Abstract
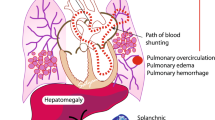
The ductus arteriosus (DA) has a paradoxical biological role in neonates with congenital heart disease (CHD) and can present with significant management challenges. Critical congenital cardiac lesions rely on the patency of the DA to provide either systemic or pulmonary blood flow. A patent DA (PDA) that remains open can also have adverse consequences depending on the degree of systemic to-pulmonary shunting and volume of ductal steal. As such, the presence of a PDA may pose a challenge in the medical management and timing of surgical repair. In this perspective article, we provide an understanding of the role of the DA in the circulatory system in neonates with CHD and discuss traditional and emerging approaches to support the pulmonary and systemic circulations with manipulation of the DA.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rios DR, Bhattacharya S, Levy PT, McNamara PJ. Circulatory insufficiency and hypotension related to the ductus arteriosus in neonates. Front Pediatr. 2018;6:62.
Chiruvolu A, Jaleel MA. Pathophysiology of patent ductus arteriosus in premature neonates. Early Hum Dev. 2009;85:143–6.
Semberova J, Sirc J, Miletin J, Kucera J, Berka I, Sebkova S, et al. Spontaneous closure of patent ductus arteriosus in infants less than 1500 g. Pediatrics. 2017;140:e20164258.
Cucerea M, Simon M, Moldovan E, Ungureanu M, Marian R, Suciu L. Congenital heart disease requiring maintenance of ductus arteriosus in critically ill newborns admitted at a tertiary neonatal intensive care unit. J Crit Care Med. 2016;2:185–91.
Hinton R, Michelfelder E. Significance of reverse orientation of the ductus arteriosus in neonates with pulmonary outflow tract obstruction for early intervention. Am J Cardiol. 2006;97:716–9.
Friedman AH, Fahey JT. The transition from fetal to neonatal circulation: normal responses and implications for infants with heart disease. Semin perinatol. 1993;17:106–21.
Turner D, Vincent J, Epstein M. Isolated right pulmonary artery discontinuity. Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2000;2:24–30.
Hornik CP, He X, Jacobs JP, Li JS, Jaquiss RD, Jacobs ML, et al. Complications after the Norwood operation: an analysis of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons Congenital Heart Surgery Database. Ann Thorac Surg. 2011;92:1734–40.
Jenkins KJ, Gauvreau K, Newburger JW, Spray TL, Moller JH, Iezzoni LI. Consensus-based method for risk adjustment for surgery for congenital heart disease. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2002;123:110–8.
Alsagheir A, Koziarz A, Makhdoum A, Contreras J, Alraddadi H, Abdalla T, et al. Duct stenting versus modified Blalock-Taussig shunt in neonates and infants with duct-dependent pulmonary blood flow: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2021;161:379–90.
Petrucci O, O’Brien SM, Jacobs ML, Jacobs JP, Manning PB, Eghtesady P. Risk factors for mortality and morbidity after the neonatal Blalock-Taussig shunt procedure. Ann Thorac Surg. 2011;92:642–51.
Dorobantu DM, Pandey R, Sharabiani MT, Mahani AS, Angelini GD, Martin RP, et al. Indications and results of systemic to pulmonary shunts: results from a national database. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2016;49:1553–63.
O’Connor MJ, Ravishankar C, Ballweg JA, Gillespie MJ, Gaynor JW, Tabbutt S, et al. Early systemic-to-pulmonary artery shunt intervention in neonates with congenital heart disease. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011;142:106–12.
Mayer JE Jr., Hill K, Jacobs JP, Overman DM, Kumar SR. The Society of Thoracic Surgeons Congenital Heart Surgery Database: 2020 update on outcomes and research. Ann Thorac Surg. 2020;110:1809–18.
Hirsch JC, Gurney JG, Donohue JE, Gebremariam A, Bove EL, Ohye RG. Hospital mortality for Norwood and arterial switch operations as a function of institutional volume. Pediatr Cardiol. 2008;29:713–7.
Ciociola EC, Kumar KR, Zimmerman KO, Thompson EJ, Harward M, Sullivan LN, et al. Association between preoperative respiratory support and outcomes in paediatric cardiac surgery. Cardiol Young-. 2020;30:66–73.
Bentham JR, Zava NK, Harrison WJ, Shauq A, Kalantre A, Derrick G, et al. Duct stenting versus modified blalock-taussig shunt in neonates with duct-dependent pulmonary blood flow: associations with clinical outcomes in a multicenter national study. Circulation 2018;137:581–8.
Gewillig M, Boshoff DE, Dens J, Mertens L, Benson LN. Stenting the neonatal arterial duct in duct-dependent pulmonary circulation: new techniques, better results. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43:107–12.
Gibbs JL, Rothman MT, Rees MR, Parsons JM, Blackburn ME, Ruiz CE. Stenting of the arterial duct: a new approach to palliation for pulmonary atresia. Br Heart J. 1992;67:240–5.
Alwi M, Choo KK, Latiff HA, Kandavello G, Samion H, Mulyadi MD. Initial results and medium-term follow-up of stent implantation of patent ductus arteriosus in duct-dependent pulmonary circulation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44:438–45.
Sivakumar K, Bhagyavathy A, Coelho R, Satish R, Krishnan P. Longevity of neonatal ductal stenting for congenital heart diseases with duct-dependent pulmonary circulation. Congenit Heart Dis. 2012;7:526–33.
