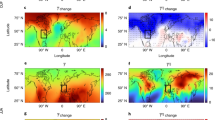
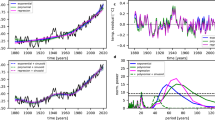
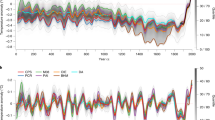
Abstract
IT has been suggested1–5 that solar variability may be a significant contributor to the long-term warming trend that has been observed in global mean surface air temperature since the mid-nineteenth century. Here we consider the role of long-term solar irradiance changes associated with sunspot fluctuations, extending an earlier analysis by Reid4. We find that solar variability is unlikely to have accounted for more than a small fraction of the observed warming.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hansen, J. et al. Science 213, 957–966 (1981).
Gilliland, R. L. Clim. Change 4, 111–131 (1982).
Gilliland, R. L. & Schneider, S. H. Nature 310, 38–41 (1984).
Reid, G. C. Nature 329, 142–143 (1987).
Seitz, F., Jastrow, R. & Nierenberg, W. A. Scientific Perspectives on the Greenhouse Problem (George C. Marshall Institute, Washington, DC, 1989).
Hoffert, M. I. Callegari, A. J. & Hsieh, C-T. J. geophys. Res. 85, 6667–6679 (1980).
Hoffert, M. I. & Flannery, B. P. in Projecting the Climatic Effects of Increasing Carbon Dioxide, DOE/ER-0237 (eds MacCracken, M. C. & Luther, F. M.) 149–190 (US Department of Energy, Washington, DC, 1985).
Folland, C. K., Parker, D. E. & Kates, F. E. Nature 310, 670–673 (1984).
Wigley, T. M. L. & Raper, S. C. B. Nature 330, 127–131 (1987).
Hansen, J. & Lacis, A. Nature 346, 713–719 (1990).
Lean, J. & Foukal, P. Science 240, 906–908 (1988).
Foukal, P. & Lean J. Science 247, 556–558 (1990).
Wigley, T. M. L. & Raper, S.C.B. Geophys. Res. Lett. (in the press)
Wigley, T. M. L. & Kelly, P. M. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A330, 547–560 (1990).
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Scientific Assessment of Climate Change, Working Group 1 Report (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change/World Meteorological Organization/United Nations Environment Programme, Geneva, 1990).
Gage, K. & Reid, G. C. Geophys, Res. Lett. 8, 187–190 (1981).
Wigley, T. M. L., Angell, J. K. & Jones, P. D. in Detecting the Climatic Effects of Increasing Carbon Dioxide, DOE/ER-0235 (eds MacCracken, M. C. & Luther, F. M.) 55–90 (US Department of Energy, Washington, DC, 1985).
Jones, P. D., Wigley, T. M. L. & Wright, P. B. Nature 322, 430–434 (1986).
Jones, P. D. et al. J. Clim. appl. Met. 25, 161–179 (1986).
Jones, P. D., Raper, S. C. B. & Wigley, T. M. L. J. Clim. appl. Met. 25, 1213–1230 (1986).
Wigley, T. M. L. & Raper, S. C. B. Nature 344, 324–327 (1990).
Wigley, T. M. L. & Barnett, T. P. in Scientific Assessment of Climate Change. Working Group 1 Report (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change/World Meteorological Organization/United Nations Environment Programme, Geneva, 1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kelly, P., Wigley, T. The influence of solar forcing trends on global mean temperature since 1861. Nature 347, 460–462 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1038/347460a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/347460a0
This article is cited by
-
Evolution of long-term trends and variability in air temperatures of Kazakhstan for the period 1963–2020
Theoretical and Applied Climatology (2024)
-
Severe weather disasters in China linked to solar activity during 1-1825 Common Era
Geoscience Letters (2022)
-
Annual, Seasonal and Monthly Trend Analysis of Temperature in Kazakhstan During 1970–2017 Using Non-parametric Statistical Methods and GIS Technologies
Earth Systems and Environment (2021)
-
Solar Forcing of Global Temperature Change Since AD 1400
Climatic Change (2005)
-
Development of a risk-hedging CO2-emission policy, part I: Risks of unrestrained emissions
Climatic Change (1996)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.