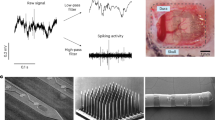
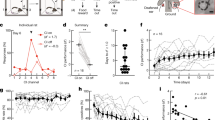
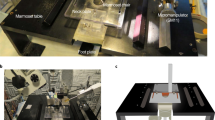
Abstract
The advent of cranial implants revolutionized primate neurophysiological research because they allow researchers to stably record neural activity from monkeys during active behavior. Cranial implants have improved over the years since their introduction, but chronic implants still increase the risk for medical complications including bacterial contamination and resultant infection, chronic inflammation, bone and tissue loss and complications related to the use of dental acrylic. These complications can lead to implant failure and early termination of study protocols. In an effort to reduce complications, we describe several refinements that have helped us improve cranial implants and the wellbeing of implanted primates.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
We are sorry, but there is no personal subscription option available for your country.
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Evarts, E.V. Methods for recording activity of individual neurons in moving animals. in Methods in Medical Resesarch (ed. Rushmer, R.F.) 241–250 (Year Book Medical Publishers, Chicago, IL, 1966).
Adams, D.L., Economides, J.R., Jocson, C.M., Parker, J.M. & Horton, J.C. A watertight acrylic-free titanium recording chamber for electrophysiology in behaving monkeys. J. Neurophysiol. 106, 1581–1590 (2011).
Betelak, K.F., Margiotti, E.A., Wohlford, M.E. & Suzuki, D.A. The use of titanium implants and prosthodontic techniques in the preparation of non-human primates for long-term neuronal recording studies. J. Neurosci. Methods 112, 9–20 (2001).
Foeller, P. & Tychsen, L. Eye movement training and recording in alert macaque monkeys: 1. Operant visual conditioning; 2. Magnetic search coil and head restraint surgical implantation; 3. Calibration and recording. Strabismus 10, 5–22 (2002).
Isoda, M. et al. Design of a head fixation device for experiments in behaving monkeys. J. Neurosci. Methods 141, 277–282 (2005).
Kalwani, R.M., Bloy, L., Elliott, M.A. & Gold, J.I. A method for localizing microelectrode trajectories in the macaque brain using MRI. J. Neurosci. Methods 176, 104–111 (2009).
McAndrew, R.M., Lingo VanGilder, J.L., Naufel, S.N. & Helms Tillery, S.I. Individualized recording chambers for non-human primate neurophysiology. J. Neurosci. Methods 207, 86–90 (2012).
Miocinovic, S. et al. Stereotactic neurosurgical planning, recording, and visualization for deep brain stimulation in non-human primates. J. Neurosci. Methods 162, 32–41 (2007).
Pigarev, I.N., Nothdurft, H.C. & Kastner, S. A reversible system for chronic recordings in macaque monkeys. J. Neurosci. Methods 77, 157–162 (1997).
Rebert, C.S., Hurd, R.E., Matteucci, M.J., De LaPaz, R. & Enzmann, D.R. A procedure for using proton magnetic resonance imaging to determine stereotaxic coordinates of the monkey's brain. J. Neurosci. Methods 39, 109–113 (1991).
Yakushin, S.B., Reisine, H., Buttner-Ennever, J., Raphan, T. & Cohen, B. Functions of the nucleus of the optic tract (NOT). I. Adaptation of the gain of the horizontal vestibulo-ocular reflex. Exp. Brain Res. 131, 416–432 (2000).
Gardiner, T.W. & Toth, L.A. Stereotactic surgery and long-term maintenance of cranial implants in research animals. Contemp. Top. Lab. Anim. Sci. 38, 52–63 (1999).
Dannemiller, S.D., Watson, J.R. & Rozmiarek, H. Fluconazole therapy in a rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta) with epidural Trichosporon beigelii in a cephalic recording cylinder. Lab. Anim. Sci. 45, 31–35 (1995).
Lee, G., Danneman, P., Rufo, R., Kalesnykas, R. & Eng, V. Use of chlorine dioxide for antimicrobial prophylactic maintenance of cephalic recording devices in rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta). Contemp. Top. Lab. Anim. Sci. 37, 59–63 (1998).
Bergin, I.L., Chien, C.C., Marini, R.P. & Fox, J.G. Isolation and characterization of Corynebacterium ulcerans from cephalic implants in macaques. Comp. Med. 50, 530–535 (2000).
