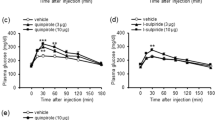
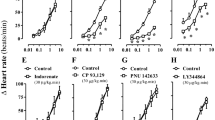
Abstract
IT is now generally accepted that α-methyldihydroxyphenylalanine (α-methyldopa) is an effective means of lowering the blood pressure in cases of hypertension. The mechanism of its action, however, is by no means clear. One of the known actions of α-methyldopa is the inhibition of the enzyme dopadecarboxylase, and, as this enzyme is involved in the synthesis of noradrenaline, it was thought that its inhibition could explain the lowering of the blood pressure. It was found1,2 that α-methyldopa caused depletion of noradrenaline in the brain and heart, and at first this seemed to support the ideas about its hypotensive action. The duration of tissue noradrenaline depletion was, however, far greater than the duration of the dopadecarboxylase inhibition and the lowering of blood pressure. Furthermore, stronger decarboxylase inhibitors than α-methyldopa do not cause a lowering of blood pressure in hypertensive patients3. Animal experiment has shown4 that, despite noradrenaline depletion of tissues, α-methyldopa does not interfere with the effects of sympathetic nerve stimulation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hess, S. M., Connamacher, R. H., Ozaki, M., and Udenfriend, S., J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therap., 134, 129 (1961).
Porter, C. C., Totaro, J. A., and Leiby, C. M., J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therap., 134, 139 (1961).
Gillespie, L., Oates, J. A., Crout, J. R., and Sjoerdsma, A., Circulation, 25, 281 (1962).
Day, M. D., and Rand, M. J., Brit. J. Pharmacol., 22, 72 (1964).
Brown, G. L., and Gillespie, J. S., J. Physiol., 138, 81 (1957).
Varma, D. R., and Benfey, B. G., J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therap., 141, 310 (1963).
Stone, C. A., Ross, C. A., Wenger, H. C., Ludden, C. T., Blessing, J. A., Totaro, J. A., and Porter, C. C., J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therap., 136, 80 (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DAVIES, B. α-Methyldihydroxyphenylalanine and Release of Noradrenaline. Nature 210, 957–958 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1038/210957a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/210957a0
This article is cited by
-
Der Einflu� der Verabreichung von Aminos�uren, speziell von L-Dopa und ?-Methyldopa, auf die Zusammensetzung des Liquor cerebrospinalis bei extrapyramidalen Syndromen
Deutsche Zeitschrift f�r Nervenheilkunde (1969)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.