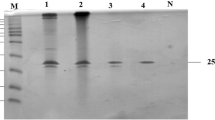
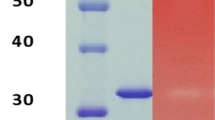
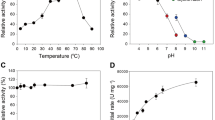
Abstract
XYLAN is hydrolysed in animals, plants, and by a large number of micro-organisms. Sørensen1 recently gave evidence that certain bacteria act on xylan to produce xylose-containing oligosaccharides and D-xylose. Whistler et al.2 reported that an enzyme preparation from the medium of Aspergillus foedidus hydrolysed corn-cob xylan primarily to xylobiose with no production of D-xylose. An extract of the mould mycelium was separated into two fractions : one which hydrolysed xylan and the oligosaccharides to D-xylose without producing significant amounts of oligosaccharides, and one which hydrolysed xylan to a mixture of D-xylose and oligosaccharides.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sørensen, H., Phys. Plantarum, 5, 183 (1952).
Whistler, R. L., and Masak, E., J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 77, 1241 (1955).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
INAOKA, M., SODA, H. Crystalline Xylanase. Nature 178, 202–203 (1956). https://doi.org/10.1038/178202a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/178202a0
This article is cited by
-
Xylan structure, microbial xylanases, and their mode of action
World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology (1992)
-
Purification and properties of endo-1,4-?-xylanase from Trichosporon cutaneum
European Journal of Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (1982)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.