Abstract
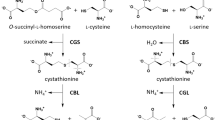
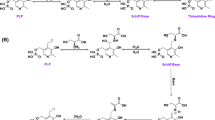
IN a previous communication from this laboratory, results were presented which show that the enzymatic formation of hydrogen sulphide from L-cysteine in the liver of the rat occurs through two pathways1. During the course of purification of the pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzyme present in the non-particulate fraction of the liver (which we referred to as ‘soluble’ desulphurase), it has been observed that the purified enzyme which catalyses the formation of hydrogen sulphide and ammonia from L-cysteine is also responsible for the formation of ammonia from some other substrates and particularly from DL( + )-allo-cystathionine; the ratio of specific activities of the enzymatic preparations towards cystathionine and towards cysteine remained the same even after an approximately 300-fold purification. We concluded2 that the soluble cysteine desulphurase was probably identical with the cystathionase-homoserine deaminase crystallized by Matsuo and Greenberg3; but, from the results of some inhibition experiments, we suggested that the mechanism of action of cystathionase appeared to consist of the deamination of substrates leading to the labilization of γ-substituents rather than the reverse mechanism proposed by Matsuo and Greenberg. Recently, Goswami et al.4 observed that the L-cysteine desulphydrase activity in an homogenate of chick liver (where the two pathways demonstrated in rat liver are also present5) was increased if L-cysteine or L-histidine were injected to the animals for 4 days, while other amino-acids (DL-methionine, L-arginine, L-glutamic acid) were not effective.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chatagner, F., Jollés-Bergeret, B., and Labouesse, J., C.R. Acad. Sci., Paris, 251, 3097 (1960).
Chatagner, F., Labouesse, J., Trautmann, O., and Jollés-Bergeret, B., C.R. Acad. Sci., Paris, 253, 742 (1961).
Matsuo, Y., and Greenberg, D. M., J. Biol. Chem., 230, 545, 561 (1958); 234, 507, 516 (1959).
Goswami, N. D., Robblee, A. R., and McElroy, L. W., J. Nutrition, 68, 671 (1959).
Chatagner, F., and Trautmann, O. (unpublished work).
Lin, E. C. C., and Knox, W. E., J. Biol., Chem., 233, 1186 (1958).
Jollés-Bergeret, B., Labouesse, J., and Chatagner, F., Bull. Soc. Chim. Biol., 42, 51 (1960).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
CHATAGNER, F., TRAUTMANN, O. ‘Soluble’ Cysteine Desulphurase of Rat Liver as an Adaptive Enzyme. Nature 194, 1281–1282 (1962). https://doi.org/10.1038/1941281a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1941281a0
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.