Venezia, J. et al. Characterization of Corynebacterium species in macaques. J. Med. Microbiol. 61, 1401–1408 (2012).
Newsome, J.T. & Portnoy, L.G. Neuromuscular weakness in a baboon. Lab. Anim. Sci. 49, 349–357 (1999).
Adams, D.L., Economides, J.R., Jocson, C.M. & Horton, J.C. A biocompatible titanium headpost for stabilizing behaving monkeys. J. Neurophysiol. 98, 993–1001 (2007).
Spitler, K.M. & Gothard, K.M. A removable silicone elastomer seal reduces granulation tissue growth and maintains the sterility of recording chambers for primate neurophysiology. J. Neurosci. Methods 169, 23–26 (2008).
Leblanc, M., Berry, K., McCort, H. & Reuter, J.D. Brain abscess in a rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta) with a cephalic implant. Comp. Med. 63, 367–372 (2013).
Hamlen, H.J. & Olson, E. Methylmethacrylate-associated thermal injury during cranioplasty in a nonhuman primate. Contemp. Top. Lab. Anim. Sci. 34, 73–75 (1995).
Albrektsson, T. & Linder, L. Bone injury caused by curing bone cement. A vital microscopic study in the rabbit tibia. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 183, 280–287 (1984).
Straub, R.H. Systemic disease sequelae in chronic inflammatory diseases and chronic psychological stress: comparison and pathophysiological model. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1318, 7–17 (2014).
Simons, J.P. et al. Pathogenetic mechanisms of amyloid A amyloidosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110, 16115–20 (2013).
Institute for Laboratory Animal Research. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals 8th edn. (National Academies Press, Washington, DC, 2011).
Animal Welfare Act Regulations. Code of Federal Regulations. Title 9, Part 3, Subpart D.
Chen, A.V. et al. Description and validation of a magnetic resonance imaging-guided stereotactic brain biopsy device in the dog. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 53, 150–156 (2012).
Frey, S., Comeau, R., Hynes, B., Mackey, S. & Petrides, M. Frameless stereotaxy in the nonhuman primate. Neuroimage 23, 1226–1234 (2004).
Herbert, C.E. et al. Effect of bite tray impression technique on relocation accuracy in frameless stereotactic radiotherapy. Med. Dosim. 28, 27–30 (2003).
Gupta, S.K., Saxena, P., Pant, V.A. & Pant, A.B. Adhesion and biologic behavior of human periodontal fibroblast cells to resin ionomer Geristore: a comparative analysis. Dent. Traumatol. 29, 389–393 (2013).
Al-Sabek, F., Shostad, S. & Kirkwood, K.L. Preferential attachment of human gingival fibroblasts to the resin ionomer Geristore. J. Endod. 31, 205–208 (2005).
Al-Sa'eed, O.R., Al-Hiyasat, A.S. & Darmani, H. The effects of six root-end filling materials and their leachable components on cell viability. J. Endod. 34, 1410–1414 (2008).
Al-Hiyasat, A.S., Al-Sa′ eed, O.R. & Darmani, H. Quality of cellular attachment to various root-end filling materials. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 20, 82–88 (2010).
Arora, R. & Deshpande, S.D. Shear bond strength of resin-modified restorative glass-ionomer cements to dentin—an in vitro study. J. Indian Soc. Pedod. Prev. Dent. 16, 130–133 (1998).
Chung, C.H., Brendlinger, E.J., Brendlinger, D.L., Bernal, V. & Mante, F.K. Shear bond strengths of two resin-modified glass ionomer cements to porcelain. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial Orthop. 115, 533–535 (1999).
Eggers, G., Klein, J., Blank, J. & Hassfeld, S. Piezosurgery: an ultrasound device for cutting bone and its use and limitations in maxillofacial surgery. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 42, 451–453 (2004).
Leclercq, P., Zenati, C., Amr, S. & Dohan, D.M. Ultrasonic bone cut part 1: State-of-the-art technologies and common applications. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 66, 177–182 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnston, J., Cohen, Y., Shirley, H. et al. Recent refinements to cranial implants for rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta). Lab Anim 45, 180–186 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/laban.997
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/laban.997