Abstract
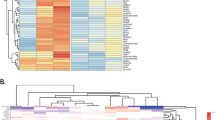
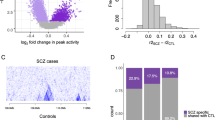
A recent study using a ‘partial’ rodent model of schizophrenia has employed amygdalar activation to induce reported changes in the expression of hippocampal genes associated with metabolic and signaling pathways in response to amygdalar activation. The amygdalo–hippocampal pathway plays a central role in the regulation of the stress response and emotional learning. In the current study, we have performed a chromosome mapping analysis to determine whether genes showing changes in response to environmental stress may form clusters and, if so, whether they might show a topographical association with linkage sites for schizophrenia. When the hippocampal genes showing changes in expression were topographically mapped on specific rat chromosomes, significant clustering was observed on chromosomes 1, 4 and 8, although chromosome 1 showed the largest amount of clustering. When these same rodent genes were mapped to human chromosomes, most of the genes found on chromosome 1 in rat mapped to chromosome 11 in human. The vast majority of the genes showing changes in regulation were excluded from known linkage sites for schizophrenia. Based on these findings, we postulate that environmental factors may contribute to the endophenotype for schizophrenia through the activation and/or deactivation of specific genetic clusters, ones that do not appear to be directly associated with susceptibility genes for this disorder.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kopnisky KL, Cowan WM, Hyman SE . Levels of analysis in psychiatric research. Dev Psychopathol 2002; 14: 437–461.
Barondes SH, Alberts BM, Andreasen NC, Bargmann C, Benes F, Goldman-Rakic P et al. Workshop on schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 1612–1614.
Bray NJ, Owen MJ . Searching for schizophrenia genes. Trends Mol Med 2001; 7: 169–174.
Gottesman II, Gould TD . The endophenotype concept in psychiatry: etymology and strategic intentions. Am J Psychiatry 2003; 160: 636–645.
Sullivan PF, Kendler KS, Neale MC . Schizophrenia as a complex trait: evidence from a meta-analysis of twin studies. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2003; 60: 1187–1192.
Benes FM, Berretta S . Amygdalo-entorhinal inputs to the hippocampal formation in relation to schizophrenia. Ann NY Acad Sci 2000b; 911: 293–304.
Ledoux J . The amygdala and emotion. In: Aggleton JP (ed). The Amygdala. Oxford University Press: Oxford, 2000, pp 289–310.
Simpson MD, Slater P, Deakin JF, Royston MC, Skan WJ . Reduced GABA uptake sites in the temporal lobe in schizophrenia. Neurosci Lett 1989; 107: 211–215.
Reynolds GP, Czudek C, Andrews H . Deficit and hemispheric asymmetry of GABA uptake sites in the hippocampus in schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 1990; 27: 1038–1044.
Benes FM, Khan Y, Vincent SL, Wickramasinghe R . Differences in the subregional and cellular distribution of GABAA receptor binding in the hippocampal formation of schizophrenic brain. Synapse 1996; 22: 338–349.
Todtenkopf MS, Benes FM . Distribution of glutamate decarboxylase65 immunoreactive puncta on pyramidal and nonpyramidal neurons in hippocampus of schizophrenic brain. Synapse 1998; 29: 323–332.
Benes FM, Berretta S . Amygdalo-entorhinal inputs to the hippocampal formation in relation to schizophrenia. Ann NY Acad Sci 2000a; 911: 293–304.
Benes FM, Berretta S . GABAergic interneurons: implications for understanding schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. PG-1-27. Neuropsychopharmacology 2001; 25: 1–27.
Joyal CC, Laakso MP, Tiihonen J, Syvalahti E, Vilkman H, Laakso A et al. The amygdala and schizophrenia: a volumetric magnetic resonance imaging study in first-episode, neuroleptic-naive patients. Biol Psychiatry 2003a; 54: 1302–1304.
Smith GN, Lang DJ, Kopala LC, Lapointe JS, Falkai P, Honer WG . Developmental abnormalities of the hippocampus in first-episode schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 2003a; 53: 555–561.
