Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting and improving complex beer flavor through machine learning
Predicting and improving complex beer flavor through machine learning
Perception and appreciation of food flavour depends on many factors, posing a challenge for effective prediction. Here, the authors combine extensive chemical and sensory analyses of 250 commercial Belgian beers to train machine learning models that enable flavour and consumer appreciation prediction.
- Michiel Schreurs
- , Supinya Piampongsant
- & Kevin J. Verstrepen
-
Article
| Open Access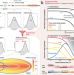 Fire suppression makes wildfires more severe and accentuates impacts of climate change and fuel accumulation
Fire suppression makes wildfires more severe and accentuates impacts of climate change and fuel accumulation
Fire suppression removes less-extreme wildfires, concentrating fires under extreme conditions. The authors use model simulations to show how this “suppression bias” intensifies fire behavior and effects, beyond fuel accumulation and climate change impacts.
- Mark R. Kreider
- , Philip E. Higuera
- & Andrew J. Larson
-
Article
| Open Access Face and context integration in emotion inference is limited and variable across categories and individuals
Face and context integration in emotion inference is limited and variable across categories and individuals
People infer emotions using faces and situations, yet little is known about how these are integrated. Here, the authors show that situations are often sufficient to infer emotions, with variability in integration across categories and individuals.
- Srishti Goel
- , Julian Jara-Ettinger
- & Maria Gendron
-
Article
| Open Access Projecting the long-term effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on U.S. population structure
Projecting the long-term effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on U.S. population structure
The COVID-19 pandemic affected mortality, fertility, and migration. Using the cohort component projection method, the authors find that if the pandemic had not occurred, the expected population of the U.S. would have been 2.1 million more people in 2025 and 1.7 million more people in 2060.
- Andrea M. Tilstra
- , Antonino Polizzi
- & Evelina T. Akimova
-
Article
| Open Access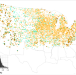 Imprint of urbanization on snow precipitation over the continental USA
Imprint of urbanization on snow precipitation over the continental USA
This study shows that urban areas in the continental US are associated with decreased snowfall likelihood and frequency, in large part due to surface albedo contrasts with neighboring areas. They also see a faster decline in snow precipitation frequency with time.
- Kaustubh Anil Salvi
- & Mukesh Kumar
-
Article
| Open Access Effect of mobile food environments on fast food visits
Effect of mobile food environments on fast food visits
Using large-scale mobility data, the authors examine how the quality of food in mobile environments away from home affects food choice.
- Bernardo García Bulle Bueno
- , Abigail L. Horn
- & Esteban Moro
-
Article
| Open Access The atlas of unburnable oil for supply-side climate policies
The atlas of unburnable oil for supply-side climate policies
The global atlas of unburnable oil shows that the most socio-environmentally sensitive areas, such as protected areas or biodiversity hotspots, need to be kept entirely off-limits to oil extraction in order to keep global warming under 1.5 °C.
- Lorenzo Pellegrini
- , Murat Arsel
- & Martí Orta-Martínez
-
Article
| Open Access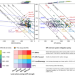 Trade-offs in land-based carbon removal measures under 1.5 °C and 2 °C futures
Trade-offs in land-based carbon removal measures under 1.5 °C and 2 °C futures
This study demonstrates how land-based carbon removals and the market-mediated responses are sensitive to mitigation policy strength and scope, illustrating that, despite trade-offs, both forestation and BECCS are integral to cost-effective 2 °C pathways.
- Xin Zhao
- , Bryan K. Mignone
- & Haewon C. McJeon
-
Article
| Open Access Intranational synergies and trade-offs reveal common and differentiated priorities of sustainable development goals in China
Intranational synergies and trade-offs reveal common and differentiated priorities of sustainable development goals in China
The paper reveals areas of common and differentiated SDG priority at the national and subnational levels in China considering synergy and trade-off. The findings suggest that provincial governments should formulate more targeted policy aligning with national priority to achieve SDGs.
