Abstract
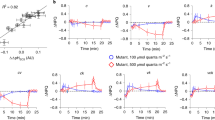
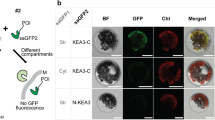
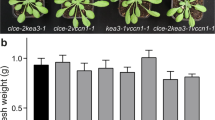
Two explanations have been put forward for the mechanism by which a pH gradient is formed through mitochondrial and chloroplast membranes. According to Mitchell's chemi-osmotic theory1 the energy of the electron current is used for separating H+ and OH− on either side of the membrane. The electrochemical potential set up as a result of this separation is the driving force for synthesis of ATP. By appropriate rapid alterations of the pH of chloroplast suspensions Jagendorf and Uribe induced phosphorylation in the dark2. An alternative explanation links the formation of the pH gradient with the energy-dependent translocation of cations through the membrane3,4. We have found that the presence of alkali metal cations is a prerequisite for the formation of a pH gradient through a chloroplast membrane in the light.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mitchell, P., Nature, 191, 144 (1961).
Jagendorf, A. T., and Uribe, E., Proc. US Nat. Acad. Sci., 55, 170 (1966).
Chance, B., and Mela, L., Nature, 212, 369 (1966).
Tager, J. M., Veldsma-Currie, R. D., and Slater, E. C., Nature, 212, 376 (1966).
Dilley, R. A., and Vernon, L. P., Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 111, 365 (1965).
Gear, A. R. L., and Lehninger, L., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 28, 840 (1967).
Rossi, C., Azzi, A., and Azzone, G. F., J. Biol. Chem., 242, 951 (1967).
Shavit, N., and Avron, M., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 131, 516 (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MOLOTKOVSKY, Y., DZYUBENKO, V. Light-induced pH Gradient through Chloroplast Membrane and Translocation of Cations. Nature 219, 496–498 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1038/219496a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/219496a0
This article is cited by
-
Effect of protons and cations on chloroplast membranes as visualized by the bound ANS fluorescence
Biophysics of Structure and Mechanism (1977)
-
Die Wirkung von Dinactin auf die cyclische Photophosphorylierung, die lichtinduzierte ATP-Pa-Austauschreaktion und den lichtinduzierten Protonentransport in Chloroplasten
Planta (1969)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.