Joyal CC, Laakso MP, Tiihonen J, Syvalahti E, Vilkman H, Laakso A et al. The amygdala and schizophrenia: a volumetric magnetic resonance imaging study in first-episode, neuroleptic-naive patients. Biol Psychiatry 2003b; 54: 1302–1304.
Smith GN, Lang DJ, Kopala LC, Lapointe JS, Falkai P, Honer WG . Developmental abnormalities of the hippocampus in first-episode schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 2003b; 53: 555–561.
Sanders SK, Shekhar A . Regulation of anxiety by GABAA receptors in the rat amygdala. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1995; 52: 701–706.
Berretta S, Munno DW, Benes FM . Amygdalar activation alters the hippocampal GABA system: ‘partial’ modelling for postmortem changes in schizophrenia. J Comp Neurol 2001; 431: 129–138.
Benes FM, Burke R, Walsh JP, Berretta S, Konradi C, Minns M . Acute amygdalar activation induces an upregulation of multiple monoamine G protein coupled pathways in rat hippocampus. Mol Psychiatry 2004a; 9: 932–945.
Akirav I, Richter-Levin G . Biphasic modulation of hippocampal plasticity by behavioral stress and basolateral amygdala stimulation in the rat. J Neurosci 1999; 19: 10530–10535.
Roozendaal B, Nguyen BT, Power AE, McGaugh JL . Basolateral amygdala noradrenergic influence enables enhancement of memory consolidation induced by hippocampal glucocorticoid receptor activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 11642–11647.
Jaenisch R, Bird A . Epigenetic regulation of gene expression: how the genome integrates intrinsic and environmental signals. Nat Genet 2003; 33 (Suppl): 245–254.
O’Donovan MC, Williams NM, Owen MJ . Recent advances in the genetics of schizophrenia. Hum Mol Genet 2003; 12 (Spec No 2): R125–R133.
Li C, Hung Wong W . Model-based analysis of oligonucleotide arrays: model validation, design issues and standard error application. Genome Biol 2001; 2, RESEARCH0032.
Li C, Wong WH . Model-based analysis of oligonucleotide arrays: expression index computation and outlier detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 31–36.
Dahlquist KD, Salomonis N, Vranizan K, Lawlor SC, Conklin BR . GenMAPP, a new tool for viewing and analyzing microarray data on biological pathways. Nat Genet 2002; 31: 19–20.
Liu G, Loraine AE, Shigeta R, Cline M, Cheng J, Valmeekam V et al. NetAffx: Affymetrix probesets and annotations. Nucleic Acids Res 2003; 31: 82–86.
Karolchik D, Baertsch R, Diekhans M, Furey TS, Hinrichs A, Lu YT et al. The UCSC Genome Browser Database. Nucleic Acids Res 2003; 31: 51–54.
Adler D . In: U.o.W.D.o. (Ed.) Pathology 1994. http://www.pathology.washington.edu/research/cytopages/idiograms/human.
Wheeler DL, Church DM, Federhen S, Lash AE, Madden TL, Pontius JU . et al. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology. Nucleic Acids Res 2003; 31: 28–33.
NCBI Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man, OMIM (TM). Johns Hopkins University. MIM Numbers: 181 500, 603 342, 181 510, 600 511, 603 013, 603 176, 605 419, 603 206, 600 850, 192 430, 188 400, 604 906. Baltimore, MD, 2003; http://www.ncbi.nlm.nlh.gov/omim/.
Sokal R, Rohlf FJ . Biometry: The Principles and Practice of Statistics in Biological Research. W.H. Freeman and Co.: New York, 1995, pp 727–741.
Versteeg R, van Schaik BD, van Batenburg MF, Roos M, Monajemi R, Caron H et al. The human transcriptome map reveals extremes in gene density, intron length, GC content, and repeat pattern for domains of highly and weakly expressed genes. Genome Res 2003; 13: 1998–2004.
Zhong S, Li C, Wong WH . ChipInfo: Software for extracting gene annotation and gene ontology information for microarray analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 2003; 31: 3483–3486.
Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW, Dempfle L . Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 2002; 30: e36.
Jones PA, Takai D . The role of DNA methylation in mammalian epigenetics. Science 2001; 293: 1068–1070.
