Abstract
Pathological activation of kidney angiotensin II (Ang II) type 1 receptor (AT1R) signaling stimulates tubular sodium transporters, including epithelial sodium channels, to increase sodium reabsorption and blood pressure. During a search for a means to functionally and selectively modulate AT1R signaling, a molecule directly interacting with the carboxyl-terminal cytoplasmic domain of AT1R was identified and named AT1R-associated protein (ATRAP/Agtrap). We showed that ATRAP promotes constitutive AT1R internalization to inhibit pathological AT1R activation in response to certain stimuli. In the kidney, ATRAP is abundantly distributed in epithelial cells along the proximal and distal tubules. Results from genetically engineered mice with modified ATRAP expression show that ATRAP plays a key role in the regulation of renal sodium handling and the modulation of blood pressure in response to pathological stimuli and further suggest that the function of kidney tubule ATRAP may be different between distal tubules and proximal tubules, implying that ATRAP is a target of interest in hypertension.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dzau VJ. Tissue renin-angiotensin system in myocardial hypertrophy and failure. Arch Intern Med. 1993;153:937–42.
Tamura K, Umemura S, Fukamizu A, Ishii M, Murakami K. Recent advances in the study of renin and angiotensinogen genes: from molecules to the whole body. Hypertens Res. 1995;18:7–18.
Azushima K, Morisawa N, Tamura K, Nishiyama A. Recent research advances in renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system receptors. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2020;22:22.
Kamo T, Akazawa H, Komuro I. Pleiotropic effects of angiotensin II receptor signaling in cardiovascular homeostasis and aging. Int Heart J. 2015;56:249–54.
Mehta PK, Griendling KK. Angiotensin II cell signaling: physiological and pathological effects in the cardiovascular system. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007;292:C82–97.
Yamamoto K, Rakugi H. Angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors: comprehensive review and implications in hypertension treatment. Hypertens Res. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-021-00706-1.
Mogi M, Iwai M, Horiuchi M. Emerging concepts of regulation of angiotensin II receptors: new players and targets for traditional receptors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007;27:2532–9.
Kobori H, Nangaku M, Navar LG, Nishiyama A. The intrarenal Renin-Angiotensin system: from physiology to the pathobiology of hypertension and kidney disease. Pharm Rev. 2007;59:251–87.
Navar LG, Kobori H, Prieto MC, Gonzalez-Villalobos RA. Intratubular renin-angiotensin system in hypertension. Hypertension. 2011;57:355–62.
Coffman TM. The inextricable role of the kidney in hypertension. J Clin Invest. 2014;124:2341–7.
Miura S, Saku K, Karnik SS. Molecular analysis of the structure and function of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor. Hypertens Res. 2003;26:937–43.
Horiuchi M, Iwanami J, Mogi M. Regulation of angiotensin II receptors beyond the classical pathway. Clin Sci. 2012;123:193–203.
Nishida M, Ogushi M, Suda R, Toyotaka M, Saiki S, Kitajima N, et al. Heterologous down-regulation of angiotensin type 1 receptors by purinergic P2Y2 receptor stimulation through S-nitrosylation of NF-kappaB. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:6662–7.
Bellot M, Galandrin S, Boularan C, Matthies HJ, Despas F, Denis C, et al. Dual agonist occupancy of AT1-R-alpha2C-AR heterodimers results in atypical Gs-PKA signaling. Nat Chem Biol. 2015;11:271–9.
Balakumar P, Jagadeesh G. A century old renin-angiotensin system still grows with endless possibilities: AT1 receptor signaling cascades in cardiovascular physiopathology. Cell Signal. 2014;26:2147–60.
Cabana J, Holleran B, Leduc R, Escher E, Guillemette G, Lavigne P. Identification of distinct conformations of the angiotensin-II type 1 receptor associated with the Gq/11 protein pathway and the beta-arrestin pathway using molecular dynamics simulations. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:15835–54.
