Abstract
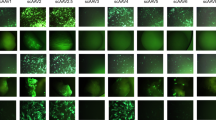
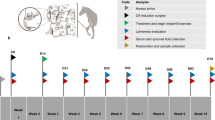
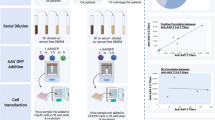
With the long-term goal of developing a gene-based treatment for osteoarthritis (OA), we performed studies to evaluate the equine joint as a model for adeno-associated virus (AAV)-mediated gene transfer to large, weight-bearing human joints. A self-complementary AAV2 vector containing the coding regions for human interleukin-1-receptor antagonist (hIL-1Ra) or green fluorescent protein was packaged in AAV capsid serotypes 1, 2, 5, 8 and 9. Following infection of human and equine synovial fibroblasts in culture, we found that both were only receptive to transduction with AAV1, 2 and 5. For these serotypes, however, transgene expression from the equine cells was consistently at least 10-fold higher. Analyses of AAV surface receptor molecules and intracellular trafficking of vector genomes implicate enhanced viral uptake by the equine cells. Following delivery of 1 × 1011 vector genomes of serotypes 2, 5 and 8 into the forelimb joints of the horse, all three enabled hIL-1Ra expression at biologically relevant levels and effectively transduced the same cell types, primarily synovial fibroblasts and, to a lesser degree, chondrocytes in articular cartilage. These results provide optimism that AAV vectors can be effectively adapted for gene delivery to large human joints affected by OA.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arend WP, Malyak M, Guthridge CJ, Gabay C . Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist: role in biology. Annu Rev Immunol 1998; 16: 27–55.
So A, De Smedt T, Revaz S, Tschopp J . A pilot study of IL-1 inhibition by anakinra in acute gout. Arthritis Res Ther 2007; 9: R28.
Burls A, Jobanputra P . The trials of anakinra. Lancet 2004; 364: 827–828.
Evans CH, Ghivizzani SC, Robbins PD . Orthopedic gene therapy in 2008. Mol Ther 2009; 17: 231–244.
Zhang HG, Xie J, Yang P, Wang Y, Xu L, Liu D et al. Adeno-associated virus production of soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor neutralizes tumor necrosis factor alpha and reduces arthritis. Hum Gene Ther 2000; 11: 2431–2442.
Oligino T, Ghivizzani S, Wolfe D, Lechman E, Krisky D, Mi Z et al. Intra-articular delivery of a herpes simplex virus IL-1Ra gene vector reduces inflammation in a rabbit model of arthritis. Gene Therapy 1999; 6: 1713–1720.
Frisbie DD, Ghivizzani SC, Robbins PD, Evans CH, McIlwraith CW . Treatment of experimental equine osteoarthritis by in vivo delivery of the equine interleukin-1 receptor antagonist gene. Gene Therapy 2002; 9: 12–20.
Apparailly F, Millet V, Noel D, Jacquet C, Sany J, Jorgensen C . Tetracycline-inducible interleukin-10 gene transfer mediated by an adeno-associated virus: application to experimental arthritis. Hum Gene Ther 2002; 13: 1179–1188.
Gouze E, Pawliuk R, Gouze JN, Pilapil C, Fleet C, Palmer GD et al. Lentiviral-mediated gene delivery to synovium: potent intra-articular expression with amplification by inflammation. Mol Ther 2003; 7: 460–466.
Adriaansen J, Fallaux FJ, de Cortie CJ, Vervoordeldonk MJ, Tak PP . Local delivery of beta interferon using an adeno-associated virus type 5 effectively inhibits adjuvant arthritis in rats. J Gen Virol 2007; 88 (Pt 6): 1717–1721.
Gouze E, Gouze JN, Palmer GD, Pilapil C, Evans CH, Ghivizzani SC . Transgene persistence and cell turnover in the diarthrodial joint: implications for gene therapy of chronic joint diseases. Mol Ther 2007; 15: 1114–1120.
Goater J, Muller R, Kollias G, Firestein GS, Sanz I, O'Keefe RJ et al. Empirical advantages of adeno associated viral vectors in vivo gene therapy for arthritis. J Rheumatol 2000; 27: 983–989.
Wu Z, Asokan A, Samulski RJ . Adeno-associated virus serotypes: vector toolkit for human gene therapy. Mol Ther 2006; 14: 316–327.
McCarty DM, Fu H, Monahan PE, Toulson CE, Naik P, Samulski RJ . Adeno-associated virus terminal repeat (TR) mutant generates self-complementary vectors to overcome the rate-limiting step to transduction in vivo. Gene Therapy 2003; 10: 2112–2118.
McCarty DM, Monahan PE, Samulski RJ . Self-complementary recombinant adeno-associated virus (scAAV) vectors promote efficient transduction independently of DNA synthesis. Gene Therapy 2001; 8: 1248–1254.
