Abstract
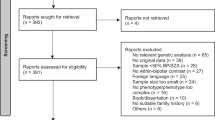
The serotonin transporter (5-HTT) is a candidate gene for bipolar disorder (BPD). It has been investigated for association with the illness in a series of studies, but overall results have been inconsistent and its role in the disorder remains controversial. Systematic reviews using meta-analytical techniques are a useful method for objectively and reproducibly assessing individual studies and generating combined results. We performed two meta-analyses of published studies—both population-based and family-based studies—investigating the association between BPD and the 5-HTT gene-linked polymorphic region (5-HTTLPR) and the intron 2 variable numbers of tandem repeats (VNTR) polymorphisms. The literature was searched using Medline and Embase to identify studies for inclusion. We statistically joined population-based and family-based studies into a single meta-analysis. For both polymorphisms, our review revealed significant pooled odds ratios (ORs): 1.12 (95% CI 1.03–1.21) for the 5-HTTLPR and 1.12 (95% CI 1.02–1.22) for the intron 2 VNTR. Meta-regression showed that neither the study type (population-based vs family-based; P=0.41 for the 5-HTTLPR and P=0.91 for the intron 2 VNTR) nor the sample ethnicity (Caucasian vs non-Caucasian; P=0.35 for the 5-HTTLPR and P=0.66 for the intron 2 VNTR) significantly contributed to the heterogeneity of the meta-analyses. The observed ORs could be regarded simply as a very small but detectable effect of the 5-HTT, which has an additive effect when combined with other susceptibility loci. Alternative hypotheses on this finding were also discussed: a stronger effect of the haplotypes involving the two polymorphisms or other SNP markers; a more direct effect of these polymorphisms on specific phenotypes of BPD; and the presence of gene–environment interaction as a mediator of the genetic effects of 5-HTT.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bebbington P, Ramana R . The epidemiology of bipolar affective disorder. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 1995; 30: 279–292.
Muller-Oerlinghausen B, Berghofer A, Bauer M . Bipolar disorder. Lancet 2002; 359: 241–247.
Craddock N, Jones I . Genetics of bipolar disorder. J Med Genet 1999; 36: 585–594.
Craddock N, Jones I . Molecular genetics of bipolar disorder. Br J Psychiatry Suppl 2001; 41: s128–s133.
Wender PH, Kety SS, Rosenthal D, Schulsinger F, Ortmann J, Lunde I . Psychiatric disorders in the biological and adoptive families of adopted individuals with affective disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1986; 43: 923–929.
Potash JB, DePaulo Jr JR . Searching high and low: a review of the genetics of bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord 2000; 2: 8–26.
Segurado R, Detera-Wadleigh SD, Levinson DF, Lewis CM, Gill M, Nurnberger Jr JI et al. Genome scan meta-analysis of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, part III: Bipolar disorder. Am J Hum Genet 2003; 73: 49–62.
Craddock N, Dave S, Greening J . Association studies of bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord 2001; 3: 284–298.
*Rotondo A, Mazzanti C, Dell'Osso L, Rucci P, Sullivan P, Bouanani S et al. Catechol o-methyltransferase, serotonin transporter, and tryptophan hydroxylase gene polymorphisms in bipolar disorder patients with and without comorbid panic disorder. Am J Psychiatry 2002; 159: 23–29.
Kirov G, Murphy KC, Arranz MJ, Jones I, McCandles F, Kunugi H et al. Low activity allele of catechol-O-methyltransferase gene associated with rapid cycling bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry 1998; 3: 342–345.
Ho LW, Furlong RA, Rubinsztein JS, Walsh C, Paykel ES, Rubinsztein DC . Genetic associations with clinical characteristics in bipolar affective disorder and recurrent unipolar depressive disorder. Am J Med Genet 2000; 96: 36–42.
*Mynett-Johnson L, Kealey C, Claffey E, Curtis D, Bouchier-Hayes L, Powell C et al. Multimarkerhaplotypes within the serotonin transporter gene suggest evidence of an association with bipolar disorder. Am J Med Genet 2000; 96: 845–849.
Lesch KP, Bengel D, Heils A, Sabol SZ, Greenberg BD, Petri S et al. Association of anxiety-related traits with a polymorphism in the serotonin transporter gene regulatory region. Science 1996; 274: 1527–1531.
*Collier DA, Stober G, Li T, Heils A, Catalano M, Di Bella D et al. A novel functional polymorphism within the promoter of the serotonin transporter gene: possible role in susceptibility to affective disorders. Mol Psychiatry 1996a; 1: 453–460.
