Abstract
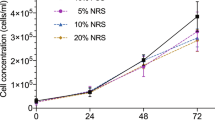
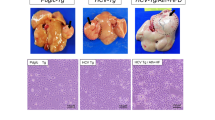
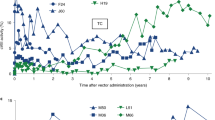
THE immunizing ability of several chemically and virus induced tumours and immuno-chemical studies suggest that neoplasms of animals and man are characterized by a changed antigenic composition1–3. As yet, however, no regularity in these changes has been observed, probably due to the small amount of data available. It remains unknown whether the cell type of a tumour, the carcinogens used for tumour induction, or the genetic composition of the neoplastic cells affect the kind and degree of these antigenic changes. To obtain information about some of these problems we compared the loss of liver antigens in fourteen hepatomas. Although these tumours were selected on the basis of the histological features characteristic of hepatomas it is doubtful whether they are strictly comparable. First, the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) content of the stemline is not the same in different hepatomas. This agrees with our previous observation that even two hepatomas of the same liver lobe can consist of cells with different DNA values4. Secondly, some of these hepatomas consist of a uniform population of cells whereas others are characterized by a heterogenous population of cells with varying amounts of DNA.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prehn, R. T., Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 101, 107 (1962).
Sjögren, H. O., Hellström, I., and Klein, G., Exp. Cell Res., 23, 204 (1961).
Zilber, L. A., Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 101, 264 (1962).
Stich, H. F., J. Nat. Cancer Inst., 24, 1283 (1960).
Öuchterlony, Ö., Prog. in Allergy, 5, 1 (1958).
Crowle, A. J., J. Lab. Clin. Med., 52, 784 (1958).
Weiler, E., Z. Naturf., 11, 31 (1956).
Weiler, E., Brit. J. Cancer, 10, 553 (1956).
Nairn, R. C., McEntegart, M. G., Fothergill, I. E., and Porteous, I. B., Lancet, ii, 109 (1961).
Nairn, R. C., Richmond, H. G., McEntegart, M. G., and Fothergill, I. E., Brit. Med. J., ii, 1335 (1961).
Stich, H. F., and Steele, H. D., J. Nat. Cancer Inst., 28, 1207 (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KALNINS, V., STICH, H. Loss of Liver Cell Antigens in Azo-dye Induced Hepatomas of Rats. Nature 200, 189–190 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1038/200189b0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/200189b0
This article is cited by
-
Antigen Deletions in Carcinogen-induced Rat Hepatomata
Nature (1967)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.