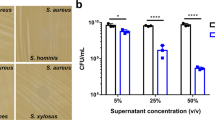
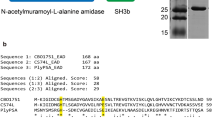
Abstract
PENICILLINASE is more difficult to prepare from Staphylococci than from Bacillus cereus because staphylococcal penicillinase diffuses little, if at all, from the bacterial cells into the medium in which they are grown, whereas that produced from B. cereus diffuses freely. In fact, some authors state that they could not detect ‘extracellular’ staphylococcal penicillinase1–5, although others claim that they could detect it in supernatant fluids6,7 or filtrates8,9 or by its diffusion into agar10. Some of the preparations used as staphylococcal penicillinase consisted of whole culture or cells3,11, acetone and ether extracts12, or cells disrupted by sonic vibration13 or in a Nossal tissue disintegration5. The possibility of using phagelysed Staphylococci as a source of penicillinase was suggested by Wallmark, G. (personal communication), while he was working in this laboratory. The following method was evolved.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kirby, W. M. M., J. Clin. Invest., 24, 170 (1945).
Spink, W. W., and Ferris, V., J. Clin. Invest., 26, 379 (1947).
Bondi, A., et al., Arch. Biochem. and Biophys., 53, 348 (1954).
Gilson, B. St. C., and Parker, R. F., J. Bact., 55, 801 (1948).
Saz, A. K., et al., J. Bact., 82, 298 (1961).
Luria, S. E., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. and Med., 61, 46 (1946).
Wallmark, G., Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand., 34, 182 (1954).
McKee, C. M., et al., J. Bact., 47, 187 (1944).
Eriksen, K. R., and Hansen, D., Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand., 35, 169 (1954).
Gots, J. S., Science, 102, 309 (1945).
Rolinson, G. N., et al., Lancet, ii, 564 (1960).
Harper, G. J., Lancet, ii, 569 (1943).
Geronimus, L. H., and Cohen, S., J. Bact., 76, 117 (1958).
Wallmark, G., and Finland, M., Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. and Med. 106, 78 (1961).
Grove, D. C., and Randall, W. A., Assay Methods of Antibiotics, A Laboratory Manual, 14 (Medical Encyclopedia, Inc., New York).
Wise, W. S., and Twigg, G. H., Analyst, 75, 106 (1950).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SABATH, L., FINLAND, M. Sterile Penicillinase from Phage-lysed Staphylococci. Nature 193, 272–273 (1962). https://doi.org/10.1038/193272a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/193272a0
This article is cited by
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.