Fiskerstrand CE, Lovejoy EA, Quinn JP . An intronic polymorphic domain often associated with susceptibility to affective disorders has allele dependent differential enhancer activity in embryonic stem cells. FEBS Lett 1999; 458: 171–174.
Munafo MR, Flint J . Meta-analysis of genetic association studies. Trends Genet 2004; 20: 439–444.
Lohmueller KE, Pearce CL, Pike M, Lander ES, Hirschhorn JN . Meta-analysis of genetic association studies supports a contribution of common variants to susceptibility to common disease. Nat Genet 2003; 33: 177–182.
Anguelova M, Benkelfat C, Turecki G . A systematic review of association studies investigating genes coding for serotonin receptors and the serotonin transporter: I. Affective disorders. Mol Psychiatry 2003; 8: 574–591.
Lotrich FE, Pollock BG . Meta-analysis of serotonin transporter polymorphisms and affective disorders. Psychiatr Genet 2004; 14: 121–129.
StataCorp. Stata Statistical Software. Stata Corporation: College Station, Texas, 2002.
Davey Smith G, Egger M, Phillips AN . Meta-analysis. Beyond the grand mean? BMJ 1997; 315: 1610–1614.
Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, Minder C . Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997; 315: 629–634.
Wang MC, Bushman BJ . Using the normal quantile plot to explore meta-analytic data sets. Psychol Methods 1998; 3: 46–54.
Munafo MR, Clark TG, Flint J . Assessing publication bias in genetic association studies: evidence from a recent meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res 2004; 129: 39–44.
NCSS. PASS Power Analysis and Sample Size Software. NCSS Statistical Software: Kaysville, Utah, 2002.
Angst J, Frey R, Lohmeyer B, Zerbin-Rudin E . Bipolar manic-depressive psychoses: results of a genetic investigation. Hum Genet 1980; 55: 237–254.
*Bellivier F, Laplanche JL, Leboyer M, Feingold J, Bottos C, Allilaire JF et al. Serotonin transporter gene and manic depressive illness: an association study. Biol Psychiatry 1997; 41: 750–752.
Bellivier F, Leroux M, Henry C, Rayah F, Rouillon F, Laplanche J-L et al. Serotonin transporter gene polymorphism influences age at onset in patients with bipolar affective disorder. Neurosci Lett 2002; 334: 17–20.
Bellivier F, Szoke A, Henry C, Lacoste J, Bottos C, Nosten-Bertrand M et al. Possible association between serotonin transporter gene polymorphism and violent suicidal behavior in mood disorders. Biol Psychiatry 2000; 48: 319–322.
Benedetti F, Serretti A, Colombo C, Campori E, Barbini B, di Bella D et al. Influence of a functional polymorphism within the promoter of the serotonin transporter gene on the effects of total sleep deprivation in bipolar depression. Am J Psychiatry 1999; 156: 1450–1452.
Di Bella D, Catalano M, Balling U, Smeraldi E, Lesch KP . Systematic screening for mutations in the coding region of the human serotonin transporter (5-HTT) gene using PCR and DGGE. Am J Med Genet 1996; 67: 541–545.
*Esterling LE, Yoshikawa T, Turner G, Badner JA, Bengel D, Gershon ES et al. Serotonin transporter (5-HTT) gene and bipolar affective disorder. Am J Med Genet 1998; 81: 37–40.
*Furlong RA, Ho L, Walsh C, Rubinsztein JS, Jain S, Paykel ES et al. Analysis and meta-analysis of two serotonin transporter gene polymorphisms in bipolar and unipolar affective disorders. Am J Med Genet 1998; 81: 58–63.
*Hauser J, Leszczynska A, Samochowiec J, Czerski PM, Ostapowicz A, Chlopocka M et al. Association analysis of the insertion/deletion polymorphism in serotonin transporter gene in patients with affective disorder. Eur Psychiatry 2003; 18: 129–132.
*Heiden A, Schussler P, Itzlinger U, Leisch F, Scharfetter J, Gebhardt C et al. Association studies of candidate genes in bipolar disorders. Neuropsychobiology 2000; 42: 18–21.
Kelsoe JR, Remick RA, Sadovnick AD, Kristbjarnarson H, Flodman P, Spence MA et al. Genetic linkage study of bipolar disorder and the serotonin transporter. Am J Med Genet 1996; 67: 215–217.
Kirov G, Lowry CA, Stephens M, Oldfield S, O'Donovan MC, Lightman SL et al. Screening ABCG1, the human homologue of the Drosophila white gene, for polymorphisms and association with bipolar affective disorder. Mol Psychiatry 2001; 6: 671–677.
