Abstract
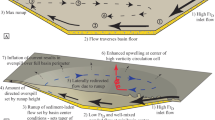
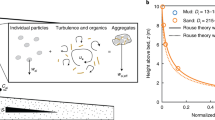
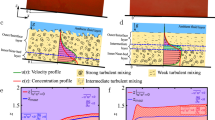
Turbidity current deposits of mud have recently been found up to 10m in thickness resulting from single depositional events1,2. Turbidites 1–5 m thick from the Madeira Abyssal Plain3,4 display long segments with little vertical change of grain size5,6. This suggests that the currents 'froze' in some way, making them unable to sort sediment. Here we suggest that a decline in flow speed of these currents led to a concentration gradient in silt close to the bed that was sufficiently steep to stratify the flow. A concentration gradient of 18 kg m–3 over 1.5 m height gives a layer Richardson number above the critical value of 0.25 for damping of turbulence. We propose that, with turbulence severely damped, a dense suspension of fine material consolidates like a static suspension while continuing to flow downslope. The current changes from a fully turbulent flow to a decelerating flow with suppressed turbulence and increasing density. In the latter state interparticle forces prevent differential settling of the coarser grains.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blanpied, C. & Stanley, D. J. Smithson. Contribs. mar. Sci. 13, 1–40 (1981).
Cita, M. B. et al. Mar. Geol. 55, 79–102 (1984).
Weaver, P. P. E., Searle, R. C. & Kuijpers, A. Spec. Publs geol. Soc. Land. 21, 131–143 (1986).
Weaver, P. P. E. & Rothwell, R. G. Spec. Publs geol. Soc. Lond. 31, 71–86 (1987).
Hieke, W. Mar. Geol. 55, 63–78 (1984).
Jones, K. P. N., McCave, I. N. & Patel, P. D. Sedimentology 35, 163–172 (1988).
Stow, D. A. V. & Bowen, A. J. Sedimentology 27, 31–46 (1980).
McCave, I. N. & Swift, S. A. Bull. geol. Soc. Am. 87, 541–546 (1976).
Stanley, D. J. Geo-mar. Lett. 1, 77–83 (1981).
Been, K. & Sills, G. C. Géotechnique 71, 519–535 (1981).
Allen, G. P. thesis, Univ. Bordeaux (1972).
Kirby, R. & Parker, W. R. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 40 (suppl. 1), 83–95 (1983).
Parker, W. R. Continental Shelf Res. 7, 1285–1293 (1986).
Wells, J. T. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 40 (suppl. 1), 130–142 (1983).
Stein, R. J. sedim. Petrol. 55, 590–593 (1985).
Hunter, R. J. Adv. Coll. Interface Sci. 17, 197–211 (1982).
Williams, D. J. A. in Estuarine Cohesive Sediment Dynamics (ed. Mehta, A. J.) 110–125 (Springer, Heidelberg, 1986).
Komar, P. D. In The Sea Vol. 6 (Marine Modelling) (eds Goldberg, E. D. et al) 603–621 (Wiley, New York, 1977).
Woodcock, C. R. & Mason, J. S. Bulk Solids Handling, 128–150 (L. Hill, Glasgow & London, 1987).
Wang, M., Zhan, Y., Liu, J., Duan, W. & Wu, W. In Proc. 2nd Int. Symp. River Sedimentation 45–53 (Water Resources and Electrical Power Press, Nanjing, 1983).
Hunt, J. R. in Estuarine Cohesive Sediment Dynamics (ed. Mehta, A. J.) 85–109 (Springer, Heidelberg, 1986).
McCave, I. N. Spec. Publs geol. Soc. Lond. 14, 35–69 (1984).
Simpson, J. E. A. Rev. Fluid, Mech. 14, 213–234 (1982).
Turner, J. S. Buoyancy Effects in Fluids (Cambridge University Press, 1973).
van Rijn, L. C. J. hydraul. Engng. 110, 1613–1641.
Smith, J. D. in The Sea Vol. 6 (Marine Modelling) (eds Goldberg, E. D. et al.), 539–577 (Wiley, New York, 1977).
Sinclair, C. G. in Interaction Between Fluids and Particles 78–86 (Inst. Chem. Engrs., London, 1962).
Pierson, T. C. & Costa, J. E. Rev. Engng. Geol. 7, 1–12 (1987).
Stow, D. A. V. & Piper, J. D. W. Fine Grained Sediments: Deep Water Processes and Facies. Spec. Publs geol. Soc. Lond. 15, 659 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCave, I., Jones, K. Deposition of ungraded muds from high-density non-turbulent turbidity currents. Nature 333, 250–252 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1038/333250a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/333250a0
This article is cited by
-
Detailed monitoring reveals the nature of submarine turbidity currents
Nature Reviews Earth & Environment (2023)
-
Onset of submarine debris flow deposition far from original giant landslide
Nature (2007)
-
Post-depositional stability of long-chain alkenones under contrasting redox conditions
Nature (1989)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.