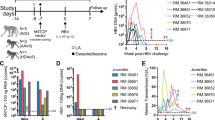
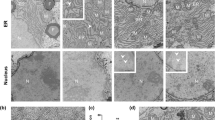
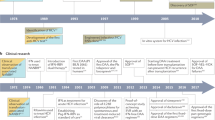
Abstract
Despite the existence of a preventative vaccine, HBV represents a substantial threat to public health, suggesting the need for research to develop new treatments to combat the disease. The authors review the available in vitro and in vivo models, including recently developed transgenic and chimeric mouse models.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
We are sorry, but there is no personal subscription option available for your country.
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ganem, D. & Varmus, H.E. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 56, 651–693 (1987).
Encke, J., zu Putlitz, J., Geissler, M. & Wands, J.R. Genetic immunization generates cellular and humoral immune responses against the nonstructural proteins of the hepatitis C virus in a murine model. J. Immunol. 161(9), 4917–4923 (1998).
Neurath, A.R., Kent, S.B., Strick, N. & Parker, K. Identification and chemical synthesis of a host cell receptor binding site on hepatitis B virus. Cell 46(1), 429–436 (1986).
Tuttleman, J.S., Pourcel, C. & Summers, J. Formation of the pool of covalently closed circular viral DNA in hepadnavirus-infected cells. Cell 47(3), 451–460 (1986).
Summers, J. & Mason, W.S. Replication of the genome of a hepatitis B–like virus by reverse transcription of an RNA intermediate. Cell 29(2), 403–415 (1982).
Spandau, D.F. & Lee, C.H. Trans-activation of viral enhancers by the hepatitis B virus X protein. J. Virol. 62(2), 427–434 (1988).
Standring, D.N., Ou, J.H., Masiarz, F.R. & Rutter, W.J. A signal peptide encoded within the precore region of hepatitis B virus directs the secretion of a heterogeneous population of e antigens in Xenopus oocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85(22), 8405–8409 (1988).
Bartenschlager, R. & Lohmann, V. Replication of hepatitis C virus. J. Gen. Virol. 81(Pt 7), 1631–1648 (2000).
Gripon, P., Diot, C. & Guguen-Guillouzo, C. Reproducible high level infection of cultured adult human hepatocytes by hepatitis B virus: effect of polyethylene glycol on adsorption and penetration. Virology 192(2), 534–540 (1993).
Sprinzl, M.F., Oberwinkler, H., Schaller, H. & Protzer, U. Transfer of hepatitis B virus genome by adenovirus vectors into cultured cells and mice: crossing the species barrier. J. Virol. 75(11), 5108–5118 (2001).
Blumberg, B.S., Alter, H.J. & Visnich, S. A “new” antigen in leukemia sera. JAMA 191, 541–546 (1965).
Blumberg, B.S., Gerstley, B.J., Hungerford, D.A., London, W.T. & Sutnick, A.I. A serum antigen (Australia antigen) in Down's syndrome, leukemia, and hepatitis. Ann. Intern. Med. 66(5), 924–931 (1967).
Prince, A.M. An antigen detected in the blood during the incubation period of serum hepatitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 60(3), 814–821 (1968).
Lichter, E.A. Chimpanzee antibodies to Australia antigen. Nature 224(221), 810–811 (1969).
Lander, H.J., Holland, P.V., Alter, H.J., Chanock, R.M. & Purcell, R.H. Antibody to hepatitis-associated antigen. Frequency and pattern of response as detected by radioimmunoprecipitation. JAMA 220(8), 1079–1082 (1972).
MacDonald, D.M., Holmes, E.C., Lewis, J.C. & Simmonds, P. Detection of hepatitis B virus infection in wild-born chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes verus): phylogenetic relationships with human and other primate genotypes. J. Virol. 74(9), 4253–4257 (2000).
Takahashi, K., Brotman, B., Usuda, S., Mishiro, S. & Prince, A.M. Full-genome sequence analyses of hepatitis B virus (HBV) strains recovered from chimpanzees infected in the wild: implications for an origin of HBV. Virology 267(1), 58–64 (2000).
