Abstract
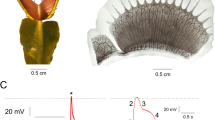
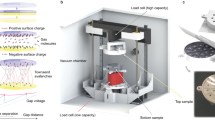
THE so-called geoelectric potential, which develops between the upper and lower side of a plant when it is placed in a horizontal position, has been investigated by many workers1–5 using different types of fluid electrodes which were applied directly to both sides of the plant. The original explanation of the cause of this potential given by Brauner6 has lately proved to be unsatisfactory7 and a new theory was proposed8. To test this theory it was necessary to carry out electric measurements on plants during much longer periods of time than has been done earlier. This was possible by using electrodes some-what similar to those devised by Clark5. The results obtained by this method were difficult to reproduce and differed generally from those reported by earlier workers. During extensive measurements on Avena coleoptiles, Pisum, Helianthus and Zea mays, it was found that the results are often strongly influenced by the direct-contact electrodes. Therefore, it was thought necessary to measure these potentials without touching the plants at all, and to this end an entirely new measuring technique was developed.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bose, J. C., “Comparative Electrophysiology”, 434 (London, 1907).
Brauner, L., Jahrb. f. wiss. Botanik, 66, 381 (1927).
Schrank, A. R., Plant Physiol., 20, 133 (1945); “Bioelectric Field and Growth”, 75, edit. by Lund, E. I. (1947).
Amlong, H. U., Planta, 21, 211 (1933).
Clark, W. G., Plant Physiol., 12, 409 (1937).
Brauner, L., Rev. Fac. Sci. Univ. Istanbul, 10, 1 (1945).
Brauner, L., Planta, 53, 449 (1959).
Hertz, C. H., and Grahm, L., Naturwiss., 45, 624 (1958).
Palensky, H., Swank, R. K., and Grenchik, R., Rev. Sci. Instr., 18, 298 (1947).
Hertz, C. H., and Siesjö, B., Acta physiol. Scand., 47, 115 (1959).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HERTZ, C. Electrostatic Measurement of the Geoelectric Effect in Coleoptiles. Nature 187, 320–321 (1960). https://doi.org/10.1038/187320a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/187320a0
This article is cited by
-
Origin of the Geoelectric Effect in Plants
Nature (1965)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.