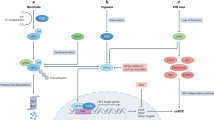
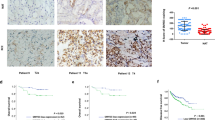
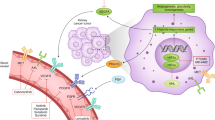
Abstract
Mutations in VHL underlie von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) disease, a hereditary cancer syndrome with several subtypes depending on the risk of developing certain combination of classic features, such as clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), hemangioblastoma and pheochromocytoma. Although numerous potential substrates and functions of pVHL have been described over the past decade, the best-defined role of pVHL has remained as the negative regulator of the heterodimeric hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) transcription factor via the oxygen-dependent ubiquitin-mediated degradation of HIF-α subunit. Despite the seminal discoveries that led to the molecular elucidation of the mammalian oxygen-sensing VHL–HIF axis, which have provided several rational therapies, the mechanisms underlying the complex genotype–phenotype correlation in VHL disease are unclear. This review will discuss and highlight the studies that have provided interesting insights as well as uncertainties to the underlying mechanisms governing VHL disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Robinson CM, Ohh M . The multifaceted von Hippel–Lindau tumour suppressor protein. FEBS Lett 2014; 588: 2704–2711.
Gallou C, Joly D, Mejean A, Staroz F, Martin N, Tarlet G et al. Mutations of the VHL gene in sporadic renal cell carcinoma: definition of a risk factor for VHL patients to develop an RCC. Hum Mutat 1999; 13: 464.
Whaley JM, Naglich J, Gelbert L, Hsia YE, Lamiell JM, Green JS et al. Germ-line mutations in the von Hippel–Lindau tumor-suppressor gene are similar to somatic von Hippel–Lindau aberrations in sporadic renal cell carcinoma. Am J Hum Genet 1994; 55: 1092.
Kanno H, Kondo K, Ito S, Yamamoto I, Fujii S, Torigoe S et al. Somatic mutations of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene in sporadic central nervous system hemangioblastomas. Cancer Res 1994; 54: 4845–4847.
Lee J-Y, Dong S-M, Park W-S, Yoo N-J, Kim C-S, Jang J-J et al. Loss of heterozygosity and somatic mutations of the VHL tumor suppressor gene in sporadic cerebellar hemangioblastomas. Cancer Res 1998; 58: 504–508.
Lindau A . Zur Frage der Angiomatosis retinae und ihrer Hirnkomplikationen. Acta Ophthalmol 1926; 4: 193–226.
v. Hippel E . Ueber eine sehr seltene Erkrankung der Netzhaut. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 1904; 59: 83–106.
Maher E, Yates J, Ferguson-Smith M . Statistical analysis of the two stage mutation model in von Hippel-Lindau disease, and in sporadic cerebellar haemangioblastoma and renal cell carcinoma. J Med Genet 1990; 27: 311–314.
Latif F, Tory K, Gnarra J, Yao M, Duh FM, Orcutt ML et al. Identification of the von Hippel-Lindau disease tumor suppressor gene. Science 1993; 260: 1317–1320.
Iliopoulos O, Kibel A, Gray S, Kaelin WG Jr . Tumour suppression by the human von Hippel-Lindau gene product. Nat Med 1995; 1: 822–826.
Gossage L, Eisen T, Maher ER . VHL, the story of a tumour suppressor gene. Nat Rev Cancer 2015; 15: 55–64.
Chen F, Kishida T, Yao M, Hustad T, Glavac D, Dean M et al. Germline mutations in the von Hippel–Lindau disease tumor suppressor gene: correlations with phenotype. Hum Mutat 1995; 5: 66–75.
Brauch H, Kishida T, Glavac D, Chen F, Pausch F, Höfler H et al. Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease with pheochromocytoma in the Black Forest region of Germany: evidence for a founder effect. Hum Genet 1995; 95: 551–556.
Neumann HP, Eng C, Mulligan LM, Glavac D, Zäuner I, Ponder BA et al. Consequences of direct genetic testing for germline mutations in the clinical management of families with multiple endocrine neoplasia, type II. JAMA 1995; 274: 1149–1151.
Maher ER, Kaelin WG Jr . von Hippel-Lindau disease. Medicine (Baltimore) 1997; 76: 381–391.