Hayashi H, Hess DT, Zhang R, Sugi K, Gao H, Tan BL, et al. S-nitrosylation of beta-arrestins biases receptor signaling and confers ligand independence. Mol Cell. 2018;70:473–87.
Namkung Y, LeGouill C, Kumar S, Cao Y, Teixeira LB, Lukasheva V, et al. Functional selectivity profiling of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor using pathway-wide BRET signaling sensors. Sci Signal. 2018;11:eaat1631.
Wisler JW, Rockman HA, Lefkowitz RJ, Biased G. Protein-coupled receptor signaling: changing the paradigm of drug discovery. Circulation. 2018;137:2315–7.
Lu S, He X, Yang Z, Chai Z, Zhou S, Wang J, et al. Activation pathway of a G protein-coupled receptor uncovers conformational intermediates as targets for allosteric drug design. Nat Commun. 2021;12:4721.
Aplin M, Bonde MM, Hansen JL. Molecular determinants of angiotensin II type 1 receptor functional selectivity. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2009;46:15–24.
Takahashi T, Huang Y, Yamamoto K, Hamano G, Kakino A, Kang F. et al. The endocytosis of oxidized LDL via the activation of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor. iScience. 2021;24:102076.
Miura S, Fujino M, Hanzawa H, Kiya Y, Imaizumi S, Matsuo Y, et al. Molecular mechanism underlying inverse agonist of angiotensin II type 1 receptor. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:19288–95.
Garcia-Nafria J, Nehme R, Edwards PC, Tate CG. Cryo-EM structure of the serotonin 5-HT1B receptor coupled to heterotrimeric Go. Nature. 2018;558:620–3.
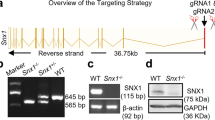
Liu C, Li X, Fu J, Chen K, Liao Q, Wang J, et al. Increased AT1 receptor expression mediates vasoconstriction leading to hypertension in Snx1(-/-) mice. Hypertens Res. 2021;44:906–17.
Wu N, Olechwier AM, Brunner C, Edwards PC, Tsai CJ, Tate CG, et al. High-mass MALDI-MS unravels ligand-mediated G protein-coupling selectivity to GPCRs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2021;118:e2024146118.
Violin JD, Crombie AL, Soergel DG, Lark MW. Biased ligands at G-protein-coupled receptors: promise and progress. Trends Pharm Sci. 2014;35:308–16.
De Groof TWM, Bergkamp ND, Heukers R, Giap T, Bebelman MP, Goeij-de Haas R, et al. Selective targeting of ligand-dependent and -independent signaling by GPCR conformation-specific anti-US28 intrabodies. Nat Commun. 2021;12:4357.
Guo DF, Tardif V, Ghelima K, Chan JS, Ingelfinger JR, Chen X, et al. A novel angiotensin II type 1 receptor-associated protein induces cellular hypertrophy in rat vascular smooth muscle and renal proximal tubular cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:21109–20.
Guo S, Lopez-Ilasaca M, Dzau VJ. Identification of calcium-modulating cyclophilin ligand (CAML) as transducer of angiotensin II-mediated nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) activation. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:12536–41.
Tamura K, Tanaka Y, Tsurumi Y, Azuma K, Shigenaga A, Wakui H, et al. The role of angiotensin AT1 receptor-associated protein in renin-angiotensin system regulation and function. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2007;9:121–7.
Cook JL, Re RN, deHaro DL, Abadie JM, Peters M, Alam J. The trafficking protein GABARAP binds to and enhances plasma membrane expression and function of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor. Circ Res. 2008;102:1539–47.
Garner K, Li M, Ugwuanya N, Cockcroft S. The phosphatidylinositol transfer protein RdgBbeta binds 14-3-3 via its unstructured C-terminus, whereas its lipid-binding domain interacts with the integral membrane protein ATRAP (angiotensin II type I receptor-associated protein). Biochem J. 2011;439:97–111.
