Abstract
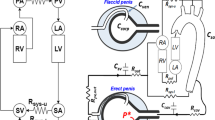
Intracavernosal injection of a vasodilating agent, followed by color Doppler ultrasonography of the penis, is used to diagnose vascular impotence. The vasodilating agent is usually injected into one of the corpora cavernosa and the peak systolic velocity (PSV) of the cavernosal arteries is measured on both sides, presuming that the connection between the two cavernosal bodies will distribute the drug uniformly on both sides and will consequently affect the cavernosal arteries and sinusoids equally. According to our experience, the PSV of the injection side is higher than that of the contralateral side. This difference could affect the results of the evaluation. In this study, our objective was to compare the results of both-side injections with those of one-side injection. A total number of 60 patients with a normal Doppler study of the penis were enrolled in the study and were randomly divided into three groups. In the first and second group, 60 mg papaverine was injected into the right and left corpus cavernosa each. In the third group, half of the dose was injected into each side. The mean maximum PSV was measured and compared in each group. The mean maximum PSV in the group with the right-side injection was 47.7±10.8 and 40.3±9.2 on the right and left side, respectively. The mean maximum PSV in the group with the left side injection was 44.4±7.1 and 51.4±7.1 on the right and the left side, respectively. The mean maximum PSV in the group with bilateral injection was 47±9.9 on the right side and 46.7±10.7 on the left side. In the first two groups, there was significant difference between the mean maximum PSV of the right and left cavernosal arteries, but in the third group, there was no significant difference between the mean maximum PSV of both side cavernosal arteries. Injecting papaverine in only one corpus cavernosum, despite a perfect postinjection manipulation of the penis, will affect the sinusoids and cavernosal artery at the same side of the injection more than the contralateral side. This results in a higher increase in the blood flow and PSV on that side and results in an artifactual difference between the velocity of the right and left side, which could ultimately exaggerate or mask the actual difference between the two sides. Dividing the total dose of the vasodilating agent and injecting half of the dose into each corpus cavernosum separately prevents artifactual difference between blood flow and velocity on the right and left side.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Uslu N, Gorgulu S, Alper AT, Eren M, Nurkalem Z, Yildirim A et al. Erectile dysfunction as a generalized vascular dysfunction. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2006; 19: 341–346.
Kirby RS . Fortnightly Review: impotence: diagnosis and management of male erectile dysfunction. BMJ 1994; 308: 957–961.
McMahan CG . Erectile dysfunction. Med J Aust 2000; 173: 492–497.
Kendirchi M, Trost L, Sikka SC . The effect of vascular risk factors on penile vascular status in men with erectile dysfunction. J Urol 2007; 178: 2516–2520.
Connolly JA, Borirakchanyavat S, Lue TF . Ultrasound evaluation of the penis for assessment of impotence. J Clin Ultrasound 1996; 24: 481–486.
Krane RJ, Goldstein I, Saenz de Tejada I . Medical progress: impotence. N Engl J Med 1989; 321: 1648–1659.
Sen J, Godara R, Singh R, Airon RK . Colour doppler sonography of flaccid penis in evaluation of erectile dysfunction. Asian J Surg 2007; 30: 122–125.
Golijanin D, Singer E, Davis R, Bhatt S, Seftel A, Dogra V . Doppler evaluation of erectile dysfunction -part 2. Int J Impot Res 2007; 19: 43–48.
Golubinski AJ, Sikorski A . Usefulness of power Doppler ultrasonography in evaluating erectile dysfunction. BJU International 2002; 89: 779–782.
Quam JP, King BF, James EM, Lewis RW, Brakke DM, llstrup DM et al. Duplex and color Doppler sonographic evaluation of vasculogenic impotence. AJR 1989; 153: 1141–1147.
Artinkilic B, Hauck EW, Weidner W . Evaluation of penile perfusion by color-coded duplex sonography in the management of erectile dysfunction. World J Urol 2004; 22: 361–364.
Benson CB, Vickers MA . Sexual impotence caused by vascular disease: diagnosis with duplex sonography. AJR 1989; 153: 1149–1153.
Hattery RR, King BF, Lewis RW, James EM, McKusick MA . Vasculogenic impotence: duplex and color Doppler imaging. Radiol Clin North Am 1991; 29: 629–645.
Herbener TE, Seftel AD, Nehro A, Goldstein I . penile ultrasound. Semin Urol 1994; 12: 320–332.
Fitzgerald SW, Erickson SJ, Foley WD, Lipchik EO, Lawson TL . Color doppler sonography in the evaluation of erectile dysfunction: patterns of temporal response to papaverine. AJR 1991; 157: 331–336.
Meuleman EJ, Bemelmans BL, van Asten WN, Doesburg WH, Skotnicki SH, Debruyne FM . Assessment of penile blood flow by duplex ultrasonography in 44 men with normal erectile potency in different phases of erection. J Urol 1992; 147: 51–56.
Schwartz AN, Lowe M, Berger RE, Wang KY, Mack LA, Richardson ML . Assessment of normal and abnormal erectile function: color Doppler flow sonography versus conventional techniques. Radiology 1991; 180: 105–109.
Shabsigh R, Fishman IJ, Quesada ET, Seale-Hawkins CK, Dunn JK . Evaluation of vasculogenic erectile impotence using penile duplex ultrasonography. J Urol 1989; 142: 1469–1474.
Acknowledgements
This study was founded by a medical research grant from the research deputy of Iran University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghafoori, M., Hoseini, K. & Shakiba, M. Comparison of one-side and bilateral intracavernosal papaverine injection on a Doppler study of the penis. Int J Impot Res 21, 382–386 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2009.50
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2009.50
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
What is the current role of intracavernosal injection in management of erectile dysfunction?
International Journal of Impotence Research (2016)