Vida VL, Speggiorin S, Maschietto N, Padalino MA, Tessari C, Biffanti R, et al. Cardiac operations after patent ductus arteriosus stenting in duct-dependent pulmonary circulation. Ann Thorac Surg. 2010;90:605–9.
Amoozgar H, Cheriki S, Borzoee M, Ajami G, Soltani M, Ahmadipour M, et al. Short-term result of ductus arteriosus stent implantation compared with surgically created shunts. Pediatr Cardiol. 2012;33:1288–94.
Mallula K, Vaughn G, El-Said H, Lamberti JJ, Moore JW. Comparison of ductal stenting versus surgical shunts for palliation of patients with pulmonary atresia and intact ventricular septum. Catheter Cardiovasc Inter. 2015;85:1196–202.
Glatz AC, Petit CJ, Goldstein BH, Kelleman MS, McCracken CE, McDonnell A, et al. Comparison between patent ductus arteriosus stent and modified Blalock–Taussig shunt as palliation for infants with ductal-dependent pulmonary blood flow: insights from the congenital catheterization research collaborative. Circulation. 2018;137:589–601.
Santoro G, Palladino MT, Capozzi G, Iacono C, Russo MG, Calabro R. Pulmonary artery growth following arterial duct stenting in congenital heart disease with duct-dependent pulmonary circulation. Catheter Cardiovasc Inter. 2009;74:1072–6.
Goldstein BH, O’Byrne ML, Petit CJ, Qureshi AM, Dai D, Griffis HM, et al. Differences in cost of care by palliation strategy for infants with ductal-dependent pulmonary blood flow. Circ Cardiovasc Inter. 2019;12:e007232.
Bauser-Heaton H, Qureshi AM, Goldstein BH, Glatz AC, Ligon RA, Gartenberg A, et al. Comparison of patent ductus arteriosus stent and Blalock–Taussig shunt as palliation for neonates with sole source ductal-dependent pulmonary blood flow: results from the congenital catheterization research collaborative. Pediatr Cardiol 2022;43:121–31.
Li D, Zhou X, Li M. Arterial duct stent versus surgical shunt for patients with duct-dependent pulmonary circulation: a meta-analysis. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021;21:9.
Bacha EA, Daves S, Hardin J, Abdulla RI, Anderson J, Kahana M, et al. Single-ventricle palliation for high-risk neonates: the emergence of an alternative hybrid stage I strategy. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006;131:163–162.
Caldarone CA, Benson L, Holtby H, Li J, Redington AN, Van, et al. Initial experience with hybrid palliation for neonates with single-ventricle physiology. Ann Thorac Surg. 2007;84:1294–1300.
Nwankwo UT, Morell EM, Trucco SM, Morell VO, Kreutzer J. Hybrid strategy for neonates with ductal-dependent systemic circulation at high risk for Norwood. Ann Thorac Surg. 2018;106:595–601.
Simsic JM, Phelps C, Kirchner K, Carpenito KR, Allen R, Miller-Tate H, et al. Interstage outcomes in single ventricle patients undergoing hybrid stage 1 palliation. Congenit Heart Dis. 2018;13:757–63.
Baba K, Chaturvedi R, Lee KJ, Caldarone CA, Benson LN. Fate of the ductal stent after hybrid palliation for hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Ann Thorac Surg. 2013;95:1660–4.
Rahkonen O, Chaturvedi RR, Benson L, Honjo O, Caldarone CA, Lee KJ. Pulmonary artery stenosis in hybrid single-ventricle palliation: High incidence of left pulmonary artery intervention. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2015;149:1102–10 e1102.
Cleveland JD, Tran S, Takao C, Wells WJ, Starnes VA, Kumar SR. Need for pulmonary arterioplasty during glenn independently predicts inferior surgical outcome. Ann Thorac Surg. 2018;106:156–64.
Khan AH, Hoskoppal D, Kumar TKS, Bird L, Allen K, Lloyd H, et al. Utility of the Medtronic microvascular plug as a transcatheter implantable and explantable pulmonary artery flow restrictor in a swine model. Catheter Cardiovasc Inter. 2019;93:1320–8.
Schranz D, Esmaeili A, Akintuerk H. Hypoplastic left heart: stage-I will be performed interventionally, soon. Pediatr Cardiol. 2021;42:727–35.
Schranz D, Esmaeili A, Schrewe R, Kerst G, Akintuerk H. Hypoplastic left heart stage I: no norwood, no hybrid. Circulation 2020;142:1402–4.
Nageotte S, Shahanavaz S, Eghtesady P, Balzer D. Total transcatheter stage 1: a word of caution. Pediatr Cardiol. 2021;42:1410–5.
Sathanandam SK, Gutfinger D, O’Brien L, Forbes TJ, Gillespie MJ, Berman DP, et al. Amplatzer Piccolo Occluder clinical trial for percutaneous closure of the patent ductus arteriosus in patients ≥700 grams. Catheter Cardiovasc Inter. 2020;96(6):1266–76.
Lam JY, Lopushinsky SR, Ma IWY, Dicke F, Brindle ME. Treatment options for pediatric patent ductus arteriosus: systematic review and meta-analysis. Chest. 2015;14:784–93.
Vali P, Lakshminrusimha S, Pelech A, Underwood M, Ing F. Patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants: is early transcatheter closure a paradigm shift? J Perinatol. 2019;39:1449–61.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PL, SS, RW conceptualized the study, shared writing of the first draft critically reviewed the manuscript, and approved submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wheeler, C.R., Sen, S. & Levy, P.T. The ductus arteriosus in neonates with critical congenital heart disease. J Perinatol 42, 1708–1713 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-022-01449-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-022-01449-8