*Kunugi H, Hattori M, Kato T, Tatsumi M, Sakai T, Sasaki T et al. Serotonin transporter gene polymorphisms: ethnic difference and possible association with bipolar affective disorder. Mol Psychiatry 1997; 2: 457–462.
Kunugi H, Tatsumi M, Sakai T, Hattori M, Nanko S . Serotonin transporter gene polymorphism and affective disorder. Lancet 1996; 347: 1340.
Lesch KP, Gross J, Franzek E, Wolozin BL, Riederer P, Murphy DL . Primary structure of the serotonin transporter in unipolar depression and bipolar disorder. Biol Psychiatry 1995; 37: 215–223.
*Liu W, Gu N, Feng G, Li S, Bai S, Zhang J et al. Tentative association of the serotonin transporter with schizophrenia and unipolar depression but not with bipolar disorder in Han Chinese. Pharmacogenetics 1999; 9: 491–495.
*Mundo E, Walker M, Tims H, Macciardi F, Kennedy JL . Lack of linkage disequilibrium between serotonin transporter protein gene (SLC6A4) and bipolar disorder. Am J Med Genet 2000; 96: 379–383.
Murphy VE, Mynett-Johnson LA, Claffey E, Shields DC, McKeon P . No association between 5HT-2A and bipolar disorder irrespective of genomic imprinting. Am J Med Genet 2001; 105: 422–425.
Ogilvie AD, Battersby S, Bubb VJ, Fink G, Harmar AJ, Goodwin GM et al. Polymorphism in serotonin transporter gene associated with susceptibility to major depression. Lancet 1996; 347: 731–733.
Oruc L, Verheyen GR, Furac I, Jakovljevic M, Ivezic S, Raeymaekers P et al. Association analysis of the 5-HT2C receptor and 5-HT transporter genes in bipolar disorder. Am J Med Genet 1997; 74: 504–506.
*Ospina-Duque J, Duque C, Carvajal-Carmona L, Ortiz-Barrientos D, Soto I, Pineda N et al. An association study of bipolar mood disorder (type I) with the 5-HTTLPR serotonin transporter polymorphism in a human population isolate from Colombia. Neurosci Lett 2000; 292: 199–202.
*Saleem Q, Ganesh S, Vijaykumar M, Reddy YCJ, Brahmachari SK, Jain S . Association analysis of 5HT transporter gene in bipolar disorder in the Indian population. Am J Med Genet 2000; 96: 170–172.
Vincent JB, Masellis M, Lawrence J, Choi V, Gurling HM, Parikh SV et al. Genetic association analysis of serotonin system genes in bipolar affective disorder. Am J Psychiatry 1999; 156: 136–138.
*Yen F-C, Hong C-J, Hou S-J, Wang J-K, Tsai S-J . Association study of serotonin transporter gene VNTR polymorphism and mood disorders, onset age and suicide attempts in a Chinese sample. Neuropsychobiology 2003; 48: 5–9.
*Sun HS, Wang HC, Lai TJ, Wang TJ, Li CM . Sequence variants and haplotype analysis of serotonin transporter gene and association with bipolar affective disorder in Taiwan. Pharmacogenetics 2004; 14: 173–179.
*Mellerup E, Bennike B, Bolwig T, Dam H, Hasholt L, Jorgensen MB et al. Platelet serotonin transporters and the transporter gene in control subjects, unipolar patients and bipolar patients. Acta Psychiatr Scand 2001; 103: 229–233.
*Dimitrova A, Georgieva L, Nikolov I, Poriazova N, Krastev S, Toncheva D et al. Major psychiatric disorders and the serotonin transporter gene (SLC6A4): family-based association studies. Psychiatr Genet 2002; 12: 137–141.
*Piccardi MP, Ardau R, Chillotti C, Deleuze JF, Mallet J, Meloni R et al. Manic-depressive illness: an association study with the inositol polyphosphate 1-phosphatase and serotonin transporter genes. Psychiatr Genet 2002; 12: 23–27.
*Battersby S, Ogilvie AD, Smith CA, Blackwood DH, Muir WJ, Quinn JP et al. Structure of a variable number tandem repeat of the serotonin transporter gene and association with affective disorder. Psychiatr Genet 1996; 6: 177–181.
Battersby S, Ogilvie AD, Blackwood DH, Shen S, Muqit MM, Muir WJ et al. Presence of multiple functional polyadenylation signals and a single nucleotide polymorphism in the 3′ untranslated region of the human serotonin transporter gene. J Neurochem 1999; 72: 1384–1388.