Doblinger E, Hocherl K, Mederle K, Kattler V, Walter S, Hansen PB, et al. Angiotensin AT1 receptor-associated protein Arap1 in the kidney vasculature is suppressed by angiotensin II. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2012;302:F1313–24.
Tamura K, Wakui H, Azushima K, Uneda K, Haku S, Kobayashi R, et al. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor binding molecule ATRAP as a possible modulator of renal sodium handling and blood pressure in pathophysiology. Curr Med Chem. 2015;22:3210–6.
Hein L, Meinel L, Pratt RE, Dzau VJ, Kobilka BK. Intracellular trafficking of angiotensin II and its AT1 and AT2 receptors: evidence for selective sorting of receptor and ligand. Mol Endocrinol. 1997;11:1266–77.
Daviet L, Lehtonen JY, Tamura K, Griese DP, Horiuchi M, Dzau VJ. Cloning and characterization of ATRAP, a novel protein that interacts with the angiotensin II type 1 receptor. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:17058–62.
Cui T, Nakagami H, Iwai M, Takeda Y, Shiuchi T, Tamura K, et al. ATRAP, novel AT1 receptor associated protein, enhances internalization of AT1 receptor and inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell growth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;279:938–41.
Lopez-Ilasaca M, Liu X, Tamura K, Dzau VJ. The angiotensin II type I receptor-associated protein, ATRAP, is a transmembrane protein and a modulator of angiotensin II signaling. Mol Biol Cell. 2003;14:5038–50.
Wang W, Huang Y, Zhou Z, Tang R, Zhao W, Zeng L, et al. Identification and characterization of AGTRAP, a human homolog of murine Angiotensin II Receptor-Associated Protein (Agtrap). Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2002;34:93–102.
Tsurumi Y, Tamura K, Tanaka Y, Koide Y, Sakai M, Yabana M, et al. Interacting molecule of AT1 receptor, ATRAP, is colocalized with AT1 receptor in the mouse renal tubules. Kidney Int. 2006;69:488–94.
Masuda S, Tamura K, Wakui H, Maeda A, Dejima T, Hirose T, et al. Expression of angiotensin II type 1 receptor-interacting molecule in normal human kidney and IgA nephropathy. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2010;299:F720–31.
Dejima T, Tamura K, Wakui H, Maeda A, Ohsawa M, Kanaoka T, et al. Prepubertal angiotensin blockade exerts long-term therapeutic effect through sustained ATRAP activation in salt-sensitive hypertensive rats. J Hypertens. 2011;29:1919–29.
Oshita A, Iwai M, Chen R, Ide A, Okumura M, Fukunaga S. et al. Attenuation of inflammatory vascular remodeling by angiotensin II type 1 receptor-associated protein. Hypertension. 2006;48:671–6.
Wakui H, Tamura K, Matsuda M, Bai Y, Dejima T, Shigenaga A, et al. Intrarenal suppression of angiotensin II type 1 receptor binding molecule in angiotensin II-infused mice. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2010;299:F991–F1003.
Wakui H, Tamura K, Tanaka Y, Matsuda M, Bai Y, Dejima T. et al. Cardiac-specific activation of angiotensin II type 1 receptor-associated protein completely suppresses cardiac hypertrophy in chronic angiotensin II-infused mice. Hypertension. 2010;55:1157–64.
Tamura K, Wakui H, Maeda A, Dejima T, Ohsawa M, Azushima K, et al. The physiology and pathophysiology of a novel angiotensin receptor-binding protein ATRAP/Agtrap. Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19:3043–8.
Ohsawa M, Tamura K, Wakui H, Maeda A, Dejima T, Kanaoka T, et al. Deletion of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor-associated protein enhances renal sodium reabsorption and exacerbates angiotensin II-mediated hypertension. Kidney Int. 2014;86:570–81.