Ang SO, Chen H, Hirota K, Gordeuk VR, Jelinek J, Guan Y et al. Disruption of oxygen homeostasis underlies congenital Chuvash polycythemia. Nat Genet 2002; 32: 614–621.
Sergeyeva A, Gordeuk VR, Tokarev YN, Sokol L, Prchal JF, Prchal JT . Congenital polycythemia in Chuvashia. Blood 1997; 89: 2148–2154.
Pastore Y, Jedlickova K, Guan Y, Liu E, Fahner J, Hasle H et al. Mutations of von Hippel-Lindau tumor-suppressor gene and congenital polycythemia. Am J Hum Genet 2003; 73: 412–419.
Crossey PA, Richards FM, Foster K, Prowse A, Latlf F, Lerman MI et al. Identification of intragenic mutations in the Von Hippel—Lindau disease tumour suppressor gene andcorrelation with disease phenotype. Hum Mol Genet 1994; 3: 1303–1308.
Maher ER, Webster AR, Richards FM, Green JS, Crossey PA, Payne SJ et al. Phenotypic expression in von Hippel-Lindau disease: correlations with germline VHL gene mutations. J Med Genet 1996; 33: 328–332.
Stolle C, Glenn G, Zbar B, Humphrey JS, Choyke P, Walther M et al. Improved detection of germline mutations in the von Hippel-Lindau disease tumor suppressor gene. Hum Mutat 1998; 12: 417.
Stebbins CE, Kaelin WG Jr., Pavletich NP . Structure of the VHL-ElonginC-ElonginB complex: implications for VHL tumor suppressor function. Science 1999; 284: 455–461.
Los M, Jansen GH, Kaelin WG, Lips C, Blijham GH, Voest EE . Expression pattern of the von Hippel-Lindau protein in human tissues. Lab Invest 1996; 75: 231–238.
Iliopoulos O, Ohh M, Kaelin WG Jr . pVHL19 is a biologically active product of the von Hippel-Lindau gene arising from internal translation initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 11661–11666.
Blankenship C, Naglich JG, Whaley JM, Seizinger B, Kley N . Alternate choice of initiation codon produces a biologically active product of the von Hippel Lindau gene with tumor suppressor activity. Oncogene 1999; 18: 1529–1535.
Ohh M, Park CW, Ivan M, Hoffman MA, Kim TY, Huang LE et al. Ubiquitination of hypoxia-inducible factor requires direct binding to the beta-domain of the von Hippel-Lindau protein. Nat Cell Biol 2000; 2: 423–427.
Wizigmann-Voos S, Breier G, Risau W, Plate K . Up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in von Hippel-Lindau disease-associated and sporadic hemangioblastomas. Cancer Res 1995; 55: 1358–1364.
Kibel A, Iliopoulos O, DeCaprio JA, Kaelin WG Jr . Binding of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein to Elongin B and C. Science 1995; 269: 1444–1446.
Duan DR, Pause A, Burgess WH, Aso T, Chen D, Garrett KP et al. Inhibition of transcription elongation by the VHL tumor suppressor protein. Science 1995; 269: 1402–1406.
Semenza GL, Nejfelt MK, Chi SM, Antonarakis SE . Hypoxia-inducible nuclear factors bind to an enhancer element located 3' to the human erythropoietin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1991; 88: 5680–5684.
Semenza GL, Wang GL . A nuclear factor induced by hypoxia via de novo protein synthesis binds to the human erythropoietin gene enhancer at a site required for transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol 1992; 12: 5447–5454.
Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA, Semenza GL . Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92: 5510–5514.
Huang LE, Arany Z, Livingston DM, Bunn HF . Activation of hypoxia-inducible transcription factor depends primarily upon redox-sensitive stabilization of its α subunit. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 32253–32259.
Huang LE, Gu J, Schau M, Bunn HF . Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α is mediated by an O2-dependent degradation domain via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1998; 95: 7987–7992.
Maxwell PH, Wiesener MS, Chang GW, Clifford SC, Vaux EC, Cockman ME et al. The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature 1999; 399: 271–275.
Iliopoulos O, Levy AP, Jiang C, Kaelin WG, Goldberg MA . Negative regulation of hypoxia-inducible genes by the von Hippel-Lindau protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1996; 93: 10595–10599.
