Abstract
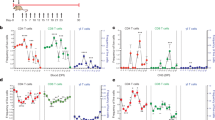
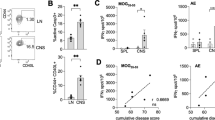
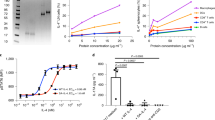
AUTOIMMUNE diseases occur when T lymphocytes become activated on recognizing self antigen linked to the autologous class II molecule of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC)1,2. The resulting complex of antigen MHC T-cell receptor could be a target for treatment of autoimmune diseases. Studies in which each component is blocked separately3–10 might be limited by interference in non-relevant immune responses that either use the same set of T-cell-receptor V gene segments or are linked to the same MHC. We report here an attack by a specific antibody on the unique antigenic site formed by the binding of two components of the trimolecular complex, the autoantigen bound to the self MHC11–14. We tested its effect in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis, an acute neurological autoimmune disease which is widely regarded as a model for autoimmune disorders15–17 and which is mediated by CD4+ T cells recognizing myelin basic protein (BP), or its peptides, in association with self Ia18,19. We made monoclonal antibodies which bound only the complex of BP and I–As. These antibodies blocked the proliferative response in vitro to the encephalitogenic determinant of BP and reduced the response to intact BP, without affecting the response to a nonrelevant antigen–purified protein derivative of tuberculin presented on syngeneic macrophages. They also inhibited experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in H–2s mice. Hence, antibodies directed specifically to the autoantigen–Ia complex, may offer a highly selective and effective treatment in autoimmune diseases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Todd, J. A. et al. Science 240, 1003–1009 (1988).
Hohlfeld, R. Ann. Neurol. 25, 532–538 (1989).
Ben-Nun, A., Wekerle, H. & Cohen, I. R. Nature 292, 60–61 (1981).
Acha-Orbea, H. et al. Cell 54, 263–273 (1988).
Vandenbark, A. A., Hashim, G. & Offner, H. Nature 341, 541–544 (1989).
Howell, M. D. et al. Science 246, 668–670 (1989).
Steinman, L., Rosenbaum, J. T., Sriram, S. & McDevitt, H. O. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 7111–7114 (1981).
Sriram, S., Topham, D. J. & Carroll, L. J. Immun. 139, 1485–1489 (1987).
Wraith, D. C., Smilek, D. E., Mitchell, D. J., Steinman, L. & McDevitt, H. O. Cell 59, 247–255 (1989).
Urban, J. L., Horvath, S. J. & Hood, L. Cell 59, 257–271 (1989).
Puri, J. & Lonai, P. Eur. J. Immun. 10, 273–281 (1980).
Babbit, B. P., Allen, P. M., Matsueda, G., Heber, E. & Unanue, E. R. Nature 317, 359–361 (1985).
Buus, S. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 3968–3971 (1986).
Brown, J. H. et al. Nature 332, 845–850 (1988).
Paterson, P. Y. in Autoimmunity (ed. Tala, N.) 644–692 (Academic, New York, 1977).
Fritz, R. B. & McFarlin, D. E. Chem. Immun. 46, 101–125 (1989).
Zamvil, S. S. & Steinman, L. A. Rev. Immun. 8, 579–621 (1990).
Offner, H., Brostoff, S. W. & Vardenbark, A. A. Cell Immun. 100, 364–373 (1986).
Fritz, R. H., Skeen, M. J., Jen-Chou, C. H., Garcia, M. & Egorov, I. K. J. Immun. 134, 2328–2332 (1985).
Demotz, S., Grey, H. M. & Sette, A. in Proc. 7th Int. Cong. Immun. (eds Melchers, F. et al) 60–67 (Springer, Berlin, 1989).
Zamvil, S. S. et al. J. exp. Med. 168, 1181–1186 (1988).
Sakai, K. et al. J. Neurolmmun. 19, 21–32 (1988).
Hirshfeld, H., Teitelbaum, D., Arnon, R. & Sela, M., FEBS Lett. 7, 317–320 (1970).
Eshhar, Z., Ofarim, M. & Waks, T. J. Immun. 124, 775–780 (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aharoni, R., Teftelbaum, D., Arnon, R. et al. Immunomodulation of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by antibodies to the antigen–Ia complex. Nature 351, 147–150 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1038/351147a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/351147a0
This article is cited by
-
TCR-like antibodies in cancer immunotherapy
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2019)
-
Stabilizing mutations increase secretion of functional soluble TCR-Ig fusion proteins
BMC Biotechnology (2010)
-
Susceptibility to anti-glomerular basement membrane disease is strongly associated with HLA-DRB1 genes
Kidney International (1997)
-
Experimental immunotherapies for multiple sclerosis
Springer Seminars in Immunopathology (1996)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.