Wakui H, Uneda K, Tamura K, Ohsawa M, Azushima K, Kobayashi R, et al. Renal tubule angiotensin II type 1 receptor-associated protein promotes natriuresis and inhibits salt-sensitive blood pressure elevation. J Am Heart Assoc. 2015;4:e001594.
Kobayashi R, Wakui H, Azushima K, Uneda K, Haku S, Ohki K, et al. An angiotensin II type 1 receptor binding molecule has a critical role in hypertension in a chronic kidney disease model. Kidney Int. 2017;91:1115–25.
Oppermann M, Gess B, Schweda F, Castrop H. Atrap deficiency increases arterial blood pressure and plasma volume. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;21:468–77.
Wakui H, Tamura K, Masuda S, Tsurumi-Ikeya Y, Fujita M, Maeda A. et al. Enhanced angiotensin receptor-associated protein in renal tubule suppresses angiotensin-dependent hypertension. Hypertension. 2013;61:1203–10.
Giani JF, Fuchs S, Gonzalez-Villalobos RA. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor-associated protein: a novel modulator of angiotensin II actions in the nephron. Hypertension. 2013;61:1150–2.
Maeda A, Tamura K, Wakui H, Dejima T, Ohsawa M, Azushima K, et al. Angiotensin receptor-binding protein ATRAP/Agtrap inhibits metabolic dysfunction with visceral obesity. J Am Heart Assoc. 2013;2:e000312.
Wakui H, Dejima T, Tamura K, Uneda K, Azuma K, Maeda A, et al. Activation of angiotensin II type 1 receptor-associated protein exerts an inhibitory effect on vascular hypertrophy and oxidative stress in angiotensin II-mediated hypertension. Cardiovasc Res. 2013;100:511–9.
Azushima K, Ohki K, Wakui H, Uneda K, Haku S, Kobayashi R, et al. Adipocyte-specific enhancement of angiotensin II type 1 receptor-associated protein ameliorates diet-induced visceral obesity and insulin resistance. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017;6:e004488.
Ohki K, Wakui H, Azushima K, Uneda K, Haku S, Kobayashi R, et al. ATRAP expression in brown adipose tissue does not influence the development of diet-induced metabolic disorders in mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18:676.
Ohki K, Wakui H, Kishio N, Azushima K, Uneda K, Haku S, et al. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor-associated protein inhibits angiotensin II-induced insulin resistance with suppression of oxidative stress in skeletal muscle tissue. Sci Rep. 2018;8:2846.
Kinguchi S, Wakui H, Azushima K, Haruhara K, Koguchi T, Ohki K, et al. Effects of ATRAP in renal proximal tubules on angiotensin-dependent hypertension. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019;8:e012395.
Kitada M, Kume S, Takeda-Watanabe A, Kanasaki K, Koya D. Sirtuins and renal diseases: relationship with aging and diabetic nephropathy. Clin Sci. 2013;124:153–64.
Li J, Liu H, Takagi S, Nitta K, Kitada M, Srivastava SP, et al. Renal protective effects of empagliflozin via inhibition of EMT and aberrant glycolysis in proximal tubules. JCI Insight. 2020;5:e129034.
Zhang C, Li N, Suo M, Zhang C, Liu J, Liu L, et al. Sirtuin 3 deficiency aggravates angiotensin II-induced hypertensive cardiac injury by the impairment of lymphangiogenesis. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25:7760–71.
Liu X, Jiang D, Huang W, Teng P, Zhang H, Wei C, et al. Sirtuin 6 attenuates angiotensin II-induced vascular adventitial aging in rat aortae by suppressing the NF-kappaB pathway. Hypertens Res. 2021;44:770–80.
Corssac GB, Bonetto JP, Campos-Carraro C, Cechinel LR, Zimmer A, Parmeggiani B, et al. Pulmonary arterial hypertension induces the release of circulating extracellular vesicles with oxidative content and alters redox and mitochondrial homeostasis in the brains of rats. Hypertens Res. 2021;44:918–31.