*Bellivier F, Henry C, Szoke A, Schurhoff F, Nosten-Bertrand M, Feingold J et al. Serotonin transporter gene polymorphisms in patients with unipolar or bipolar depression. Neurosci Lett 1998; 255: 143–146.
*Bocchetta A, Piccardi MP, Palmas MA, Chillotti C, Oi A, Del Zompo M . Family-based association study between bipolar disorder and DRD2, DRD4, DAT, and SERT in Sardinia. Am J Med Genet 1999; 88: 522–526.
*Collier DA, Arranz MJ, Sham P, Battersby S, Vallada H, Gill P et al. The serotonin transporter is a potential susceptibility factor for bipolar affective disorder. NeuroReport 1996b; 7: 1675–1679.
Craddock N, Rees M, Norton N, Feldman E, McGuffin P, Owen MJ . Association between bipolar disorder and the VNTR polymorphism in intron 2 of the human serotonin transporter (hSERT). Psychiatr Genet 1996; 6: 147.
*Gutierrez B, Arranz MJ, Collier DA, Valles V, Guillamat R, Bertranpetit J et al. Serotonin transporter gene and risk for bipolar affective disorder: an association study in Spanish population. Biol Psychiatry 1998; 43: 843–847.
*Hoehe MR, Wendel B, Grunewald I, Chiaroni P, Levy N, Morris-Rosendahl D et al. Serotonin transporter (5-HTT) gene polymorphisms are not associated with susceptibility to mood disorders. Am J Med Genet 1998; 81: 1–3.
Kirov G, Jones I, McCandles F, Craddock N, Owen MJ . Family-based associations studies of candidate genes in bipolar disorder. Am J Med Genet 1998; 81: 476–477.
*Kirov G, Rees M, Jones I, MacCandless F, Owen MJ, Craddock N . Bipolar disorder and the serotonin transporter gene: a family-based association study. Psychol Med 1999; 29: 1249–1254.
Kirov G, Jones I, McCandless F, Craddock N, Owen MJ . Family-based association studies of bipolar disorder with candidate genes involved in dopamine neurotransmission: DBH, DAT1, COMT, DRD2, DRD3 and DRD5. Mol Psychiatry 1999; 4: 558–565.
Kunugi H, Kawada Y, Tatsumi M, Sasaki T, Nanko S . Manic-depressive illness and tyrosine hydroxylase gene. Lancet 1996; 348: 336.
*Mendes de Oliveira JR, Otto PA, Vallada H, Lauriano V, Elkis H, Lafer B et al. Analysis of a novel functional polymorphism within the promoter region of the serotonin transporter gene (5-HTT) in Brazilian patients affected by bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet 1998; 81: 225–227.
Mynett-Johnson LA, Bouchier-Hayes L, Murphy VE, Claffey E, McKeon P . No evidence of an association between bipolar disorder and the serotonin transporter in the Irish population. Am J Med Genet 1998; 81: 504–505.
*Ohara K, Nagai M, Tsukamoto T, Tani K, Suzuki Y . Functional polymorphism in the serotonin transporter promoter at the SLC6A4 locus and mood disorders. Biol Psychiatry 1998; 44: 550–554.
*Oliveira JR, Carvalho DR, Pontual D, Gallindo RM, Sougey EB, Gentil V et al. Analysis of the serotonin transporter polymorphism (5-HTTLPR) in Brazilian patients affected by dysthymia, major depression and bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry 2000; 5: 348–349.
*Rees M, Norton N, Jones I, McCandless F, Scourfield J, Holmans P et al. Association studies of bipolar disorder at the human serotonin transporter gene (hSERT; 5HTT). Mol Psychiatry 1997; 2: 398–402.
Rosenthal NE, Mazzanti CM, Barnett RL, Hardin TA, Turner EH, Lam GK et al. Role of serotonin transporter promoter repeat length polymorphism (5-HTTLPR) in seasonality and seasonal affective disorder. Mol Psychiatry 1998; 3: 175–177.
Serretti A, Lattuada E, Catalano M, Smeraldi E . Serotonin transporter gene not associated with psychotic symptomatology of mood disorders. Psychiatry Res 1999; 86: 59–65.
Serretti A, Cusin C, Lattuada E, Di Bella D, Catalano M, Smeraldi E . Serotonin transporter gene (5-HTTLPR) is not associated with depressive symptomatology in mood disorders. Mol Psychiatry 1999; 4: 280–283.
