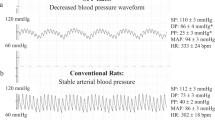
Abstract
The guinea pig is a common animal model that is used in biomedical research to study a variety of systems, including hormonal and immunological responses, pulmonary physiology, corticosteroid response and others. However, because guinea pigs are evolutionarily a prey species, they do not readily show behavioral signs of disease, which can make it difficult to detect illness in a laboratory setting. Minimally invasive blood tests, such as complete blood counts and plasma biochemistry assays, are useful in both human and veterinary medicine as an initial diagnostic technique to rule in or rule out systemic illness. In guinea pigs, phlebotomy for such tests often requires that the animals be anesthetized first. The authors evaluated hematological and plasma biochemical effects of two anesthetic agents that are commonly used with guinea pigs in a research setting: isoflurane and a combination of ketamine and xylazine. Hematological and plasma biochemical parameters were significantly different when guinea pigs were under either anesthetic, compared to when they were unanesthetized. Plasma proteins, liver enzymes, white blood cells and red blood cells appeared to be significantly altered by both anesthetics, and hematological and plasma biochemical differences were greater when guinea pigs were anesthetized with the combination of ketamine and xylazine than when they were anesthetized with isoflurane. Overall these results indicate that both anesthetics can significantly influence hematological and plasma biochemical parameters in guinea pigs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
We are sorry, but there is no personal subscription option available for your country.
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Padilla-Carlin, D.J., McMurray, D.N. & Hickey, A.J. The guinea pig as a model of infectious diseases. Comp. Med. 58, 324–340 (2008).
Suckow, M.A., Stevens, K.A. & Wilson, R.P. Ethical considerations and regulatory issues. in The Laboratory Rabbit, Guinea Pig, Hamster, and Other Rodents 10 (Elsevier, Burlington, MA, 2012).
Flecknell, P.A. Anesthesia. in Laboratory Animal Anesthesia 3rd edn. 50–55 (Elsevier, Burlington, MA, 2009).
Harkness, J.E., Turner, P.V., VandeWoude, S. & Wheeler, C. Clinical procedures. in Biology and Medicine of Rabbits and Rodents 5th edn. 122–130 (Blackwell Publishing, Ames, IA, 2010).
Wixson, S.K. & Smiler, K.L. Anesthesia and analgesia in rodents. in Anesthesia and Analgesia in Laboratory Animals (eds. Kohn, D.F., Wixson, S.K., White, W.J. & Benson, G.J.) 168–175 (Academic, New York, NY, 1997).
Thompson, J.S. et al. Early effects of tribromoethanol, ketamine/xylazine, pentobarbital, and isoflurane anesthesia on hepatic and lymphoid tissue in ICR mice. Comp. Med. 52, 63–67 (2002).
Hom, G.J. et al. Comparison of cardiovascular parameters and/or serum chemistry and hematology profiles in conscious and anesthetized rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta). Contemp. Top. Lab. Anim. Sci. 38, 60–64 (2000).
Nishiyama, T., Yokoyama, T. & Hanaoka, K. Liver and renal function after repeated sevoflurane or isoflurane anesthesia. Can. J. Anesth. 45, 789–793 (1998).
Marini, R.P. et al. Effect of isoflurane on hematologic variables in ferrets. Am. J. Vet. Res. 55, 1479–1483 (1994).
Kenna, J.G. & Jones, R.M. The organ toxicity of inhaled anesthetics. Anesth. Analg. 81, S51–S66 (1996).
Durongphongtorn, S., McDonell, W.N., Kerr, C.L., Neto, F.J. & Mirakhur, K.K. Comparison of hemodynamic, clinicopathologic, and gastrointestinal motility effects and recovery characteristics of anesthesia with isoflurane and halothane in horses undergoing arthroscopic surgery. Am. J. Vet. Res. 67, 32–42 (2006).
