Abstract
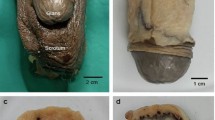
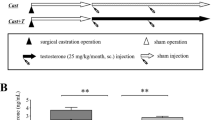
Androgens play a vital role in erectile function and are known to have a neuroprotective role in the nervous system. This study investigated, in a rat model, the effects of testosterone deprivation and replacement on the morphology of the dorsal nerve of the rat penis at the light microscopy level. Two weeks after castration, male rats were infused with vehicle alone or 44 μg of testosterone for 2 weeks. Age-matched, sham-operated control animals were used for comparisons. Penile tissue samples were removed for histological analyses. The following parameters were assessed: (1) total myelin sheath thickness; (2) density of nerve fibers; and (3) axon cross-sectional area per nerve fiber. Castration resulted in a significant increase in axon cross-sectional area compared to that of the control and testosterone-treated animals (6.97±0.59 μm2 per fiber in control animals to 14.32±0.44 μm2 per fiber in castrated animals). Qualitatively, there were signs of nerve degeneration, particularly myelin sheath degeneration, in all sample groups. We did not observe statistically significant changes in myelin sheath thickness. There was a trend of reduced nerve density. Nerve degeneration was not quantified since this study was performed at the light microscopic level. This study suggests that testosterone has a neuroprotective role in the nerve fibers of the dorsal nerve and testosterone deficiency may lead to different forms of nerve degeneration resulting in anatomic alterations, thus contributing to erectile dysfunction.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Traish AM, Kim NN . Weapons of penile smooth muscle destruction: androgen deficiency promotes accumulation of adipocytes in the corpus cavernosum. Aging Male 2005; 8: 141–146.
Mills TM, Lewis RW, Stopper VS . Androgenic maintenance of inflow and veno-occlusion during erection in the rat. Biol Reprod 1998; 59: 1413–1418.
Baba K, Yajima M, Carrier S, Morgan DM, Nunes L, Lue TF et al. Delayed testosterone replacement restores nitric oxide synthase-containing nerve fibers and the erectile response in rat penis. BJU Int 2000; 85: 953–958.
Armagan A, Kim NN, Goldstein I, Traish AM . Dose-response relationship between testosterone and erectile function: evidence for the existence of a critical threshold. J Androl 2006; 27: 517–526.
Syme DB, Corcoran NM, Bouchier-Hayes DM, Morrison WA, Costello AJ . The effect of androgen status on the structural and functional success of cavernous nerve grafting in an experimental rat model. J Urol 2007; 177: 390–394.
Giuliano F, Rampin O, Schirar A, Jardin A, Rousseau JP . Autonomic control of penile erection: modulation by testosterone in the rat. J Neuroendocrinol 1993; 5: 677–683.
Keast JR, Saunders RJ . Testosterone has potent, selective effects on the morphology of pelvic autonomic neurons which control the bladder, lower bowel, and internal reproductive organs of the male rat. Neuroscience 1998; 85: 543–556.
Keast JR . Effects of testosterone on pelvic autonomic pathways: progress and pitfalls. J Auton Nerv Sys 2000; 79: 67–73.
Keast JR, Gleeson RJ, Shulkes A, Morris MJ . Maturational and maintenance effects of testosterone on terminal axon density and neuropeptide expression in the rat vas deferens. Neuroscience 2002; 112: 391–398.
Meusburger SM, Keast JR . Testosterone and nerve growth factor have distinct but interacting effects on structure and neurotransmitter expression of adult pelvic ganglion cells in vitro. Neuroscience 2001; 108: 331–340.
Kurz EM, Sengelaub DR, Arnold AP . Androgens regulate the dendritic length of mammalian motoneurons in adulthood. Science 1986; 232: 395–398.
Baba K, Yajima M, Carrier S, Akkus E, Reman J, Nunes L et al. Effect of testosterone on the number of NADPH diaphorase-stained nerve fibers in the rat corpus cavernosum and dorsal nerve. Urology 2000; 56: 533–538.
Rogers RS, Graziottin TM, Lin CS, Kan YW, Lue TF . Intracavernosal vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) injection and adeno-associated virus-mediated VEGF gene therapy prevent and reverse venogenic erectile dysfunction in rats. Int J Impot Res 2003; 15: 26–37.
Adinolfi AM, Yamuy J, Morales FR, Chase MH . Segmental demyelination in peripheral nerves of old cats. Neurobiol Aging 1991; 12: 175–179.
Sandell JH, Peters A . Disrupted myelin and axon loss in the anterior commissure of the aged rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol 2003; 466: 14–30.
Peters A, Moss MB, Sethares C . Effects of aging on myelinated nerve fibers in monkey primary visual cortex. J Comp Neurol 2000; 419: 364–376.
Mills TM, Reilly CM, Lewis RW . Androgens and penile erection: a review. J Androl 1996; 17: 633–638.
Traish AM, Park K, Dhir V, Kim NN, Moreland RB, Goldstein I . Effects of castration and androgen replacement on erectile function in a rabbit model. Endocrinology 1999; 140: 1861–1868.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Traish for his support and guidance throughout this study and for his critical reading and editing of the manuscript. This study was supported by unrestricted educational research grants from Schering AG, Germany and Auxilium, USA and the Institute for Sexual Medicine, Boston University School of Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Armagan, A., Hatsushi, K. & Toselli, P. The effects of testosterone deficiency on the structural integrity of the penile dorsal nerve in the rat. Int J Impot Res 20, 73–78 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901614
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901614
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Estrogenic endocrine disruptor exposure directly impacts erectile function
Communications Biology (2024)
-
Testosterone replacement therapy and erectile dysfunction
International Journal of Impotence Research (2022)
-
Sexual function outcomes of radiation and androgen deprivation therapy for localized prostate cancer in men with good baseline function
Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases (2022)
-
Cavernous smooth muscles: innovative potential therapies are promising for an unrevealed clinical diagnosis
International Urology and Nephrology (2020)
-
Impact of androgen deprivation therapy on sexual function
Asian Journal of Andrology (2012)