*Serretti A, Cristina S, Lilli R, Cusin C, Lattuada E, Lorenzi C et al. Family-based association study of 5-HTTLPR, TPH, MAO-A, and DRD4 polymorphisms in mood disorders. Am J Med Genet 2002; 114: 361–369.
*Stober G, Heils A, Lesch KP . Serotonin transporter gene polymorphism and affective disorder. Lancet 1996; 347: 1340–1341.
Gelernter J, Cubells JF, Kidd JR, Pakstis AJ, Kidd KK . Population studies of polymorphisms of the serotonin transporter protein gene. Am J Med Genet 1999; 88: 61–66.
Conroy J, Meally E, Kearney G, Fitzgerald M, Gill M, Gallagher L . Serotonin transporter gene and autism: a haplotype analysis in an Irish autistic population. Mol Psychiatry 2004; 9: 587–593.
Ebstein RP, Zohar AH, Benjamin J, Belmaker RH . An update on molecular genetic studies of human personality traits. Appl Bioinformat 2002; 1: 57–68.
Reif A, Lesch KP . Toward a molecular architecture of personality. Behav Brain Res 2003; 139: 1–20.
Munafo MR, Clark TG, Flint J . Does measurement instrument moderate the association between the serotonin transporter gene and anxiety-related personality traits? A meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry 2004 Dec 14; [Epub ahead of print].
Smits KM, Smits LJ, Schouten JS, Stelma FF, Nelemans P, Prins MH . Influence of SERTPR and STin2 in the serotonin transporter gene on the effect of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in depression: a systematic review. Mol Psychiatry 2004; 9: 433–441.
Serretti A, Cusin C, Rossini D, Artioli P, Dotoli D, Zanardi R . Further evidence of a combined effect of SERTPR and TPH on SSRIs response in mood disorders. Am J Med Genet 2004; 129: 36–40.
Smeraldi E, Zanardi R, Benedetti F, Di Bella D, Perez J, Catalano M . Polymorphism within the promoter of the serotonin transporter gene and antidepressant efficacy of fluvoxamine. Mol Psychiatry 1998; 3: 508–511.
Goldberg JF, Truman CJ . Antidepressant-induced mania: an overview of current controversies. Bipolar Disord 2003; 5: 407–420.
Rousseva A, Henry C, van den Bulke D, Fournier G, Laplanche JL, Leboyer M et al. Antidepressant-induced mania, rapid cycling and the serotonin transporter gene polymorphism. Pharmacogenom J 2003; 3: 101–104.
Serretti A, Artioli P, Zanardi R, Lorenzi C, Rossini D, Cusin C et al. Genetic features of antidepressant induced mania and hypo-mania in bipolar disorder. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2004; 174: 504–511.
Mundo E, Walker M, Cate T, Macciardi F, Kennedy JL . The role of serotonin transporter protein gene in antidepressant-induced mania in bipolar disorder: preliminary findings. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2001; 58: 539–544.
Caspi A, Sugden K, Moffitt TE, Taylor A, Craig IW, Harrington H et al. Influence of life stress on depression: moderation by a polymorphism in the 5-HTT gene. Science 2003; 301: 386–389.
Carlson CS, Eberle MA, Kruglyak L, Nickerson DA . Mapping complex disease loci in whole-genome association studies. Nature 2004; 429: 446–452.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Marcus Munafò for his valuable advice and the anonymous reviewers for the constructive suggestions they have made for this paper. Dr Cho is sponsored by a scholarship from CAPES—Brazilian Ministry of Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
References marked with an asterisk indicate studies included in the meta-analyses.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, H., Meira-Lima, I., Cordeiro, Q. et al. Population-based and family-based studies on the serotonin transporter gene polymorphisms and bipolar disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry 10, 771–781 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001663
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001663
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Time moderates the interplay between 5-HTTLPR and stress on depression risk: gene x environment interaction as a dynamic process
Translational Psychiatry (2022)
-
Serotonin in psychiatry: in vitro disease modeling using patient-derived neurons
Cell and Tissue Research (2018)
-
Association between a genetic variant in the serotonin transporter gene (SLC6A4) and suicidal behavior in patients with schizophrenia
Behavioral and Brain Functions (2012)
-
Hypermethylation of serotonin transporter gene in bipolar disorder detected by epigenome analysis of discordant monozygotic twins
Translational Psychiatry (2011)
-
Parent of origin effect and allelic expression imbalance of the serotonin transporter in bipolar disorder and suicidal behaviour
European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience (2011)