Hu, X., Margolis, H.S., Purcell, R.H., Ebert, J. & Robertson, B.H. Identification of hepatitis B virus indigenous to chimpanzees. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97(4), 1661–1664 (2000).
Prince, A.M. in Hepatitis and Blood Transfusion (eds Vyas, G.N., Perkins, H.A. & Schmid, R.S.) 403–406 (Grune & Stratton, New York, 1972).
Thomssen, R. et al. Infectivity of purified hepatitis B virus particles. N. Engl. J. Med. 296(7), 396 (1977).
Prince, A.M., Vnek, J., Brotman, B., Hashimoto, N. & Van den Ende, M.C. in Viral Hepatitis (eds. Vyas, G.N., Cohn, S.N. & Schmid, R.) 507–523 (Franklin Institute Press, Philadelphia, 1978).
Prince, A.M. and Brotman, B. Perspectives on hepatitis B studies with chimpanzees. ILAR J. 42(2), 85–88 (2001).
Horowitz, B. & Prince, A.M. Laboratory and preclinical evaluation of the virus safety of coagulation factor concentrates. Dev. Biol. Stand. 67, 291–302 (1987).
Prince, A.M., Horowitz, B., Horowitz, M.S. & Zang, E. The development of virus-free labile blood derivatives—a review. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 3(2), 103–118 (1987).
Yan, R.Q., Su, J.J., Huang, D.R., Gan, Y.C., Yang, C. & Huang, G.H. Human hepatitis B virus and hepatocellular carcinoma. I. Experimental infection of tree shrews with hepatitis B virus. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 122(5), 283–288 (1996).
Walter, E., Keist, R., Niederost, B., Pult, I. & Blum, H.E. Hepatitis B virus infection of tupaia hepatocytes in vitro and in vivo. Hepatology 24(1), 1–5 (1996).
Glebe, D., Aliakbari, M., Krass, P., Knoop, E.V., Valerius, K.P. & Gerlich, W.H. Pre-S1 antigen-dependent infection of Tupaia hepatocyte cultures with human hepatitis B virus. J. Virol. 77(17), 9511–9521 (2003).
Kock, J., Nassal, M., MacNelly, S., Baumert, T.F., Blum, H.E. & von Weizsacker, F. Efficient infection of primary tupaia hepatocytes with purified human and woolly monkey hepatitis B virus. J. Virol. 75(11), 5084–5089 (2001).
Ren, S. & Nassal, M. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) virion and covalently closed circular DNA formation in primary tupaia hepatocytes and human hepatoma cell lines upon HBV genome transduction with replication-defective adenovirus vectors. J. Virol. 75(3), 1104–1116 (2001).
Li, Y., Su, J.J., Qin, L.L., Yang, C., Ban, K.C. & Yan, R.Q. Synergistic effect of hepatitis B virus and aflatoxin B1 in hepatocarcinogenesis in tree shrews. Ann. Acad. Med. Singapore 28(1), 67–71 (1999).
Yan, R.Q., Su, J.J., Huang, D.R., Gan, Y.C., Yang, C. & Huang, G.H. Human hepatitis B virus and hepatocellular carcinoma. II. Experimental induction of hepatocellular carcinoma in tree shrews exposed to hepatitis B virus and aflatoxin B1. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 122(5), 289–295 (1996).
Marion, P.L., Oshiro, L.S., Regnery, D.C., Scullard, G.H. & Robinson, W.S. A virus in Beechey ground squirrels that is related to hepatitis B virus of humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77(5), 2941–2945 (1980).
Mason, W.S., Seal, G. & Summers, J. Virus of Pekin ducks with structural and biological relatedness to human hepatitis B virus. J. Virol. 36(3), 829–836 (1980).
Summers, J., Smolec, J.M. & Snyder, R. A virus similar to human hepatitis B virus associated with hepatitis and hepatoma in woodchucks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 75(9), 4533–4537 (1978).
