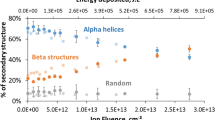
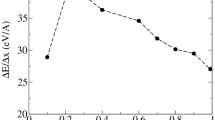
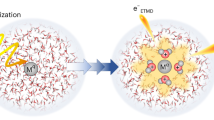
Abstract
ALEXANDER et al.1 have suggested that the ‘secondary’ structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is disorganized after irradiation by breaking the hydrogen bonds which link the two molecules together into the twin helix. “In regions of the DNA molecule where this occurs, the double molecule is opened up and becomes more flexible.” The molecule can coil up then into a smaller volume in solution and the viscosity of this solution will decrease. A further decrease in the viscosity is observed when the molecule is degraded due to breaks in the polynucleotide chain. As the loss of the viscosity is a result of different radiation effects, it is of interest to study tho effect of the irradiation on the hydrogen bonds with other methods. The wrork of Sarkar and Dounce2 provides a basis for such studies. According to these authors the formaldehyde reaction of Fraenkel-Conrat3 can be observed only when an appreciable disruption of the interstrand hydrogen bonds occurs. This formaldehyde reaction may be more sensitive than viscosity measurements for detecting a low degree of denaturation of DNA. While Sarkar and Dounce2 studied the denaturation after heating, I compared their results with the denaturation by X-ray irradiation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, P., Lett, J. T., Moroson, M., and Stancay, K. A., Immediate and Low Level Effects of Ionizing Radiation, 47 (Taylor and Francis, Ltd., London, 1960).
Sarkar, N. K., and Dounce, A. L., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 49, 160 (1961).
Fraenkel-Conrat, H., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 15, 307 (1954).
Hagen, U., Strahlentherapie, 116, 385 (1961).
Lett, J. T., and Alexander, P., Rad. Res., 15, 159 (1961).
Kirby, K. S., Biochem. J., 66, 495 (1957).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HAGEN, U. Radiosensitivity of Hydrogen Bonds in Deoxyribonucleic Acid. Nature 194, 182–183 (1962). https://doi.org/10.1038/194182a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/194182a0
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.