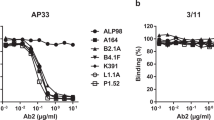
Abstract
Several studies illustrating idiotype network-directed regulation of the immune response1 have demonstrated that heterologous anti-(anti-idiotype) antibodies (1) share variable (V) region antigenic determinants with idiotype-bearing antibodies2–5, (2) lack antigen-binding activity3–6 and (3) alter the clonal profile of an immune response by stimulating/suppressing regulatory lymphocyte clones of anti-idiotype specificity2–4,6. However, the existence and significance of anti-(anti-idiotype) antibody in natural immunological responses has been questioned because of the artificial immunization procedures used to induce these antibodies. Here we describe a monoclonal mouse anti-(anti-idiotype) antibody generated in physiological conditions by immunizing BALB/c mice with a pneumococcal vaccine that elicits a humoral anti-phosphorylcholine (PC) response dominated by the T15 idiotype7. This antibody recognized an idiotope on a monoclonal anti-T15 antibody, failed to bind PC, did not exhibit detectable idiotypic cross-reactivity with T15+ immunoglobulins, utilized VH and VL genes distinct from the T15 V gene group8, and exerted a suppressive effect on the in vivo response to PC in syngeneic mice.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jerne, N. K. Annls Immun. Inst. Pasteur, Paris 125C, 373–389 (1974).
Cazenave, P. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 5122–5125 (1977).
Urbain, J., Wilkler, M., Fransen, J. D. & Collignon, C. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 5126–5130 (1977).
Bona, C., Heber-Katz, E. & Paul, W. J. exp. Med. 153, 951–967 (1981).
Wikler, M. et al. J. exp. Med. 150, 184–195 (1979).
Bona, C., Hooghe, R., Cazenave, P., Leguern, C. & Paul, W. J. exp. Med. 149, 815–823 (1979).
Sher, A. & Cohn, M. Eur. J. Immun. 2, 319–326 (1972).
Crews, S., Griffin, J., Huang, H., Calame, K. & Hood, L. Cell 25, 59–66 (1981).
Kearney, J., Radbruch, A., Liesegang, B. & Rajewsky, K. J. Immun. 123, 1548–1550 (1979).
Kearney, J., Barletta, R., Quan, Z. & Quintans, J. Eur. J. Immun. 11, 877–882 (1981).
Volanakis, J. & Kearney, J. J. exp. Med. 153, 1604–1614 (1981).
Cook, W. D., Rudikoff, S., Giusti, A. M. & Scharff, M. D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 1240–1244 (1982).
Rudikoff, S., Giusti, A. M., Cook, W. D. & Scharff, M. D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 1979–1983 (1982).
Claflin, J. L. Eur. J. Immun. 6, 666–668 (1976).
Potter, M. Adv. Immun. 25, 141–211 (1977).
Gearhart, P. J., Johnson, N. D., Douglas, R. & Hood, L. Nature 291, 29–34 (1981).
Cosenza, H., Julius, M. & Augustin, A. Eur. J. Immun. 6, 114–116 (1976).
Kim, B. S. & Greenberg, J. J. exp. Med. 154, 809–820 (1981).
Cosenza, H., Julius, M. & Augustin, A. Immun. Rev. 34, 3–33 (1977).
Towbin, H., Staehelin, T. & Gordon, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. 76, 4350–4354 (1979).
Lonai, P., Ben-Neriah, Y., Steinman, L. & Givol, D. Eur. J. Immun. 8, 827–832 (1978).
Sy, M-S. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 1143–1147 (1981).
Slack, J., Der-Balian, G., Nahm, M. & Davie, J. J. exp. Med. 151, 853–862 (1980).
Chesebro, B. & Metzgar, H. Biochemistry 11, 760–771 (1972).
Kubagawa, H. et al. J. exp. Med. 150, 792–807 (1979).
Bhown, A. S. et al. Analyt. Biochem. 102, 35–38 (1980).
Barstad, P. et al. Science 183, 962–964 (1944).
Kabat, E. A., Wu, T. & Bilofsky, H. Sequences of Immunoglobulin Chains (U.S. Department of Health, Education and Welfare, 1979).
Hämmerling, G. & Wallich, R. in Protides of the Biological Fluids, Vol. 28 (ed. Peeters, H.) 569–574 (Pergamon, Oxford, 1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pollok, B., Bhown, A. & Kearney, J. Structural and biological properties of a monoclonal auto-anti-(anti-idiotype) antibody. Nature 299, 447–449 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1038/299447a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/299447a0
This article is cited by
-
Unreasonable implications of reasonable idiotypic network assumptions
Bulletin of Mathematical Biology (1989)
-
A biological consequence of variation in the site of D–JH gene rearrangement
Nature (1984)
-
Beneficial autoimmunity?
Nature (1982)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.