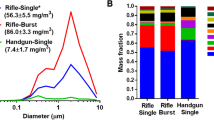
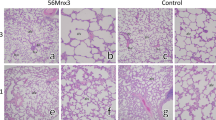
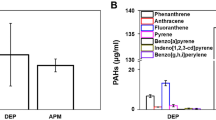
Abstract
THE herbicide paraquat (N,N′-dimethyl 4,4′-bipyridilium) can produce widespread oedema and fibrosis in the human lung after accidental ingestion1–3. In those cases where death occurs after several weeks, there are no apparent pulmonary changes during the first few days following ingestion. Animal experiments in a variety of species have shown the lung to be the major target organ4–6. After administration of paraquat to animals, the lung has a high initial concentration and retains paraquat7–9. This retention appears to be related to the development of lung damage7 (L. L. Smith and M. S. Rose, unpublished work). The mechanism of retention of paraquat by the lung is at present not understood.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bullivant, C. M., Br. med. J., 1, 1272–1273 (1966).
Bronkhorst, F. B., Van Daal, J. M., and Tan, H. D., Ned. Tijdschr. Geneesk, 112, 310–313 (1968).
Matthew, H., Logan, A., Woodruff, M. F. A., and Heard, B., Br. Med. J., 3, 759–763 (1968).
Clark, D. G., McElligott, T. F., and Weston-Hurst, E., Br. J. ind. Med., 23, 126–132 (1966).
Conning, D. M., Fletcher, K., and Swan, A. A. B., Br. med. Bull., 25, 245–249 (1969).
Murray, R. E., and Gibson, J. E., Expl molec. Path., 17, 317–325 (1972).
Sharp, C. W., Ottolenghi, A., and Posner, H. S., Toxicol. appl. Pharmac., 22, 241–251 (1972).
Litchfield, M. H., Daniel, J. W., and Longshaw, S., Toxicology, 1, 155–165 (1973).
Murray, R. E., and Gibson, J. E., Toxicol. appl. Pharmac., 27, 283–291 (1974).
Clark, D. G., and Weston-Hurst, E. W., Br. J. ind. Med., 27, 51–55 (1970).
Umbreit, W. W., Burris, R. H., and Stauffer, J. F., in Manometric Techniques, 132, (Burgess Publishing Company, 1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ROSE, M., SMITH, L. & WYATT, I. Evidence for energy-dependent accumulation of paraquat into rat lung. Nature 252, 314–315 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1038/252314b0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/252314b0
This article is cited by
-
Diosmin ameliorative effects on oxidative stress and fibrosis in paraquat-induced lung injury in mice
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2019)
-
Paraquat induces lung alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis via Nrf-2-regulated mitochondrial dysfunction and ER stress
Archives of Toxicology (2012)
-
Paraquat induces irreversible actin cytoskeleton disruption in cultured human lung cells
Cell Biology and Toxicology (1994)
-
Different distribution of paraquat and diquat in human poisoning cases after ingestion of a combined herbicide
Archives of Toxicology (1994)
-
Transport characteristics of paraquat across rat intestinal brush-border membrane
Archives of Toxicology (1993)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.