Summers, J. Three recently described animal virus models for human hepatitis B virus. Hepatology 1(2), 179–183 (1981).
Mason, W.S., Aldrich, C., Summers, J. & Taylor, J.M. Asymmetric replication of duck hepatitis B virus DNA in liver cells: Free minus-strand DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79(13), 3997–4001 (1982).
Cote, P.J. et al. Effects of age and viral determinants on chronicity as an outcome of experimental woodchuck hepatitis virus infection. Hepatology 31(1), 190–200 (2000).
Gerin, J.L., Cote, P.J., Korba, B.E. & Tennant, B.C. Hepadnavirus-induced liver cancer in woodchucks. Cancer Detect. Prev. 14(2), 227–229 (1989).
Popper, H., Roth, L., Purcell, R.H., Tennant, B.C. & Gerin, J.L. Hepatocarcinogenicity of the woodchuck hepatitis virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84(3), 866–870, 1987.
Baldwin, B.H., Tennant, B.C., Reimers, T.J., Cowan, R.G. & Concannon, P.W. Circannual changes in serum testosterone concentrations of adult and yearling woodchucks (Marmota monax). Biol. Reprod. 32(4), 804–812 (1985).
Ogston, C.W., Jonak, G.J., Rogler, C.E., Astrin, S.M. & Summers, J. Cloning and structural analysis of integrated woodchuck hepatitis virus sequences from hepatocellular carcinomas of woodchucks. Cell 29(2), 385–394 (1982).
Rogler, C.E., Hino, O. & Su, C.Y. Molecular aspects of persistent woodchuck hepatitis virus and hepatitis B virus infection and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 7(1 Suppl), 74S–78S (1987).
Rogler, C.E. & Summers, J. Cloning and structural analysis of integrated woodchuck hepatitis virus sequences from a chronically infected liver. J. Virol. 50(3), 832–837 (1984).
Seeger, C. et al. Woodchuck hepatitis virus is a more efficient oncogenic agent than ground squirrel hepatitis virus in a common host. J. Virol. 65(4), 1673–1679 (1991).
Chu, C.K. et al. Preclinical investigation of L-FMAU as an anti-hepatitis B virus agent. Antivir. Ther. 3(Suppl 3), 113–121 (1998).
Korba, B.E. et al. Enhanced antiviral benefit of combination therapy with lamivudine and ?-interferon against WHV replication in chronic carrier woodchucks. Antivir. Ther. 5(2), 95–104 (2000).
Korba, B.E., Cote, P., Hornbuckle, W., Schinazi, R., Gerin, J.L. & Tennant, B.C. Enhanced antiviral benefit of combination therapy with lamivudine and famciclovir against WHV replication in chronic WHV carrier woodchucks. Antiviral Res. 45(1), 19–32 (2000).
Korba, B.E., Cote, P., Hornbuckle, W., Tennant, B.C. & Gerin, J.L. Treatment of chronic woodchuck hepatitis virus infection in the Eastern woodchuck (Marmota monax) with nucleoside analogues is predictive of therapy for chronic hepatitis B virus infection in humans. Hepatology 31(5), 1165–1175 (2000).
Bianchi, L. & Gudat, F. Immunopathology of hepatitis B. Prog. Liver Dis. 6, 371–392 (1979).
Bianchi, L. & Gudat, F. Hepatitis B: viral antigens and histology reflect state of immune response. Pathol. Res. Pract. 164(1), 4–16 (1979).
Chisari, F.V. & Ferrari, C. Hepatitis B virus immunopathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 13, 29–60 (1995).
Chisari, F.V. et al. Molecular pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Cell 59(6), 1145–1156 (1989).
Sureau, C., Romet-Lemonne, J.L., Mullins, J.I. & Essex, M. Production of hepatitis B virus by a differentiated human hepatoma cell line after transfection with cloned circular HBV DNA. Cell 47(1), 37–47 (1986).
