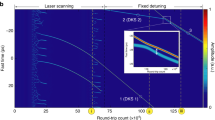
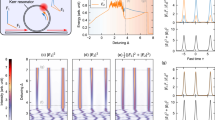
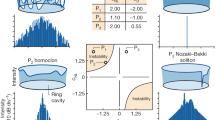
Abstract
Dissipative Kerr solitons in optical microresonators combine nonlinear optical physics with photonic-integrated technologies. They are promising for a number of applications ranging from optical coherent communications to astrophysical spectrometer calibration, and are also of fundamental interest to the physical sciences. Dissipative Kerr solitons can form a variety of stable states, including breathers and multiple-soliton formations. Among these states, soliton crystals stand out: temporally ordered ensembles of soliton pulses, which are regularly arranged by a modulation of the continuous-wave intracavity driving field. To date, however, the dynamics of soliton crystals and their defect-free generation remain unexplored. Here, we show that the chaotic operating regimes of driven optical microresonators significantly impact the dynamics of soliton crystals. We realize deterministic generation of perfect soliton crystal states, which correspond to a stable, defect-free lattice of intracavity optical pulses. We reveal a critical pump power, below which the stochastic process of soliton excitation abruptly becomes deterministic, which enables faultless, device-independent access to perfect soliton crystals. We also demonstrate the switching of these states and its relation to the regime of transient chaos. Finally, we report on other dynamical phenomena observed in soliton crystals including the formation of breathers, transitions between perfect soliton crystals, their melting and recrystallization.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to produce the plots within this paper are available at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.2809645. All other data used in this study are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
Code availability
The code used to produce the plots within this paper is available at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.2809645.
References
Haelterman, M., Trillo, S. & Wabnitz, S. Dissipative modulation instability in a nonlinear dispersive ring cavity. Opt. Commun. 91, 401–407 (1992).
Akhmediev, N. N. & Ankiewicz, A. Solitons Around Us: Integrable, Hamiltonian and Dissipative Systems 105–126 (Springer, 2003).
Kippenberg, T. J., Gaeta, A. L., Lipson, M. & Gorodetsky, M. L. Dissipative Kerr solitons in optical microresonators. Science 361, eaan8083 (2018).
Herr, T. et al. Temporal solitons in optical microresonators. Nat. Photon. 8, 145–152 (2014).
Brasch, V. et al. Photonic chip–based optical frequency comb using soliton Cherenkov radiation. Science 351, 357–360 (2016).
Raja, A. S. et al. Electrically pumped photonic integrated soliton microcomb. Nat. Commun. 10, 680–687 (2019).
Stern, B., Ji, X., Okawachi, Y., Gaeta, A. L. & Lipson, M. Battery-operated integrated frequency comb generator. Nature 562, 401–405 (2018).
Marin-Palomo, P. et al. Microresonator-based solitons for massively parallel coherent optical communications. Nature 546, 274–279 (2017).
Jost, J. D. et al. Counting the cycles of light using a self-referenced optical microresonator. Optica 2, 706–711 (2015).
Suh, M.-G., Yang, Q.-F., Yang, K. Y., Yi, X. & Vahala, K. J. Microresonator soliton dual-comb spectroscopy. Science 354, 600–603 (2016).
Yu, M. et al. Silicon-chip-based mid-infrared dual-comb spectroscopy. Nat. Commun. 9, 1869–1876 (2018).
Trocha, P. et al. Ultrafast optical ranging using microresonator soliton frequency combs. Science 359, 887–891 (2018).
Suh, M.-G. & Vahala, K. J. Soliton microcomb range measurement. Science 359, 884–887 (2018).
Liang, W. et al. High spectral purity Kerr frequency comb radio frequency photonic oscillator. Nat. Commun. 6, 7957 (2015).
Spencer, D. T. et al. An optical-frequency synthesizer using integrated photonics. Nature 557, 81–85 (2018).
Obrzud, E. et al. A microphotonic astrocomb. Nat. Photon. 13, 31–36 (2019).
Suh, M.-G. et al. Searching for exoplanets using a microresonator astrocomb. Nat. Photon. 13, 25–30 (2019).
Cole, D. C., Lamb, E. S., Del’Haye, P., Diddams, S. A. & Papp, S. B. Soliton crystals in Kerr resonators. Nat. Photon. 11, 671–677 (2017).
Wang, Y. et al. Universal mechanism for the binding of temporal cavity solitons. Optica 4, 855–863 (2017).
Taheri, H., Matsko, A. B. & Maleki, L. Optical lattice trap for Kerr solitons. Eur. Phys. J. D 71, 153–165 (2017).
