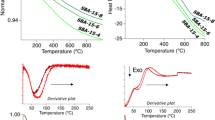
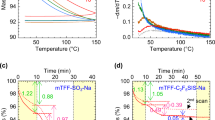
Abstract
LONG-RANGE ordered elements of water structure of micrometre dimensions have long been suspected to exist near certain aqueous/solid interfaces. However, the evidence has been inconclusive1 and it has also been argued that such ordered elements of water structure exist near a glass surface from a comparison of the diffusion coefficients of the hydrogen ion from polarography and the sintered glass diaphragm cell method2–4,10. The pore size of the sintered glass varied between 4 and 15µm. The mobility of the hydrogen ion is known to be very sensitive to the structure of water5,6. We present here convincing evidence from an IR spectroscopic study of IM HC1 in porous silica that such long-range ordering effects exist near a quartz surface and that as a consequence the excess proton mobility is reduced. Such long-range effects have not been conclusively demonstrated previously. With acid solutions the interaction between the easily polarisable hydrogen bonds of H5O2+ groupings may favour such a long-range order and as the absorbance of the polarisable hydrogen bonds is sensitively influenced by all interaction effects this order may be indicated by changes of the IR continua.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schufle, J. A., Huang, C-T. & Drost-Hansen, W. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 54, 184 (1976).
Roberts, N. K. & Northey, H. L. JCS Faraday I, 68, 1528 (1972).
Roberts, N. K. & Northey, H. L. Nature 237, 144 (1972).
Roberts, N. K. Nature 249, 594 (1974).
Roberts, N. K. J. phys. Chem. 80, 117 (1976).
Schiöberg, D. & Zundel, G. Can. J. Chem. 54, 2193 (1976).
Zundel, G. in The Hydrogen Bond, Recent Developments in Theory and Experiments (eds Schuster, P., Zundel, G. & Sandorfy, C.) ch. 15 (North Holland, Amsterdam, 1976).
Williams, M. in The Hydrogen Bond, Recent Developments in Theory and Experiments (eds Schuster, P., Zundel, G. & Sandorfy, C.) ch. 14 (North Holland, Amsterdam, 1976).
Hayd, A., Weidemann, E. G. & Zundel, G. J. chem. Phys. (in the press).
D. Glietenberg et al. Ber. Bunsenges. phys. Chem. 72, 562 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ROBERTS, N., ZUNDEL, G. IR studies of long-range surface effects—excess proton mobility in water in quartz pores. Nature 278, 726–728 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1038/278726a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/278726a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.