Lonergan KM, Iliopoulos O, Ohh M, Kamura T, Conaway RC, Conaway JW et al. Regulation of hypoxia-inducible mRNAs by the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein requires binding to complexes containing elongins B/C and Cul2. Mol Cell Biol 1998; 18: 732–741.
Ivan M, Kondo K, Yang H, Kim W, Valiando J, Ohh M et al. HIFalpha targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation: implications for O2 sensing. Science 2001; 292: 464–468.
Jaakkola P, Mole DR, Tian YM, Wilson MI, Gielbert J, Gaskell SJ et al. Targeting of HIF-alpha to the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl hydroxylation. Science 2001; 292: 468–472.
Epstein AC, Gleadle JM, McNeill LA, Hewitson KS, O'Rourke J, Mole DR et al. C. elegans EGL-9 and mammalian homologs define a family of dioxygenases that regulate HIF by prolyl hydroxylation. Cell 2001; 107: 43–54.
Berra E, Benizri E, Ginouves A, Volmat V, Roux D, Pouyssegur J . HIF prolyl-hydroxylase 2 is the key oxygen sensor setting low steady-state levels of HIF-1alpha in normoxia. EMBO J 2003; 22: 4082–4090.
Maher E, Yates J, Harries R, Benjamin C, Harris R, Moore A et al. Clinical features and natural history of von Hippel-Lindau disease. QJM 1990; 77: 1151–1163.
Raval RR, Lau KW, Tran MG, Sowter HM, Mandriota SJ, Li J-L et al. Contrasting properties of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) and HIF-2 in von Hippel-Lindau-associated renal cell carcinoma. Mol Cell Biol 2005; 25: 5675–5686.
Mandriota SJ, Turner KJ, Davies DR, Murray PG, Morgan NV, Sowter HM et al. HIF activation identifies early lesions in VHL kidneys: evidence for site-specific tumor suppressor function in the nephron. Cancer Cell 2002; 1: 459–468.
Shen C, Beroukhim R, Schumacher SE, Zhou J, Chang M, Signoretti S et al. Genetic and functional studies implicate HIF1alpha as a 14q kidney cancer suppressor gene. Cancer Discov 2011; 1: 222–235.
Kondo K, Klco J, Nakamura E, Lechpammer M, Kaelin WG Jr . Inhibition of HIF is necessary for tumor suppression by the von Hippel-Lindau protein. Cancer Cell 2002; 1: 237–246.
Kondo K, Kim WY, Lechpammer M, Kaelin WG Jr . Inhibition of HIF2alpha is sufficient to suppress pVHL-defective tumor growth. PLoS Biol 2003; 1: E83.
Zimmer M, Doucette D, Siddiqui N, Iliopoulos O . Inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor is sufficient for growth suppression of VHL−/− tumors1 1 NIH grant R29CA78358-06 (OI), Bertucci Fund for Urologic Malignancies (OI), David P. Foss Fund (OI), and VHL Family Alliance 2003 award (MZ). Mol Cancer Res 2004; 2: 89–95.
Rankin EB, Tomaszewski JE, Haase VH . Renal cyst development in mice with conditional inactivation of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 2576–2583.
Clifford SC, Cockman ME, Smallwood AC, Mole DR, Woodward ER, Maxwell PH et al. Contrasting effects on HIF-1α regulation by disease-causing pVHL mutations correlate with patterns of tumourigenesis in von Hippel-Lindau disease. Hum Mol Genet 2001; 10: 1029–1038.
Knauth K, Bex C, Jemth P, Buchberger A . Renal cell carcinoma risk in type 2 von Hippel–Lindau disease correlates with defects in pVHL stability and HIF-1α interactions. Oncogene 2006; 25: 370–377.
Li L, Zhang L, Zhang X, Yan Q, Minamishima YA, Olumi AF et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor linked to differential kidney cancer risk seen with type 2A and type 2B VHL mutations. Mol Cell Biol 2007; 27: 5381–5392.
Monzon FA, Alvarez K, Peterson L, Truong L, Amato RJ, Hernandez-McClain J et al. Chromosome 14q loss defines a molecular subtype of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma associated with poor prognosis. Mod Pathol 2011; 24: 1470–1479.
Network CGAR. Comprehensive molecular characterization of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Nature 2013; 499: 43–49.