Sells, M.A., Chen, M.L. & Acs, G. Production of hepatitis B virus particles in Hep G2 cells transfected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84(4), 1005–1009 (1987).
Babinet, C., Farza, H., Morello, D., Hadchouel, M. & Pourcel, C. Specific expression of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) in transgenic mice. Science 230(4730), 1160–1163 (1985).
Chisari, F.V. et al. A transgenic mouse model of the chronic hepatitis B surface antigen carrier state. Science 230(4730), 1157–1160 (1985).
Farza, H., Hadchouel, M., Scotto, J., Tiollais, P., Babinet, C. & Pourcel, C. Replication and gene expression of hepatitis B virus in a transgenic mouse that contains the complete viral genome. J. Virol. 62(11), 4144–4152 (1988).
Araki, K. et al. Expression and replication of hepatitis B virus genome in transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86(1), 207–211 (1989).
Guidotti, L.G., Matzke, B., Schaller, H. & Chisari, F.V. High-level hepatitis B virus replication in transgenic mice. J. Virol. 69(10), 6158–6169 (1995).
Chisari, F.V. et al. Structural and pathological effects of synthesis of hepatitis B virus large envelope polypeptide in transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84(19), 6909–6913 (1987).
Dunsford, H.A., Sell, S. & Chisari, F.V. Hepatocarcinogenesis due to chronic liver cell injury in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 50(11), 3400–3407 (1990).
Hagen, T.M. et al. Extensive oxidative DNA damage in hepatocytes of transgenic mice with chronic active hepatitis destined to develop hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91(26), 12808–12812 (1994).
Koike, K. et al. High-level expression of hepatitis B virus HBx gene and hepatocarcinogenesis in transgenic mice. Hepatology 19(4), 810–819 (1994).
Kim, C.M., Koike, K., Saito, I., Miyamura, T. & Jay, G. HBx gene of hepatitis B virus induces liver cancer in transgenic mice. Nature 351(6324), 317–320 (1991).
Lee, T.H., Finegold, M.J., Shen, R.F., DeMayo, J.L., Woo, S.L. & Butel, J.S. Hepatitis B virus transactivator X protein is not tumorigenic in transgenic mice. J. Virol. 64(12), 5939–5947 (1990).
Reifenberg, K. et al. Long-term expression of the hepatitis B virus core-e- and X-proteins does not cause pathologic changes in transgenic mice. J. Hepatol. 26(1), 119–130 (1997).
Ueda, H. et al. Functional inactivation but not structural mutation of p53 causes liver cancer. Nat. Genet. 9(1), 41–47 (1995).
Moriyama, T. et al. Immunobiology and pathogenesis of hepatocellular injury in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Science 248(4953), 361–364 (1990).
Ando, K. et al. Mechanisms of class I restricted immunopathology. A transgenic mouse model of fulminant hepatitis. J. Exp. Med. 178(5), 1541–1554 (1993).
Guidotti, L.G., Ishikawa, T., Hobbs, M.V., Matzke, B., Schreiber, R. & Chisari, F.V. Intracellular inactivation of the hepatitis B virus by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Immunity 4(1), 25–36 (1996).
Tsui, L.V., Guidotti, L.G., Ishikawa, T. & Chisari, F.V. Posttranscriptional clearance of hepatitis B virus RNA by cytotoxic T lymphocyte–activated hepatocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92(26), 12398–12402 (1995).
Heise, T., Guidotti, L.G., Cavanaugh, V.J. & Chisari, F.V. Hepatitis B virus RNA-binding proteins associated with cytokine-induced clearance of viral RNA from the liver of transgenic mice. J. Virol. 73(1), 474–481 (1999).
Nakamoto, Y., Guidotti, L.G., Kuhlen, C.V., Fowler, P. & Chisari, F.V. Immune pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Exp. Med. 188(2), 341–350 (1998).
Feitelson, M.A., DeTolla, L.J. & Zhou, X.D. A chronic carrierlike state is established in nude mice injected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. J. Virol. 62(4), 1408–1415 (1988).
