Abstract
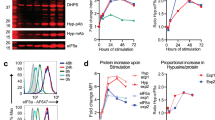
The p68 protein is a highly conserved nuclear antigen that is thought to be important in the regulation of cell growth and division. It is found in dividing cells of all mammals and amphibians tested, but not in quiescent cells. The protein shows a distinct granular distribution in the nucleus and is induced within four hours of serum stimulation of quiescent mouse fibroblasts. The p68 protein was first identified because of its specific immuno-logical cross-reaction with the DNA tumour virus nuclear oncogene SV40 large T, detected with the anti-SV40 large T monoclonal antibody DL3C4 (ref. 1), now renamed PAb204 (ref. 2). Sequencing of human complementary DNA coding for the growth-regulated p68 nuclear protein has revealed the molecular basis for its cross-reaction with SV40 large T antigen and its extensive homology with the translation initiation factor eIF-4A. The sequence similarity between p68 and eIF-4A is interesting because eIF-4A acts as an ATP-dependent RNA helicase3,4 and T antigen is an ATP-dependent DNA helicase5. We suggest that p68 could be a DNA or RNA helicase in the cell nucleus which is involved in replication, transcription or RNA processing and is required for cell growth.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lane, D. P. & Hoeffler, W. K. Nature 288, 167–170 (1980).
Crawford, L. V. & Harlow, E. J. Virol 41, 709 (1982).
Ray, B. K. et al. J. biol. Chem. 260, 7651–7658 (1985).
Abramson, R. D. et al. J. biol. Chem. 262, 3826–3832 (1987).
Stahl, H., Droge, P. & Knippers, R. EMBO J. 5, 1939–1944 (1986).
deWet, J. R. et al. DNA 3, 437–447 (1984).
Mole, S. E., Gannon J. V., Ford, M. J. & Lane, D. P. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 317, 455–469 (1987).
Mole, S. E. & Lane, D. P. J. Virol. 54, 703–710 (1985).
Ruther, U. & Muller-Hill, B. EMBO J. 2, 1791–1794 (1983).
Okayama, H. & Berg, P. Molec cell. Biol. 3, 280–289 (1983).
Okayama, H. & Berg, P. Molec. cell. Biol. 5, 1136–1142 (1985).
Nielsen, P. J., McMaster, G. K. & Traschel, H. Nucleic Acids Res. 13, 6867–6880 (1985).
Walker, J. E., Saraste, M., Runswick, M. J. & Gay, N. J. EMBO J. 1, 945–951 (1982).
Nakayama, N., Arai, N., Bond, M. W., Kaziro, Y. & Arai, K. J. biol. Chem. 259, 97–101 (1984).
Finch, P. W. et al. Nucleic Acid Res. 14, 8573–8582 (1986).
Pinkham, J. L. & Platt, T. Nucleic. Acid Res. 11, 3531–3545 (1983).
Finch, P. W. & Emmerson, P. T. Nucleic Acid Res. 12, 5789–5799 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ford, M., Anton, I. & Lane, D. Nuclear protein with sequence homology to translation initiation factor eIF-4A. Nature 332, 736–738 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1038/332736a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/332736a0
This article is cited by
-
P68 RNA helicase as a molecular target for cancer therapy
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2014)
-
DEAD-box protein p68 is regulated by β-catenin/transcription factor 4 to maintain a positive feedback loop in control of breast cancer progression
Breast Cancer Research (2014)
-
DDX5 is a positive regulator of oncogenic NOTCH1 signaling in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Oncogene (2013)
-
Phosphorylated p68 RNA helicase activates snail1 transcription by promoting HDAC1 dissociation from the snail1 promoter
Oncogene (2010)
-
P68 RNA helicase is a nucleocytoplasmic shuttling protein
Cell Research (2009)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.