- Qiang Xing
- , Chaoyang Wu
- & Zhenci Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Cost-effectiveness uncertainty may bias the decision of coal power transitions in China
Cost-effectiveness uncertainty may bias the decision of coal power transitions in China
China’s use of coal is complex to establish a clean and low-carbon transition for the country. With an uncertainty assessment framework, this study displays the risks of missing opportunities in obtaining cumulative positive net benefits and identifying an optimal transition strategy.
- Xizhe Yan
- , Dan Tong
- & Yu Lei
-
Article
| Open Access Policy and market forces delay real estate price declines on the US coast
Policy and market forces delay real estate price declines on the US coast
Subsidies for coastal management and tax advantages for high-income property owners dampen the negative effects of climate risks on coastal property values. Without subsidies or tax advantages market prices better reflect climate risks, but coastal gentrification could accelerate.
- Dylan E. McNamara
- , Martin D. Smith
- & Craig E. Landry
-
Article
| Open Access Strategies for robust renovation of residential buildings in Switzerland
Strategies for robust renovation of residential buildings in Switzerland
Building renovation is an urgent requirement to reduce the environmental impact associated with the building stock. In this paper, authors identify strategies for robust renovation considering uncertainties on the future and provide recommendations for the residential buildings in Switzerland.
- Alina Galimshina
- , Maliki Moustapha
- & Guillaume Habert
-
Article
| Open Access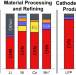 Electric vehicle battery chemistry affects supply chain disruption vulnerabilities
Electric vehicle battery chemistry affects supply chain disruption vulnerabilities
Electric vehicle battery supply chains are currently vulnerable to supply disruptions in China, but research shows that the cumulative effect of multiple supply chain steps creates additional vulnerabilities across multiple critical battery minerals.
- Anthony L. Cheng
- , Erica R. H. Fuchs
- & Jeremy J. Michalek
-
Article
| Open Access Light-responsive and ultrapermeable two-dimensional metal-organic framework membrane for efficient ionic energy harvesting
Light-responsive and ultrapermeable two-dimensional metal-organic framework membrane for efficient ionic energy harvesting
With porous structure and photothermal conversion performance, Cu-porphyrin framework membranes exhibit high efficiency in the extraction of electrical energy from salt solutions, opening avenues for renewable energy.
- Jin Wang
- , Zeyuan Song
- & Lei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Public perceptions and support of climate intervention technologies across the Global North and Global South
Public perceptions and support of climate intervention technologies across the Global North and Global South
This article establishes a global baseline of public perceptions of climate-intervention technologies. Publics across the global South are more favorable and supportive but concerned about impacts on mitigation and unequal burdens of risks on poor countries.
- Chad M. Baum
- , Livia Fritz
- & Benjamin K. Sovacool
-
Article
| Open Access Exploring the variances of climate change opinions in Germany at a fine-grained local scale
Exploring the variances of climate change opinions in Germany at a fine-grained local scale
Mewes and colleagues show substantial and systematic differences in public climate change opinions across Germany that manifest between urban vs. rural and prospering vs. declining areas. Besides these geographic features, more complex historical and cultural differences between places play an important role.
- Lars Mewes
- , Leonie Tuitjer
- & Peter Dirksmeier
-
Article
| Open Access Inequalities in healthcare use during the COVID-19 pandemic
Inequalities in healthcare use during the COVID-19 pandemic
An indirect impact of the COVID-19 pandemic was a decline in healthcare utilisation for other conditions. Here, the authors quantify this decline in the Netherlands and show that impacts were greater for individuals with lower household income, females, older people, and those with a migrant background.
- Arun Frey
- , Andrea M. Tilstra
- & Mark D. Verhagen
-
Article
| Open Access A framework for evaluating clinical artificial intelligence systems without ground-truth annotations
A framework for evaluating clinical artificial intelligence systems without ground-truth annotations
Estimating the performance of clinical AI systems on data in the wild is complicated by distribution shift and the absence of ground-truth annotations. Here, we introduce SUDO, a framework for more reliably evaluating AI systems on data in the wild.
