Abstract
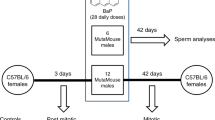
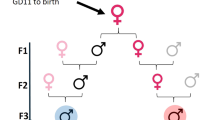
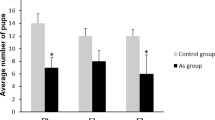
AFTER paternal exposure to mutagens and subsequent mating, adverse genetic effects are seen in the form of pre-implantation losses of fertilized ova and zygotes, early foetal deaths, and sterility and semi-sterility in F1 progeny1. Early foetal deaths are a direct quantitative index of dominant lethal mutations. These are generally concomitant with pre-implantation losses, which thus constitute a presumptive but less specific measure of mutagenicity1. A practical, sensitive assay for mutagens, based, on the induction of dominant lethal mutations in mammals, has been developed and applied to a wide range of environmental chemical pollutants and to drugs2.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Epstein, S. S., Arnold, E., Steinberg, K., Mackintosh, D., Shafner, H., and Bishop, Y., Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. (in the press).
Epstein, S. S., and Shafner, H., Nature, 219, 387 (1968).
Amoroso, E. C., and Parkes, A. S., Proc. Roy. Soc., B, 134, 57 (1947).
Chang, M. C., Hunt, D. M., and Romanoff, E. B., Anat. Rec., 129, 211 (1957).
Bedford, J. M., and Hunter, R. H. F., J. Reprod. Fert., 17, 49 (1968).
Brenneke, H., Strahlentherapie, 60, 214 (1934).
Bruce, H. M., and Austin, C. R., Proc. Soc. Study of Fert., 8, 121 (1956).
Edwards, R. G., Proc. Roy. Soc., B, 146, 469 (1957).
Edwards, R. G., Proc. Roy. Soc., B, 149, 117 (1958).
Cattanach, B. M., and Edwards, R. G., Proc Roy. Soc. Edinburgh, 67B, 54 (1958).
Generoso, W. M., Genetics, 61, 461 (1969).
Chang, M. C., J. Exp. Zool., 121, 351 (1952).
Fox, B. W., Jackson, H., Craig, A. W., and Glover, T. D., J. Reprod. Fert., 5, 13 (1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
EPSTEIN, S., JOSHI, S., ARNOLD, E. et al. Abnormal Zygote Development in Mice after Paternal Exposure to a Chemical Mutagen. Nature 225, 1260–1261 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1038/2251260a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/2251260a0
This article is cited by
-
Reduced fertility in male mice following treatment with niridazole
Experientia (1973)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.