Topal, A., Gül, N., Ilçöl, Y. & Görgül, O.S. Hepatic effects of halothane, isoflurane, or sevoflurane anaesthesia in dogs. J. Vet. Med. A Physiol. Pathol. Clin. Med. 50, 530–533 (2003).
Gaertner, D.J. et al. Anesthesia and analgesia for laboratory rodents. in Anesthesia and Analgesia in Laboratory Animals 2nd edn. (eds. Fish, R.E., Brown, M.J., Danneman, P.J. & Karas, A.Z.) 280 (Academic, Burlington, MA, 2008).
Plate, A.Y., Crankshaw, D.L. & Gallaher, D.D. The effect of anesthesia by diethyl ether or isoflurane on activity of cytochrome P450 2E1 and P450 reductases in rat liver. Anesth. Analg. 101, 1063–1064 (2005).
Lugo-Roman, L.A., Rico, P.J., Sturdivant, R., Burks, R. & Settle, T.L. Effects of serial anesthesia using ketamine or ketamine/medetomidine on hematology and serum biochemistry values in rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta). J. Med. Primatol. 39, 41–49 (2010).
González Gil, A., Illera, J.C., Silván, G. & Illera, M. Effects of the anaesthetic/tranquilizer treatments on selected plasma biochemical parameters in NZW rabbits. Lab. Anim. 37, 155–161 (2003).
Denghani, S., Sharifnia, N., Yahyaei, M.R. & Souri, A. Clinical, haematological and biochemical effects of xylazine, ketamine and their combination in caprine and feline. Vet. Anaesth Analg. 18, 129–133 (1991).
Mautz, W.W., Seal, U.S. & Boardman, C.B. Blood serum analyses of chemically and physically restrained white-tailed deer. J. Wildl. Manag. 44, 343–351 (1980).
Williams, W.R. & Kendall, L.V. Blood collection in the guinea pig (Cavia porcellus). Lab Anim (NY) 44, 1–2 (2015).
Manning, P.J., Wagner, J.E. & Harkness, J.E. Biology and diseases of guinea pigs. in Laboratory Animal Medicine (eds. Fox, J.G., Anderson, L.C., Loew, F.M. & Quimby, F.W.) 208 (Academic, San Diego, CA, 2002).
Clemons, D.J. & Terril-Robb, L.A. The Laboratory Guinea Pig (CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1997).
Cote, E. Clinical Veterinary Advisor Dogs and Cats (Elsevier, Burlington, MA, 2014).
Wood, R.D. Leukogram Abnormalities. in Merck Veterinary Manual (eds. Aiello, S.E., Moses, M.A. & Steigerwald, M.A.) http://www.merckvetmanual.com/mvm/circulatory_system/leukocyte_disorders/leukogram_abnormalities.html. Accessed 18 November 2015.
Duncan, J.R., Prasse, K.W. & Mahaffey, E.A. Veterinary Laboratory Medicine: Clinical Pathology 3rd edn. (Iowa State, Ames, IA, 1994).
Heard, D.J. & Huft, V.J. The effects of short-term physical restraint and isoflurane anesthesia on hematology and plasma biochemistry in the island flying fox (Pteropus hypomelanus). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 29, 14–17 (1998).
Steffey, E.P., Zinkl, J. & Howland, D. Minimal changes in blood cell counts and biochemical values associated with prolonged isoflurane anesthesia in horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 40, 1646–1648 (1979).
Hijazi, Y. & Boulieu, R. Contribution of CYP3A4, CYP2B6, and CYP2C9 isoforms to N-demethylation of ketamine in human liver microsomes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 30, 853–858 (2002).
Veilleux-Lemieux, D., Castel, A., Carrier, D., Beaudry, F. & Vachon, P. Pharmacokinetics of ketamine and xylazine in young and old Sprague-Dawley rats. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 52, 567–570 (2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Williams, W., Johnston, M., Higgins, S. et al. Blood profiles in unanesthetized and anesthetized guinea pigs (Cavia porcellus). Lab Anim 45, 35–41 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/laban.911
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/laban.911