Larkin, J. et al. Hepatitis B virus transgenic mouse model of chronic liver disease. Nat. Med. 5(8), 907–912 (1999).
Baron, J.L., Gardiner, L., Nishimura, S., Shinkai, K., Locksley, R. & Ganem, D. Activation of a nonclassical NKT cell subset in a transgenic mouse model of hepatitis B virus infection. Immunity 16(4), 583–594 (2002).
Kato, K., Kaneda, Y., Sakurai, M., Nakanishi, M. & Okada, Y. Direct injection of hepatitis B virus DNA into liver induced hepatitis in adult rats. J. Biol. Chem. 266(33), 22071–22074 (1991).
Yang, P.L., Althage, A., Chung, J. & Chisari, F.V. Hydrodynamic injection of viral DNA: a mouse model of acute hepatitis B virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99(21), 13825–13830 (2002).
Gupta, S., Aragona, E., Vemuru, R.P., Bhargava, K.K., Burk, R.D. & Chowdhury, J.R. Permanent engraftment and function of hepatocytes delivered to the liver: implications for gene therapy and liver repopulation. Hepatology 14(1), 144–149 (1991).
Ponder, K.P. et al. Mouse hepatocytes migrate to liver parenchyma and function indefinitely after intrasplenic transplantation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88(4), 1217–1221 (1991).
Brown, J.J. et al. A long-term hepatitis B viremia model generated by transplanting nontumorigenic immortalized human hepatocytes in Rag-2-deficient mice. Hepatology 31(1), 173–181 (2000).
Ohashi, K. et al. Sustained survival of human hepatocytes in mice: a model for in vivo infection with human hepatitis B and hepatitis delta viruses. Nat. Med. 6(3), 327–331 (2000).
Guha, C., Deb, N.J., Sappal, B.S., Ghosh, S.S., Roy-Chowdhury, N. & Roy-Chowdhury, J. Amplification of engrafted hepatocytes by preparative manipulation of the host liver. Artif. Organs 25(7), 522–528 (2001).
Sandgren, E.P., Palmiter, R.D., Heckel, J.L., Daugherty, C.C., Brinster, R.L. & Degen, J.L. Complete hepatic regeneration after somatic deletion of an albumin-plasminogen activator transgene. Cell 66(2), 245–256 (1991).
Rhim, J.A., Sandgren, E.P., Palmiter, R.D. & Brinster, R.L. Complete reconstitution of mouse liver with xenogeneic hepatocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92(11), 4942–4946 (1995).
Overturf, K. et al. Hepatocytes corrected by gene therapy are selected in vivo in a murine model of hereditary tyrosinaemia type I [see comments] [published erratum appears in Nat. Genet. 12(4), 458 (1996)]. Nat. Genet. 12(3), 266–273 (1996).
Laconi, E. et al. Long-term, near-total liver replacement by transplantation of isolated hepatocytes in rats treated with retrorsine. Am. J. Pathol. 153(1), 319–329 (1998).
Guha, C. et al. Normal hepatocytes correct serum bilirubin after repopulation of Gunn rat liver subjected to irradiation/partial resection. Hepatology 36(2), 354–362 (2002).
Guha, C. et al. Amelioration of radiation-induced liver damage in partially hepatectomized rats by hepatocyte transplantation. Cancer Res. 59(23), 5871–5874 (1999).
Rhim, J.A., Sandgren, E.P., Degen, J.L., Palmiter, R.D. & Brinster, R.L. Replacement of diseased mouse liver by hepatic cell transplantation. Science 263(5150), 1149–1152 (1994).
Petersen, J., Dandri, M., Gupta, S. & Rogler, C.E. Liver repopulation with xenogeneic hepatocytes in B and T cell-deficient mice leads to chronic hepadnavirus infection and clonal growth of hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95(1), 310–315 (1998).
Dandri, M. et al. Repopulation of mouse liver with human hepatocytes and in vivo infection with hepatitis B virus. Hepatology 33(4), 981–988 (2001).