Gudas LJ, Fu L, Minton DR, Mongan NP, Nanus DM . The role of HIF1α in renal cell carcinoma tumorigenesis. J Mol Med 2014; 92: 825–836.
Beroukhim R, Brunet J-P, Di Napoli A, Mertz KD, Seeley A, Pires MM et al. Patterns of gene expression and copy-number alterations in von-hippel lindau disease-associated and sporadic clear cell carcinoma of the kidney. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 4674–4681.
Shen C, Kaelin WG Jr. The VHL/HIF axis in clear cell renal carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol 2013; 23: 18–25.
Fu L, Wang G, Shevchuk MM, Nanus DM, Gudas LJ . Generation of a mouse model of von Hippel–Lindau kidney disease leading to renal cancers by expression of a constitutively active mutant of HIF1α. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 6848–6856.
Fu L, Minton DR, Zhang T, Nanus DM, Gudas LJ . Genome-wide profiling of TRACK kidneys shows similarity to the human ccRCC transcriptome. Mol Cancer Res 2015; 13: 870–878.
Fu L, Wang G, Shevchuk MM, Nanus DM, Gudas LJ . Activation of HIF2α in kidney proximal tubule cells causes abnormal glycogen deposition but not tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 2013; 73: 2916–2925.
Albers J, Rajski M, Schönenberger D, Harlander S, Schraml P, von Teichman A et al. Combined mutation of Vhl and Trp53 causes renal cysts and tumours in mice. EMBO Mol Med 2013; 5: 949–964.
Schönenberger D, Harlander S, Rajski M, Jacobs RA, Lundby A-K, Adlesic M et al. Formation of renal cysts and tumors in Vhl/Trp53-deficient mice requires HIF1α and HIF2α. Cancer Res 2016; 76: 2025–2036.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011; 144: 646–674.
Semenza GL . HIF-1 mediates metabolic responses to intratumoral hypoxia and oncogenic mutations. J Clin Invest 2013; 123: 3664–3671.
Nargund AM, Pham CG, Dong Y, Wang PI, Osmangeyoglu HU, Xie Y et al. The SWI/SNF protein PBRM1 restrains VHL-loss-driven clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cell Rep 2017; 18: 2893–2906.
Gu Y-F, Cohn S, Christie A, McKenzie T, Wolff NC, Do QN et al. Modeling renal cell carcinoma in mice: Bap1 and Pbrm1 inactivation drive tumor grade. Cancer Discov 2017; 7: 900–917.
Dart A . Tumour metabolism: translating the undruggable target. Nat Rev Cancer 2016; 16: 675–675.
Chen W, Hill H, Christie A, Kim MS, Holloman E, Pavia-Jimenez A et al. Targeting renal cell carcinoma with a HIF-2 antagonist. Nature 2016; 539: 112–117.
Cho H, Du X, Rizzi JP, Liberzon E, Chakraborty AA, Gao W et al. On-target efficacy of a HIF-2α antagonist in preclinical kidney cancer models. Nature 2016; 539: 107–111.
Wallace EM, Rizzi JP, Han G, Wehn PM, Cao Z, Du X et al. A small-molecule antagonist of HIF2α is efficacious in preclinical models of renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 2016; 76: 5491–5500.
Garcia-Donas J, Leandro-Garcia L, Del Alba AG, Morente M, Alemany I, Esteban E et al. Prospective study assessing hypoxia-related proteins as markers for the outcome of treatment with sunitinib in advanced clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Ann Oncol 2013; 24: 2409–2414.
Morris MR, Hughes DJ, Tian Y-M, Ricketts CJ, Lau KW, Gentle D et al. Mutation analysis of hypoxia-inducible factors HIF1A and HIF2A in renal cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res 2009; 29: 4337–4343.
Hergovich A, Lisztwan J, Barry R, Ballschmieter P, Krek W . Regulation of microtubule stability by the von Hippel-Lindau tumour suppressor protein pVHL. Nat Cell Biol 2003; 5: 64–70.
Lolkema MP, Mans DA, Snijckers CM, van Noort M, van Beest M, Voest EE et al. The von Hippel–Lindau tumour suppressor interacts with microtubules through kinesin‐2. FEBS Lett 2007; 581: 4571–4576.
