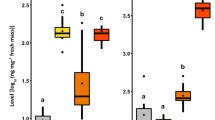
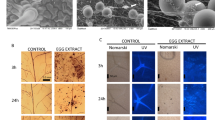
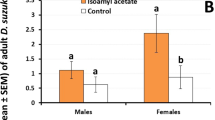
Abstract
IT has been shown that endogenous gibberellin-like substances are translocated in the phloem of plants1 by using the aphid Tuberolachnus salignus (Gmelin) to obtain sieve tube sap samples. It has also been suggested2 that steroid moulting hormones of insects have effects similar to those of gibberellins in plant bioassays, and both insects and plants have been shown to contain similar steroid hormones that are active in bringing about moulting in insect assays3. In view of these findings, some of these hormones were obtained in crystalline form and tested to determine whether they are promotive in plant assays for gibberellins. The earlier work2 was also repeated using extracts of whole locusts (Schistocerca gregaria) and their prothoracic glands.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoad, G. V., and Bowen, M. R., Planta, 82, 22 (1968).
Carlisle, D. D., Osborne, D. J., Ellis, P. E., and Moorhouse, J. E., Nature, 200, 1230 (1963).
Williams, C. R., in Chemical Ecology (edit. by Sondheimer, E., and Simeone, J. B.), 103 (Academic Press, New York and London, 1970).
Frankland, B., and Wareing, P. F., Nature, 185, 255 (1960).
Phillips, I. D. J., and Jones, R. L., Planta, 63, 269 (1964).
Brian, P. W., and Hemming, H. G., Physiol. Plant., 8, 669 (1955).
Nitsch, J. P., and Nitsch, C., Plant Physiol., 31, 94 (1956).
Michniewicz, M., Acta Soc. Bot. Pol., 30, 553 (1961).
Whyte, P., and Luckwill, L. C., Nature, 210, 1360 (1966).
Morgan, E. D., and Woodbridge, A. P., Chem. Commun., 475 (1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HOAD, G., ELLIS, P. Ecdysones and Locust Extracts in Plant Bioassays. Nature 237, 108–109 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1038/237108a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/237108a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.