. researched literature for the article and contributed to discussion of content and writing. T.B. and D.M. contributed to discussion and reviewing/editing the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goswami, N., Bhattacharya, T. & Maiti, D. Transient directing ligands for selective metal-catalysed C–H activation. Nat Rev Chem 5, 646–659 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-021-00311-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-021-00311-3
This article is cited by
-
Transition metal-catalysed directed C–H functionalization with nucleophiles
Nature Synthesis (2022)