Abstract
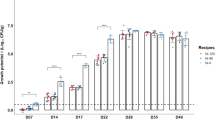
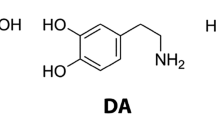
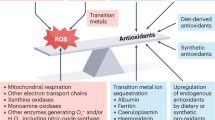
THE dangers to health from nitrite in the environment generally, and its use in meat processing in particular, have been pointed out by several groups1–3. These dangers are associated with the production of nitrous acid in the acid environment of the stomach and the further reaction of this substance with naturally occurring and synthetic secondary and tertiary amines to form nitroso compounds which may be carcinogenic, mutagenic and cytotoxic. Ascorbic acid has been shown to effectively compete with amines for nitrous acid in vitro4 and it has been suggested that co-administration of ascorbic acid with potentially nitrosatable drugs, and foods containing nitrite, may reduce the hazards associated with ingestion of these substances4.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lijinsky, W., and Epstein, S. S., Nature, 225, 21 (1970).
Magee, P. N., Food Cosmet. Toxicol., 9, 207 (1971).
Wolff, I. A., and Wasserman, A. E., Science N.Y., 177, 15 (1972).
Mirvish, S. S., Wallcave, L., Eagen, M., and Shubik, P., Science N.Y., 177, 65 (1972).
Kamm, J. J., Dashman, T., Conney, A. H., and Burns, J. J., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 70, 747 (1973).
Buncel, E., Jackson, K. G. A., and Jones, J. K. N., Chemy Ind., 89 (1965).
Jackson, K. G. A., and Jones, J. K. N., Can. J. Chem., 43, 450 (1965).
Kiss, G., and Neukom, H., Helv. chim. Acta, 49, 989 (1965).
Kiss, G., and Neukom, H., Experientia, 24, 326 (1968).
Ross, W. C. J., in Biological Alkylating Agents (Butter-worths, London, 1962).
Kutaćék, M., Porcházka, Ž., and Verěs, K., Nature, 194, 393 (1962).
Piironen, E., and Virtanen, A. I., Acta chem. scand., 16, 1286 (1962).
Gmelin, R., and Virtanen, A. I., Suomal. Tiedeakat. Toim, A, II Chemica No. 107, 1 (1961).
Burns, J. J., Evans, C., and Trousof, N., J. biol. Chem. 227, 785 (1957).
Conney, A. H., Bray, G. A., Evans, C., and Burns, J. J., Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 92, 115 (1961).
Williams, D. J., and Rabin, B. R., Nature, 232, 102 (1971).
Ross, R., and Benditt, E. P., J. Cell Biol., 22, 365 (1964).
Ferfnández-Madrid, F., and Pita, J. in Chemistry and Molecular Biology of the Intercellular Matrix. (edit by Balazs, E. A.) 1, 439 (Academic, London 1970).
Sim, A. K., Chemy Ind., 160 (1972).
Pandya, K. P., Singh, G. B., and Joshi, N. C., Acta pharmac. tox., 28, 499 (1970).
Singh, G. B., and Zaidi, S. H., J. Indian med. Ass., 53, 588 (1969).
Nachtomi, E., Alumot, E., and Bondi, A., Israel J. Chem., 6, 803 (1968).
Schirardin, H., Bauer, M., and Warter, J., C.r. Séanc Soc. Biol., 163, 1673 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
EDGAR, J. Ascorbic acid and biological alkylating agents. Nature 248, 136–137 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1038/248136a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/248136a0
This article is cited by
-
Protective effect of ascorbic acid against oxidative damage induced by hydrogen peroxide in cultured human peripheral blood lymphocytes
Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry (2009)
-
Radical intermediates and antioxidant activity of ascorbic acid
Reviews of Chemical Intermediates (1988)
-
The effect of antioxidants on MNNG-induced stomach carcinogenesis in rats
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (1986)
-
In vivo effect of L-ascorbic acid on benzo(α)pyrene metabolite-DNA adduct formation in rat liver
Journal of Biosciences (1982)
-
Vitamin C und D�nndarmkrebs
Langenbecks Archiv f�r Chirurgie (1981)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.