Wang, W. et al. Robust soliton crystals in a thermally controlled microresonator. Opt. Lett. 43, 2002–2005 (2018).
Karpov, M. et al. Dynamics of soliton crystals in optical microresonators. In Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics FTu1D.2 (Optical Society of America, 2017).
Lu, Z. et al. Raman self-frequency-shift of soliton crystal in a high index doped silica micro-ring resonator. Opt. Mater. Express 8, 2662–2669 (2018).
Luke, K., Dutt, A., Poitras, C. B. & Lipson, M. Overcoming Si3N4 film stress limitations for high quality factor ring resonators. Opt. Express 21, 22829–22833 (2013).
Pfeiffer, M. H. P. et al. Photonic Damascene process for integrated high-Q microresonator based nonlinear photonics. Optica 3, 20–25 (2016).
Kordts, A., Pfeiffer, M. H. P., Guo, H., Brasch, V. & Kippenberg, T. J. Higher order mode suppression in high-Q anomalous dispersion SiN microresonators for temporal dissipative Kerr soliton formation. Opt. Lett. 41, 452–455 (2016).
Grudinin, I. S. et al. High-contrast Kerr frequency combs. Optica 4, 434–437 (2017).
Lugiato, L. A. & Lefever, R. Spatial dissipative structures in passive optical systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 58, 2209–2211 (1987).
Guo, H. et al. Universal dynamics and deterministic switching of dissipative Kerr solitons in optical microresonators. Nat. Phys. 13, 94–102 (2017).
Anderson, M., Leo, F., Coen, S., Erkintalo, M. & Murdoch, S. G. Observations of spatiotemporal instabilities of temporal cavity solitons. Optica 3, 1071–1074 (2016).
Lu, Z. et al. Deterministic generation and switching of dissipative Kerr soliton in a thermally controlled micro-resonator. AIP Adv. 9, 025314–025319 (2019).
Xue, X. et al. Mode-locked dark pulse Kerr combs in normal-dispersion microresonators. Nat. Photon. 9, 594–600 (2015).
Xue, X. et al. Normal-dispersion microcombs enabled by controllable mode interactions. Laser Photon. Rev. 9, L23–L28 (2015).
Lucas, E., Karpov, M., Guo, H., Gorodetsky, M. & Kippenberg, T. Breathing dissipative solitons in optical microresonators. Nat. Commun. 8, 736–746 (2017).
Joshi, C. et al. Thermally controlled comb generation and soliton modelocking in microresonators. Opt. Lett. 41, 2565–2568 (2016).
Sun, C., Askham, T. & Kutz, J. N. Stability and dynamics of microring combs: elliptic function solutions of the Lugiato–Lefever equation. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 35, 1341–1353 (2018).
Del’Haye, P., Arcizet, O., Gorodetsky, M. L., Holzwarth, R. & Kippenberg, T. J. Frequency comb assisted diode laser spectroscopy for measurement of microcavity dispersion. Nat. Photon. 3, 529–533 (2009).
Herr, T. et al. Mode spectrum and temporal soliton formation in optical microresonators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 123901–123906 (2014).
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge fruitful discussions with E. Lucas and M. Anderson. This publication was supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, Air Force Material Command, USAF under award no. FA9550-15-1-0099 and by funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Marie Sklodowska-Curie IF grant agreement no. 753749 (SOLISYNTH). This publication was supported by contract D18AC00032 (DRINQS) from the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, Defense Sciences Office. M.K. acknowledges the support from the European Space Technology Centre with ESA contract no. 4000116145/16/NL/MH/GM. Si3N4 samples were fabricated and grown in the Center of MicroNanoTechnology (CMi) at EPFL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.K. developed the idea, designed and performed experiments and simulations, and processed the data. M.H.P.P. fabricated samples with the assistance of J.L. M.K. wrote the manuscript with input from T.J.K., H.G. and W.W. T.J.K. supervised the project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary figures and notes.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karpov, M., Pfeiffer, M.H.P., Guo, H. et al. Dynamics of soliton crystals in optical microresonators. Nat. Phys. 15, 1071–1077 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-019-0635-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-019-0635-0
This article is cited by
-
Strong interactions between solitons and background light in Brillouin-Kerr microcombs
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Nozaki–Bekki solitons in semiconductor lasers
Nature (2024)
-
Breaking the efficiency limitations of dissipative Kerr solitons using nonlinear couplers
Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy (2024)
-
Symmetrically dispersion-engineered microcombs
Communications Physics (2023)
-
Nonlinear dynamics and Kerr frequency comb formation in lattices of coupled microresonators
Communications Physics (2023)