Abstract
Objective
To investigate acute kidney injury (AKI) in neonates with a patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) including incidence, risk factors, and possible correlations between PDA-related echocardiographic measurements and AKI incidence.
Study design
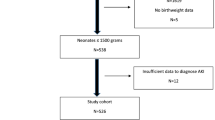
We conducted a single-center retrospective cohort study of infants admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit with a diagnosis of a PDA between July 2015 and July 2017. Infants were evaluated for development of AKI based on the KDIGO criteria and a multivariable logistic regression analysis was performed.
Results
A total of 142 neonates with moderate or large PDAs were included, 43 (30%) developed AKI. Patients who developed AKI had longer length of stay, lower birth weights, lengths, and gestational ages. No echocardiographic measurements were predictive of an increased risk for developing AKI.
Conclusion
There are no significant differences in commonly measured echocardiographic markers of PDA hemodynamic significance in neonates who develop AKI.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heymann MA, Rudolph AM, Silverman NH. Closure of the ductus arteriosus in premature infants by inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis. N. Engl J Med. 1976;295:530–3.
Sivanandan S, Agarwal R. Pharmacological closure of patent ductus arteriosus: selecting the agent and route of administration. Paediatr Drugs. 2016;18:123–38.
Ramos FG, Rosenfeld CR, Roy L, Koch J, Ramaciotti C. Echocardiographic predictors of symptomatic patent ductus arteriosus in extremely-low-birth-weight preterm neonates. J Perinatol. 2010;30:535–9.
Clyman RI, Couto J, Murphy GM. Patent ductus arteriosus: are current neonatal treatment options better or worse than no treatment at all? Semin Perinatol. 2012;36:123–9.
Mercanti I, Boubred F, Simeoni U. Therapeutic closure of the ductus arteriosus: benefits and limitations. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2009;22:14–20.
Kindler A, Seipolt B, Heilmann A, Range U, Rudiger M, Hofmann SR. Development of a diagnostic clinical score for hemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus. Front Pediatr. 2017;5:280.
Nagasawa H, Terazawa D, Kohno Y, Yamamoto Y, Kondo M, Sugawara M, et al. Novel treatment criteria for persistent ductus arteriosus in neonates. Pediatr Neonatol. 2014;55:250–5.
van der Laan ME, Roofthooft MT, Fries MW, Berger RM, Schat TE, van Zoonen AG, et al. A hemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus does not affect cerebral or renal tissue oxygenation in preterm infants. Neonatology. 2016;110:141–7.
Momtaz HE, Sabzehei MK, Rasuli B, Torabian S. The main etiologies of acute kidney injury in the newborns hospitalized in the neonatal intensive care unit. J Clin Neonatol. 2014;3:99–102.
Daga A, Dapaah-Siakwan F, Rajbhandari S, Arevalo C, Salvador A. Diagnosis and risk factors of acute kidney injury in very low birth weight infants. Pediatr Neonatol. 2017;58:258–63.
Liborio AB, Branco KM, Torres de Melo Bezerra C. Acute kidney injury in neonates: from urine output to new biomarkers. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:601568.
Selewski DT, Charlton JR, Jetton JG, Guillet R, Mhanna MJ, Askenazi DJ, et al. Neonatal acute kidney injury. Pediatrics. 2015;136:e463–73.
Weintraub AS, Connors J, Carey A, Blanco V, Green RS. The spectrum of onset of acute kidney injury in premature infants less than 30 weeks gestation. J Perinatol. 2016;36:474–80.
Velazquez DM, Reidy KJ, Sharma M, Kim M, Vega M, Havranek T. The effect of hemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus on acute kidney injury and systemic hypertension in extremely low gestational age newborns. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019;32:3209–14.
Carmody JB, Swanson JR, Rhone ET, Charlton JR. Recognition and reporting of AKI in very low birth weight infants. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014;9:2036–43.
Shalaby MA, Sawan ZA, Nawawi E, Alsaedi S, Al-Wassia H, Kari JA. Incidence, risk factors, and outcome of neonatal acute kidney injury: a prospective cohort study. Pediatr Nephrol. 2018;33:1617–24.
Nagaraj N, Berwal PK, Srinivas A, Berwal A. A study of acute kidney injury in hospitalized preterm neonates in NICU. J Neonatal Perinat Med. 2016;9:417–21.
El-Khuffash A, James AT, Corcoran JD, Dicker P, Franklin O, Elsayed YN, et al. A patent ductus arteriosus severity score predicts chronic lung disease or death before discharge. J Pediatr. 2015;167:1354–61 e1352.
Smith A, McNamara PJ, El-Khuffash AF. Non-pharmacological management of a hemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018;23:245–9.
Condo M, Evans N, Bellu R, Kluckow M. Echocardiographic assessment of ductal significance: retrospective comparison of two methods. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2012;97:F35–8.
Arlettaz R. Echocardiographic evaluation of patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants. Front Pediatr. 2017;5:147.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Andres Contreras-Vega for his assistance in data collection on this project.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency, commercial or not-for-profit sectors. SMC was supported by NIH/NHLBI HL133447.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coffman, Z., Steflik, D., Chowdhury, S.M. et al. Echocardiographic predictors of acute kidney injury in neonates with a patent ductus arteriosus. J Perinatol 40, 510–514 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-019-0560-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-019-0560-1