Kay JD, Gouze E, Oligino TJ, Gouze JN, Watson RS, Levings PP et al. Intra-articular gene delivery and expression of interleukin-1Ra mediated by self-complementary adeno-associated virus. J Gene Med 2009; 11: 605–614.
Zolotukhin S, Byrne BJ, Mason E, Zolotukhin I, Potter M, Chesnut K et al. Recombinant adeno-associated virus purification using novel methods improves infectious titer and yield. Gene Therapy 1999; 6: 973–985.
McIlwraith CW . From Arthroscopy to Gene Therapy--30 Years of Looking in Joints. In: 51st Annual Convention of the American Association of Equine Practitioners—AAEP, 2005—Seattle, WA, USA. American Association of Equine Practitioners: Lexington KY, 2005, p 2613.
Goodrich LR, Nixon AJ . Medical treatment of osteoarthritis in the horse - a review. Vet J 2006; 171: 51–69.
Ekman L, Nilsson G, Persson L, Lumsden JH . Volume of the synovia in certain joint cavities in the horse. Acta Vet Scand 1981; 22: 23–31.
Goodrich LR, Choi VW, Carbone BA, McIlwraith CW, Samulski RJ . Ex vivo serotype-specific transduction of equine joint tissue by self-complementary adeno-associated viral vectors. Hum Gene Ther 2009; 20: 1697–1702.
Rabinowitz JE, Rolling F, Li C, Conrath H, Xiao W, Xiao X et al. Cross-packaging of a single adeno-associated virus (AAV) type 2 vector genome into multiple AAV serotypes enables transduction with broad specificity. J Virol 2002; 76: 791–801.
Vande Broek I, Vanderkerken K, De Greef C, Asosingh K, Straetmans N, Van Camp B et al. Laminin-1-induced migration of multiple myeloma cells involves the high-affinity 67 kD laminin receptor. Br J Cancer 2001; 85: 1387–1395.
Akache B, Grimm D, Pandey K, Yant SR, Xu H, Kay MA . The 37/67-kilodalton laminin receptor is a receptor for adeno-associated virus serotypes 8, 2, 3, and 9. J Virol 2006; 80: 9831–9836.
Montuori N, Selleri C, Risitano AM, Raiola AM, Ragno P, Del Vecchio L et al. Expression of the 67-kDa laminin receptor in acute myeloid leukemia cells mediates adhesion to laminin and is frequently associated with monocytic differentiation. Clin Cancer Res 1999; 5: 1465–1472.
Boissier MC, Lemeiter D, Clavel C, Valvason C, Laroche L, Begue T et al. Synoviocyte infection with adeno-associated virus (AAV) is neutralized by human synovial fluid from arthritis patients and depends on AAV serotype. Hum Gene Ther 2007; 18: 525–535.
Cottard V, Valvason C, Falgarone G, Lutomski D, Boissier MC, Bessis N . Immune response against gene therapy vectors: influence of synovial fluid on adeno-associated virus mediated gene transfer to chondrocytes. J Clin Immunol 2004; 24: 162–169.
Ishihara A, Bartlett JS, Bertone AL . Inflammation and immune response of intra-articular serotype 2 adeno-associated virus or adenovirus vectors in a large animal model. Arthritis 2012; 2012: 735472.
Grimm D, Kern A, Rittner K, Kleinschmidt JA . Novel tools for production and purification of recombinant adenoassociated virus vectors. Hum Gene Ther 1998; 9: 2745–2760.
Zhao W, Zhong L, Wu J, Chen L, Qing K, Weigel-Kelley KA et al. Role of cellular FKBP52 protein in intracellular trafficking of recombinant adeno-associated virus 2 vectors. Virology 2006; 353: 283–293.
Hirt B . Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol 1967; 26: 365–369.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants AR048566 and AR057422 from the NIH and the National Institute of Arthritis Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Dr Ghivizzani has an equity interest in Molecular Orthopaedics Inc., a company pursuing gene-based treatments for arthritic disease. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watson, R., Broome, T., Levings, P. et al. scAAV-mediated gene transfer of interleukin-1-receptor antagonist to synovium and articular cartilage in large mammalian joints. Gene Ther 20, 670–677 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2012.81
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2012.81
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Serotype-specific transduction of canine joint tissue explants and cultured monolayers by self-complementary adeno-associated viral vectors
Gene Therapy (2023)
-
A pilot study to determine the optimal dose of scAAVIL-1ra in a large animal model of post-traumatic osteoarthritis
Gene Therapy (2023)
-
Innovation in Targeted Intra-articular Therapies for Osteoarthritis
Drugs (2023)
-
Arthritis gene therapy is becoming a reality
Nature Reviews Rheumatology (2018)
-
Safety and biodistribution assessment of sc-rAAV2.5IL-1Ra administered via intra-articular injection in a mono-iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis rat model
Molecular Therapy - Methods & Clinical Development (2016)