Mercer, D.F. et al. Hepatitis C virus replication in mice with chimeric human livers. Nat. Med. 7(8), 927–933 (2001).
Eren, R. et al. Human monoclonal antibodies specific to hepatitis B virus generated in a human/mouse radiation chimera: the Trimera system. Immunology 93(2), 154–161 (1998).
Ilan, E. et al. The hepatitis B virus-trimera mouse: a model for human HBV infection and evaluation of anti-HBV therapeutic agents. Hepatology 29(2), 553–562 (1999).
Bocher, W.O. et al. Induction of strong hepatitis B virus (HBV) specific T-helper cell and cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses by therapeutic vaccination in the trimera mouse model of chronic HBV infection. Eur. J. Immunol. 31(7), 2071–2079 (2001).
Wu, C.H., Ouyang, E.C., Walton, C.M. & Wu, G.Y. Human hepatocytes transplanted into genetically immunocompetent rats are susceptible to infection by hepatitis B virus in situ. J. Viral. Hepat. 8(2), 111–119 (2001).
Guha, C. et al. Liver irradiation: a potential preparative regimen for hepatocyte transplantation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 49(2), 451–457 (2001).
Guidotti, L.G. et al. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes inhibit hepatitis B virus gene expression by a noncytolytic mechanism in transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91(9), 3764–3768 (1994).
Burk, R.D., DeLoia, J.A., elAwady, M.K. & Gearhart, J.D. Tissue preferential expression of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) surface antigen gene in two lines of HBV transgenic mice. J. Virol. 62(2), 649–654 (1988).
DeLoia, J.A., Burk, R.D. & Gearhart, J.D. Developmental regulation of hepatitis B surface antigen expression in two lines of hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. J. Virol. 63(9), 4069–4073 (1989).
Chisari, F.V. et al. Expression of hepatitis B virus large envelope polypeptide inhibits hepatitis B surface antigen secretion in transgenic mice. J. Virol. 60(3), 880–887 (1986).
Wirth, S., Guidotti, L.G., Ando, K., Schlicht, H.J. & Chisari, F.V. Breaking tolerance leads to autoantibody production but not autoimmune liver disease in hepatitis B virus envelope transgenic mice. J. Immunol. 154(5), 2504–2515 (1995).
Milich, D.R., Jones, J.E., Hughes, J.L., Price, J., Raney, A.K. & McLachlan, A. Is a function of the secreted hepatitis B e antigen to induce immunologic tolerance in utero? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87(17), 6599–6603 (1990).
Guidotti, L.G., Martinez, V., Loh, Y.T., Rogler, C.E. & Chisari, F.V. Hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid particles do not cross the hepatocyte nuclear membrane in transgenic mice. J. Virol. 68(9), 5469–5475 (1994).
Milich, D.R. et al. Extrathymic expression of the intracellular hepatitis B core antigen results in T cell tolerance in transgenic mice. J. Immunol. 152(2), 455–466 (1994).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by a grant from the American Cancer Society: RPG-00-066-01-CCE (to C.G.) and the following grants from NIH: RO1-DK 46057 (to J.R.C.), RO1-DK 39137 (to N.R.C.), and the Liver Research Core Center grant DK-P30-41296.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guha, C., Mohan, S., Roy-Chowdhury, N. et al. Cell Culture and Animal Models of Viral Hepatitis. Part I: Hepatitis B. Lab Anim 33, 37–46 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/laban0704-37
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/laban0704-37
This article is cited by
-
Experimental chronic hepatitis B infection of neonatal tree shrews (Tupaia belangeri chinensis): A model to study molecular causes for susceptibility and disease progression to chronic hepatitis in humans
Virology Journal (2012)
-
Microfluidic platform for hepatitis B viral replication study
Biomedical Microdevices (2008)
-
Cell Culture Models and Animal Models of Viral Hepatitis. Part II: Hepatitis C
Lab Animal (2005)