Abstract
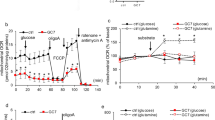
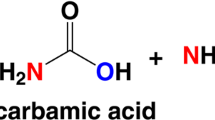
PREVIOUS investigations have shown that metabolic acidosis leads to significant increases in the activities of glutaminase and glutamine transaminase-ω-amidase (GTA) in kidneys of rats1,2 and guinea-pigs3. These changes are associated with, and thought to be related to, the adaptation of renal ammonia excretion to acidosis in the rat2,4 and guinea-pig3. The response of renal glutaminase to metabolic acidosis is not mediated by the adrenal gland5 or substrate, glutamine6, and is restricted to the kidneys5. Goldstein and Kensler5 found that administration of ethionine to guinea-pigs inhibited the acid-induced rise in renal glutaminase activity, and we suggested that metabolic acidosis stimulates the synthesis of glutaminase by renal cells. The manner in which this stimulation occurs is unknown. Kroeger7 has recently reported that alterations in the electrolyte balance of the medium bathing isolated salivary glands of the insect Chironomus thummi produced marked and specific changes in the gene activities (RNA synthesis) of the giant chromosomes found in these glands. Metabolic acidosis and the accompanying changes in electrolyte balance might have similar effects on UNA synthesis in renal cells. Actinomycin D, an antibiotic which interferes with the DNA-dependent synthesis of RNA in bacterial and animal cells8, has been shown to inhibit the synthesis of RNA in rat kidneys9. The effects of this antibiotic on the responses of renal glutaminase, GTA and ammonia excretion to metabolic acidosis were therefore investigated in the rat.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davies, B. M., and Yudkin, J., Biochem. J., 52, 407 (1952).
Goldstein, L., Nature, 201, 1229 (1964).
Goldstein, L., Richterich-van Baerle, R., and Dearborn, E. H., Proc. Soc. Expt. Biol. and Med., 93, 284 (1956).
Rector, F. C., Seldin, D. W., and Copenhaver, J. H., J. Clin. Invest., 34, 20 (1955).
Goldstein, L., and Kensler, C. J., J. Biol. Chem., 235, 1086 (1960).
Goldstein, L., and Copenhaver, J. H., Amer. J. Physiol., 198, 227 (1960).
Kroeger, H., Nature, 200, 1234 (1963).
Reich, E., Franklin, R. M., Shatkin, A. J., and Tatum, E. L., Proc. U.S. Nat. Acad. Sci., 48, 1238 (1962).
Merits, I., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm., 10, 254 (1963).
Leonard, E., and Orloff, J., Amer. J. Physiol., 182, 131 (1955).
Weber, G., Singhal, R. L., and Stamm, N. B., Science, 142, 390 (1963).
Karlson, P., Perspectives in Biol. and Med., 6, 203 (1963).
Knox, W. E., Auerbach, V. H., and Lin, E. C. C., Physiol. Rev., 36, 164 (1956).
Rector, F. C., and Orloff, J., J. Clin. Invest., 38, 366 (1959).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
GOLDSTEIN, L. Actinomycin D Inhibition of the Adaptation of Renal Glutamine-deaminating Enzyme in the Rat. Nature 205, 1330–1331 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1038/2051330a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/2051330a0
This article is cited by
-
Ammonia metabolism during acid-base disturbance
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1985)
-
Effects of fluorocitrate on renal ammoniagenesis and glutamine metabolism in the intact dog kidney
Kidney International (1979)
-
Relation of ammonia excretion adaptation to glutaminase activity in acidotic, subtotalnephrectomized rats
Kidney International (1978)
-
Control of renal production of ammonia
Kidney International (1972)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.