Esteban MA, Harten SK, Tran MG, Maxwell PH . Formation of primary cilia in the renal epithelium is regulated by the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006; 17: 1801–1806.
Lutz MS, Burk RD . Primary cilium formation requires von hippel-lindau gene function in renal-derived cells. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 6903–6907.
Schermer B, Ghenoiu C, Bartram M, Müller RU, Kotsis F, Höhne M et al. The von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein controls ciliogenesis by orienting microtubule growth. J Cell Biol 2006; 175: 547–554.
Bisgrove BW, Yost HJ . The roles of cilia in developmental disorders and disease. Development 2006; 133: 4131–4143.
Hildebrandt F, Otto E . Cilia and centrosomes: a unifying pathogenic concept for cystic kidney disease? Nat Rev Genet 2005; 6: 928–940.
Lubensky IA, Gnarra JR, Bertheau P, Walther M, Linehan W, Zhuang Z . Allelic deletions of the VHL gene detected in multiple microscopic clear cell renal lesions in von Hippel-Lindau disease patients. Am J Pathol 1996; 149: 2089.
Thoma CR, Frew IJ, Hoerner CR, Montani M, Moch H, Krek W . pVHL and GSK3β are components of a primary cilium-maintenance signalling network. Nat Cell Biol 2007; 9: 588–595.
Sun X-F, Zhang H NFKB and NFKBI polymorphisms in relation to susceptibility of tumour and other diseases. Histol Histopathol 2007; 22: 1387–1398.
Cummins EP, Berra E, Comerford KM, Ginouves A, Fitzgerald KT, Seeballuck F et al. Prolyl hydroxylase-1 negatively regulates IκB kinase-β, giving insight into hypoxia-induced NFκB activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2006; 103: 18154–18159.
Yang H, Minamishima YA, Yan Q, Schlisio S, Ebert BL, Zhang X et al. pVHL acts as an adaptor to promote the inhibitory phosphorylation of the NF-κB agonist Card9 by CK2. Mol Cell 2007; 28: 15–27.
Qi H, Ohh M . The von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein sensitizes renal cell carcinoma cells to tumor necrosis factor-induced cytotoxicity by suppressing the nuclear factor-κB-dependent antiapoptotic pathway. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 7076–7080.
An J, Fisher M, Rettig MB . VHL expression in renal cell carcinoma sensitizes to bortezomib (PS-341) through an NF-κB-dependent mechanism. Oncogene 2005; 24: 1563–1570.
Arias-González L, Moreno-Gimeno I, del Campo AR, Leticia S-O, Valero ML, Esparís-Ogando A et al. ERK5/BMK1 is a novel target of the tumor suppressor VHL: implication in clear cell renal carcinoma. Neoplasia 2013; 15: 649IN614–659IN617.
Stickle NH, Chung J, Klco JM, Hill RP, Kaelin Jr WG, Ohh M . pVHL modification by NEDD8 is required for fibronectin matrix assembly and suppression of tumor development. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 3251–3261.
Kurban G, Hudon V, Duplan E, Ohh M, Pause A . Characterization of a von Hippel Lindau pathway involved in extracellular matrix remodeling, cell invasion, and angiogenesis. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 1313–1319.
Kurban G, Duplan E, Ramlal N, Hudon V, Sado Y, Ninomiya Y et al. Collagen matrix assembly is driven by the interaction of von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor protein with hydroxylated collagen IV alpha 2. Oncogene 2008; 27: 1004–1012.
Grosfeld A, Stolze IP, Cockman ME, Pugh CW, Edelmann M, Kessler B et al. Interaction of hydroxylated collagen IV with the von hippel-lindau tumor suppressor. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 13264–13269.
Mikhaylova O, Ignacak ML, Barankiewicz TJ, Harbaugh SV, Yi Y, Maxwell PH et al. The von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein and Egl-9-Type proline hydroxylases regulate the large subunit of RNA polymerase II in response to oxidative stress. Mol Cell Biol 2008; 28: 2701–2717.
Danilin S, Sourbier C, Thomas L, Rothhut S, Lindner V, Helwig J-J et al. von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene-dependent mRNA stabilization of the survival factor parathyroid hormone-related protein in human renal cell carcinoma by the RNA-binding protein HuR. Carcinogenesis 2009; 30: 387–396.
