Abstract
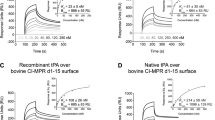
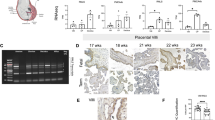
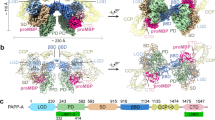
EPIDERMAL growth factor-urogastrone (EGF-URO), a singlechain polypeptide of molecular weight ∼6,000, found both in the mouse1–3 and in man4–7, is both a potent stimulant of cell proliferation and an inhibitor of gastric acid secretion. Specific membrane receptors for EGF-URO can be detected in various tissues including human placenta8–11. Although the mouse and human polypeptide sequences differ at 16 positions, they can share the same receptor site in human tissues3,12. There has been considerable recent interest in EGF-URO and its receptor, not only because of the potent mitogenic and acid-inhibitory actions of the polypeptide, but also because of the association of viral13, chemical14 and spontaneous15 cell transformation with a specific reduction in cell receptors for EGF-URO. It is also believed that EGF-URO and its receptor may be involved in the development, maintenance, and differentiation of tissues as diverse as the lens16, the palate17 and the keratin layer of skin18. In experiments aimed at the isolation of the membrane receptor for EGF-URO, we have observed that, unlike the receptor for insulin19, but like the muscarinic receptor for acetylcholine20, the EGF-URO receptor loses its ligand recognition property following solubilisation with detergents. We therefore developed an affinity-labelling technique using glutaraldehyde, that can covalently crosslink the receptor with 125I-labelled EGF-URO before solubilisation21. Independently, Das and coworkers have developed a photoaffinity-labelling technique that can also be used to radiolabel the EGF-URO receptor before solubilisation22. Here we report the success of both our previously described glutaraldehyde crosslinking technique21 (using 125I-EGF-URO for receptor labelling) and of a newly developed photoaffinity-labelling technique (using a photolabile 125I-EGF-URO crosslinking reagent) to identify the EGF-URO receptor in human placenta membranes and to effect the isolation of the affinity-labelled receptor by affinity chromatography using lectin and murine EGF-URO antibody–Agarose columns.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohen, S. J. biol. Chem. 237, 1555–1562 (1962).
Cohen, S. J. invest. Derm. 59, 13–16 (1972).
Cohen, S. & Carpenter, G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 72, 1317–1321 (1975).
Gregory, H. Nature 257, 325–327 (1975).
Gregory, H. & Preston, B. M. Int. J. Peptide Protein Res. 9, 107–118 (1977).
Gregory, H. & Willshire, I. R. Hoppe-Seylers' Z. physiol. Chem. 356, 1765–1774 (1975).
Hollenberg, M. D. Pan American Association of Biochemical Societies Symposium, 5, 265–268 (Academic, New York, 1976).
Hollenberg, M. D. & Cuatrecasas, P. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 70, 2964–2968 (1973).
O'Keefe, E., Hollenberg, M. D. & Cuatrecasas, P. Archs Biochem. Biophys. 164, 518–526 (1974).
Hollenberg, M. D. & Cuatrecasas, P. J. biol. Chem. 250, 3845–3853 (1975).
Carpenter, G., Lembach, K. J., Morrison, M. M. & Cohen, S. J. biol. Chem. 250, 4297–4304 (1975).
Hollenberg, M. D. & Gregory, H. Life Sci. 20, 267–274 (1976).
Todaro, G. J., DeLarco, J. E. & Cohen, S. Nature 264, 26–31 (1976).
Hollenberg, M. D., Barrett, I. C., Tso, P. O. P. & Berhanu, P. Cancer Res. (submitted).
Pratt, R. M. & Pastan, I. Nature 272, 68–70 (1978).
Hollenberg, M. D. Archs Biochem. Biophys. 171, 371–377 (1975).
Hassell, J. R. & Pratt, R. M. Expl. Cell Res. 106, 55–62 (1977).
Rheinwald, J. G. & Green, H. Nature 265, 421–424 (1977).
Cuatrecasas, P. Fedn. Proc. 32, 1838–1846 (1973).
Fewtrell, C. M. S. & Rang, H. P. in Drug Receptors, (ed. Rang, H. P.) 211–224 (University Park Press, Baltimore, 1973).
Sahyoun, N., Hock, R. A. & Hollenberg, M. D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 75, 1675–1679 (1978).
Das, M., Miyakawa, T., Fox, C. F., Pruss, R., Aharonov, A., Herschman, H. R. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 2790–2794 (1977).
Hock, R. A. & Hollenberg, M. D. Clin. Res. 25, 665A (1977).
Carpenter, G. & Cohen, S. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 79, 545–552 (1977).
Atlas, D. & Levitzki, A. Nature 272, 370–371 (1978).
Das, M. & Fox, C. F. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 75, 2644–2648 (1978).
Laemmli, U., Nature 272, 370–371 (1978).
March, S. C., Parikh, I. & Cuatrecasas, P. Analyt. Biochem. 60, 149–152 (1974).
Spivak, J. L., Small, D. & Hollenberg, M. D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 4633–4635 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HOCK, R., NEXØ, E. & HOLLENBERG, M. Isolation of the human placenta receptor for epidermal growth factor-urogastrone. Nature 277, 403–405 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1038/277403a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/277403a0
This article is cited by
-
Epidermal growth factor
In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology (1987)
-
Epidermal growth factor
Bioscience Reports (1986)
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA is homologous to a variety of RNAs overproduced in A431 carcinoma cells
Nature (1984)
-
Epidermal growth factor receptors
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (1981)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.