Benigni A, Corna D, Zoja C, Sonzogni A, Latini R, Salio M, et al. Disruption of the Ang II type 1 receptor promotes longevity in mice. J Clin Invest. 2009;119:524–30.
Uneda K, Wakui H, Maeda A, Azushima K, Kobayashi R, Haku S, et al. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor-associated protein regulates kidney aging and lifespan independent of angiotensin. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017;6:e006120.
Yamaji T, Yamashita A, Wakui H, Azushima K, Uneda K, Fujikawa Y, et al. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor-associated protein deficiency attenuates sirtuin1 expression in an immortalised human renal proximal tubule cell line. Sci Rep. 2019;9:16550.
Miura S, Kiya Y, Hanzawa H, Nakao N, Fujino M, Imaizumi S, et al. Small molecules with similar structures exhibit agonist, neutral antagonist or inverse agonist activity toward angiotensin II type 1 receptor. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e37974.
Pang PS, Butler J, Collins SP, Cotter G, Davison BA, Ezekowitz JA, et al. Biased ligand of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor in patients with acute heart failure: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase IIB, dose ranging trial (BLAST-AHF). Eur Heart J. 2017;38:2364–73.
Wingler LM, Elgeti M, Hilger D, Latorraca NR, Lerch MT, Staus DP. et al. Angiotensin analogs with divergent bias stabilize distinct receptor conformations. Cell. 2019;176:468–78.
Wingler LM, McMahon C, Staus DP, Lefkowitz RJ, Kruse AC. Distinctive activation mechanism for angiotensin receptor revealed by a synthetic nanobody. Cell. 2019;176:479–90.
Suomivuori CM, Latorraca NR, Wingler LM, Eismann S, King MC, Kleinhenz ALW. et al. Molecular mechanism of biased signaling in a prototypical G protein-coupled receptor. Science. 2020;367:881–7.
Wingler LM, Skiba MA, McMahon C, Staus DP, Kleinhenz ALW, Suomivuori CM. et al. Angiotensin and biased analogs induce structurally distinct active conformations within a GPCR. Science. 2020;367:888–92.
Ferraino KE, Cora N, Pollard CM, Sizova A, Maning J, Lymperopoulos A. Adrenal angiotensin II type 1 receptor biased signaling: the case for “biased” inverse agonism for effective aldosterone suppression. Cell Signal. 2021;82:109967.
Jóźwiak K, Płazińska A. Structural insights into ligand-receptor interactions involved in biased agonism of G-protein coupled receptors. Molecules. 2021;26:851.
Acknowledgements
The authors were supported by grants from Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, Uehara Memorial Foundation, and Salt Science Research Foundation (18C4, 19C4, 20C4). The authors were also supported by the Yokohama City University research grant “KAMOME Project”, Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED), and by the Translational Research program Strategic PRomotion for practical application of INnovative medical Technology (TR-SPRINT) from AMED.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tamura, K., Azushima, K., Kinguchi, S. et al. ATRAP, a receptor-interacting modulator of kidney physiology, as a novel player in blood pressure and beyond. Hypertens Res 45, 32–39 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-021-00776-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-021-00776-1
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Enhancement of angiotensin II type 1 receptor-associated protein in the paraventricular nucleus suppresses angiotensin II-dependent hypertension
Hypertension Research (2024)
-
Angiotensin II type 1 receptor-associated protein deletion combined with angiotensin II stimulation accelerates the development of diabetic kidney disease in mice on a C57BL/6 strain
Hypertension Research (2024)
-
ATRAP in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus as another key player in the control of sympathetic outflow
Hypertension Research (2024)
-
Angiotensin II type-1 receptor-associated protein interacts with transferrin receptor-1 and promotes its internalization
Scientific Reports (2022)