Yuen J, Cockman M, Sullivan M, Protheroe A, Turner G, Roberts I et al. The VHL tumor suppressor inhibits expression of the IGF1R and its loss induces IGF1R upregulation in human clear cell renal carcinoma. Oncogene 2007; 26: 6499–6508.
Massfelder T, Lang H, Schordan E, Lindner V, Rothhut S, Welsch S et al. Parathyroid hormone-related protein is an essential growth factor for human clear cell renal carcinoma and a target for the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 180–188.
Guo J, Chakraborty AA, Liu P, Gan W, Zheng X, Inuzuka H et al. pVHL suppresses kinase activity of Akt in a proline-hydroxylation–dependent manner. Science 2016; 353: 929–932.
Favier J, Amar L, Gimenez-Roqueplo A-P . Paraganglioma and phaeochromocytoma: from genetics to personalized medicine. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2015; 11: 101–111.
Hoffman MA, Ohh M, Yang H, Klco JM, Ivan M, Kaelin WG Jr. . von Hippel-Lindau protein mutants linked to type 2C VHL disease preserve the ability to downregulate HIF. Hum Mol Genet 2001; 10: 1019–1027.
Kim WY, Kaelin WG . Role of VHL gene mutation in human cancer. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 4991–5004.
Schlingensiepen K-H, Wollnik F, Kunst M, Schlingensiepen R, Herdegen T, Brysch W . The role of Jun transcription factor expression and phosphorylation in neuronal differentiation, neuronal cell death, and plastic adaptationsin vivo. Cell Mol Neurobiol 1994; 14: 487–505.
Estus S, Zaks WJ, Freeman RS, Gruda M, Bravo R, Johnson EM Jr . Altered gene expression in neurons during programmed cell death: identification of c-jun as necessary for neuronal apoptosis. J Cell Biol 1994; 127: 1717–1728.
Lee S, Nakamura E, Yang H, Wei W, Linggi MS, Sajan MP et al. Neuronal apoptosis linked to EglN3 prolyl hydroxylase and familial pheochromocytoma genes: developmental culling and cancer. Cancer Cell 2005; 8: 155–167.
Okuda H, Saitoh K, Hirai S, Iwai K, Takaki Y, Baba M et al. The von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein mediates ubiquitination of activated atypical protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 43611–43617.
Pal S, Claffey KP, Cohen HT, Mukhopadhyay D . Activation of Sp1-mediated vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor transcription requires specific interaction with protein kinase C ζ. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 26277–26280.
Russell RC, Sufan RI, Zhou B, Heir P, Bunda S, Sybingco SS et al. Loss of JAK2 regulation via a heterodimeric VHL-SOCS1 E3 ubiquitin ligase underlies Chuvash polycythemia. Nat Med 2011; 17: 845–853.
Zhuang Z, Yang C, Lorenzo F, Merino M, Fojo T, Kebebew E et al. Somatic HIF2A gain-of-function mutations in paraganglioma with polycythemia. N Engl J Med 2012; 367: 922–930.
Lorenzo FR, Yang C, Ng Tang Fui M, Vankayalapati H, Zhuang Z, Huynh T et al. A novel EPAS1/HIF2A germline mutation in a congenital polycythemia with paraganglioma. J Mol Med (Berl) 2013; 91: 507–512.
Welander J, Andreasson A, Brauckhoff M, Bäckdahl M, Larsson C, Gimm O et al. Frequent EPAS1/HIF2α exons 9 and 12 mutations in non-familial pheochromocytoma. Endocri Relat Cancer 2014; 21: 495–504.
Toledo RA, Qin Y, Srikantan S, Morales NP, Li Q, Deng Y et al. In vivo and in vitro oncogenic effects of HIF2A mutations in pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas. Endocr Relat Cancer 2013; 20: 349–359.
Ladroue C, Carcenac R, Leporrier M, Gad S, Le Hello C et al. PHD2 mutation and congenital erythrocytosis with paraganglioma. N Engl J Med 2008; 359: 2685–2692.
Pacak K, Jochmanova I, Prodanov T, Yang C, Merino MJ, Fojo T et al. New syndrome of paraganglioma and somatostatinoma associated with polycythemia. J Clin Oncol 2013; 31: 1690–1698.