Jenuwein T, Allis CD . Translating the histone code. Science 2001; 293: 1074–1080.
Dennis C . Epigenetics and disease: altered states. Nature 2003; 421: 686–688.
Verona RI, Mann MR, Bartolomei MS . Genomic imprinting: intricacies of epigenetic regulation in clusters. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2003; 19: 237–259.
Niehrs C, Pollet N . Synexpression groups in eukaryotes. Nature 1999; 402: 483–487.
Lee JM, Sonnhammer EL . Genomic gene clustering analysis of pathways in eukaryotes. Genome Res 2003; 13: 875–882.
Fukuoka Y, Inaoka H, Kohane IS . Inter-species differences of co-expression of neighboring genes in eukaryotic genomes. BMC Genomics 2004; 5: 4.
Caron H, van Schaik B, van der Mee M, Baas F, Riggins G, van Sluis P et al. The human transcriptome map: clustering of highly expressed genes in chromosomal domains. Science 2001; 291: 1289–1292.
Lercher MJ, Urrutia AO, Hurst LD . Clustering of housekeeping genes provides a unified model of gene order in the human genome. Nat Genet 2002; 31: 180–183.
Futscher BW, Oshiro MM, Wozniak RJ, Holtan N, Hanigan CL, Duan H et al. Role for DNA methylation in the control of cell type specific maspin expression. Nat Genet 2002; 31: 175–179.
Robertson KD . DNA methylation and chromatin – unraveling the tangled web. Oncogene 2002; 21: 5361–5379.
Cahill L, Vazdarjanova A, Setlow B . The basolateral amygdala complex is involved with, but is not necessary for, rapid acquisition of Pavlovian ‘fear conditioning’. Eur J Neurosci 2000; 12: 3044–3050.
Finnegan EJ . Epialleles – a source of random variation in times of stress. Curr Opin Plant Biol 2002; 5: 101–106.
Kovalchuk O, Burke P, Arkhipov A, Kuchma N, James SJ, Kovalchuk I et al. Genome hypermethylation in Pinus silvestris of Chernobyl – a mechanism for radiation adaptation? Mutat Res 2003; 529: 13–20.
Tchantchou F, Graves M, Ashline D, Morin A, Pimenta A, Ortiz D et al. Increased transcription and activity of glutathione synthase in response to deficiencies in folate, vitamin E, and apolipoprotein E. J Neurosci Res 2004; 75: 508–515.
Tremolizzo L, Carboni G, Ruzicka WB, Mitchell CP, Sugaya I, Tueting P et al. An epigenetic mouse model for molecular and behavioral neuropathologies related to schizophrenia vulnerability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 17095–17100.
Detich N, Bovenzi V, Szyf M . Valproate induces replication-independent active DNA demethylation. J Biol Chem 2003a; 278: 27586–27592.
Detich N, Hamm S, Just G, Knox JD, Szyf M . The methyl donor S-Adenosylmethionine inhibits active demethylation of DNA: a candidate novel mechanism for the pharmacological effects of S-Adenosylmethionine. J Biol Chem 2003b; 278: 20812–20820.
Petronis A . The origin of schizophrenia: genetic thesis, epigenetic antithesis, and resolving synthesis. Biol Psychiatry 2004; 55: 965–970.
Day R, Nielsen JA, Korten A, Ernberg G, Dube KC, Gebhart J et al. Stressful life events preceding the acute onset of schizophrenia: a cross-national study from the World Health Organization. Cult Med Psychiatry 1987; 11: 123–205.
Benes FM . The role of stress and dopamine–GABA interactions in the vulnerability for schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res 1997; 31: 257–275.
Castine MR, Meador-Woodruff JH, Dalack GW . The role of life events in onset and recurrent episodes of schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. J Psychiatr Res 1998; 32: 283–288.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (MH42261, MH62822, MH/NS31862) and the generosity of Menachem and Carmella Abraham, John and Virginia Taplin and Anne Allen.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burke, R., Walsh, J., Matzilevich, D. et al. Mapping of hippocampal gene clusters regulated by the amygdala to nonlinkage sites for schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 11, 158–171 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001769
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001769