Fliedner SM, Shankavaram U, Marzouca G, Elkahloun A, Jochmanova I, Daerr R et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 2α mutation-related paragangliomas classify as discrete pseudohypoxic subcluster. Neoplasia 2016; 18: 567–576.
Buffet A, Smati S, Mansuy L, Ménara M, Lebras M, Heymann M-F et al. Mosaicism in HIF2A-related polycythemia-paraganglioma syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2013; 99: E369–E373.
Yang C, Sun MG, Matro J, Huynh TT, Rahimpour S, Prchal JT et al. Novel HIF2A mutations disrupt oxygen sensing, leading to polycythemia, paragangliomas, and somatostatinomas. Blood 2013; 121: 2563–2566.
Toyoda H, Hirayama J, Sugimoto Y, Uchida K, Ohishi K, Hirayama M et al. Polycythemia and paraganglioma with a novel somatic HIF2A mutation in a male. Pediatrics 2014; 133: e1787–e1791.
Taieb D, Yang C, Delenne B, Zhuang Z, Barlier A, Sebag F et al. First report of bilateral pheochromocytoma in the clinical spectrum of HIF2A-related polycythemia-paraganglioma syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2013; 98: E908–E913.
Nichols J, Zevnik B, Anastassiadis K, Niwa H, Klewe-Nebenius D, Chambers I et al. Formation of pluripotent stem cells in the mammalian embryo depends on the POU transcription factor Oct4. Cell 1998; 95: 379–391.
Loh Y-H, Wu Q, Chew J-L, Vega VB, Zhang W, Chen X et al. The Oct4 and Nanog transcription network regulates pluripotency in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 431–440.
Schödel J, Oikonomopoulos S, Ragoussis J, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ, Mole DR . High-resolution genome-wide mapping of HIF-binding sites by ChIP-seq. Blood 2011; 117: e207–e217.
Hu CJ, Wang LY, Chodosh LA, Keith B, Simon MC . Differential roles of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) and HIF-2alpha in hypoxic gene regulation. Mol Cell Biol 2003; 23: 9361–9374.
Hu C-J, Iyer S, Sataur A, Covello KL, Chodosh LA, Simon MC . Differential regulation of the transcriptional activities of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1α) and HIF-2α in stem cells. Mol Cell Biol 2006; 26: 3514–3526.
Covello KL, Kehler J, Yu H, Gordan JD, Arsham AM, Hu C-J et al. HIF-2α regulates Oct-4: effects of hypoxia on stem cell function, embryonic development, and tumor growth. Genes Dev 2006; 20: 557–570.
Pietras A, Hansford LM, Johnsson AS, Bridges E, Sjölund J, Gisselsson D et al. HIF-2α maintains an undifferentiated state in neural crest-like human neuroblastoma tumor-initiating cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2009; 106: 16805–16810.
Comino-Méndez I, de Cubas AA, Bernal C, Sánchez-Malo C, Ramírez-Tortosa CL, Pedrinaci S et al. Tumoral EPAS1 (HIF2A) mutations explain sporadic pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma in the absence of erythrocytosis. Hum Mol Genet 2013; 22: 2169–2176.
Därr R, Nambuba J, Del Rivero J, Janssen I, Merino M, Todorovic M et al. Novel insights into the polycythemia–paraganglioma–somatostatinoma syndrome. Endocr Relat Cancer 2016; 23: 899–908.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Claire Robinson, Shelley He and Aline Zara for helpful discussions and comments. This work was supported by funds from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR, MOP 77718 and 136978). DT is a recipient of the CIHR Scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tarade, D., Ohh, M. The HIF and other quandaries in VHL disease. Oncogene 37, 139–147 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.338
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.338
This article is cited by
-
Glycogen synthase kinase GSK3α promotes tumorigenesis by activating HIF1/VEGFA signaling pathway in NSCLC tumor
Cell Communication and Signaling (2022)
-
VHL Ser65 mutations enhance HIF2α signaling and promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition of renal cancer cells
Cell & Bioscience (2022)
-
PRMT3 drives glioblastoma progression by enhancing HIF1A and glycolytic metabolism
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
A meta-analysis of different von Hippel Lindau mutations: are they related to retinal capillary hemangioblastoma?
Molecular Genetics and Genomics (2022)
-
PRMT3 promotes tumorigenesis by methylating and stabilizing HIF1α in colorectal cancer
Cell Death & Disease (2021)