- Dani Kiyasseh
- , Aaron Cohen
- & Nicholas Altieri
-
Article
| Open Access People quasi-randomly assigned to farm rice are more collectivistic than people assigned to farm wheat
People quasi-randomly assigned to farm rice are more collectivistic than people assigned to farm wheat
According to the rice theory, the demands of rice farming might make cultures more collectivistic. Here the authors provide evidence in support of this theory by showing that Chinese farmers who were quasi-randomly assigned to farm rice score higher on measures related to collectivism than those assigned to farm wheat.
- Thomas Talhelm
- & Xiawei Dong
-
Comment
| Open AccessThe bioethics of skeletal anatomy collections from India
Millions of skeletal remains from South Asia were exported in red markets (the underground economy of human tissues/organs) to educational institutions globally for over a century. It is time to recognize the personhood of the people who were systematically made into anatomical objects and acknowledge the scientific racism in creating and continuing to use them.
- Sabrina C. Agarwal
-
Article
| Open Access Concordance of randomised controlled trials for artificial intelligence interventions with the CONSORT-AI reporting guidelines
Concordance of randomised controlled trials for artificial intelligence interventions with the CONSORT-AI reporting guidelines
The CONSORT-AI extension was developed to provide specific guidance for randomised controlled trials involving Artificial Intelligence (AI) interventions. Here, the authors show that since publication of CONSORT-AI, several AI-specific considerations remain systematically underreported.
- Alexander P. L. Martindale
- , Benjamin Ng
- & Xiaoxuan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Extracting accurate materials data from research papers with conversational language models and prompt engineering
Extracting accurate materials data from research papers with conversational language models and prompt engineering
Efficient data extraction from research papers accelerates science and engineering. Here, the authors develop an automated approach which uses conversational large language models to achieve high precision and recall in extracting materials data.
- Maciej P. Polak
- & Dane Morgan
-
Article
| Open Access Open-source microscope add-on for structured illumination microscopy
Open-source microscope add-on for structured illumination microscopy
Researchers developed an open-hardware structured illumination microscopy add-on. This affordable upgrade provides super-resolution capabilities for normal optical microscopes. Detailed instructions enable easy reproduction to help democratize advanced microscopy.
- Mélanie T. M. Hannebelle
- , Esther Raeth
- & Georg E. Fantner
-
Article
| Open Access An agricultural digital twin for mandarins demonstrates the potential for individualized agriculture
An agricultural digital twin for mandarins demonstrates the potential for individualized agriculture
A digital twin represents a real world object using available data. Here, the authors develop a digital twin for mandaring orchards in Jeju island showing the value of individualized agriculture to predict fruit quality at tree level.
- Steven Kim
- & Seong Heo
-
Article
| Open Access Cases of trisomy 21 and trisomy 18 among historic and prehistoric individuals discovered from ancient DNA
Cases of trisomy 21 and trisomy 18 among historic and prehistoric individuals discovered from ancient DNA
Information on the occurrence of aneuploidies in prehistory human populations are rare. Here, from a large screen of ancient human genomes and osteological examination, the authors find genetic evidence for six cases of trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) and one case of trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome) in historic and prehistoric infants.
- Adam Benjamin Rohrlach
- , Maïté Rivollat
- & Kay Prüfer
-
Article
| Open Access Psychological well-being in Europe after the outbreak of war in Ukraine
Psychological well-being in Europe after the outbreak of war in Ukraine
The Russian invasion of Ukraine has affected the global economy, environment, and political order. Here, the authors show that it also coincided with a temporary decline in psychological well-being across Europe.
- Julian Scharbert
- , Sarah Humberg
- & Mitja D. Back
-
Article
| Open Access Leisure engagement in older age is related to objective and subjective experiences of aging
Leisure engagement in older age is related to objective and subjective experiences of aging
The benefits of different leisure activities for different aspects of aging remain unclear. Here, authors show that performing physical or creative activities is associated with important aging metrics and could help to prevent age-related decline.
- Jessica K. Bone
- , Feifei Bu
- & Daisy Fancourt
-
Article
| Open Access Changes in social norms during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic across 43 countries
Changes in social norms during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic across 43 countries
Tightness-looseness theory predicts that social norms strengthen following threat. Here the authors test this and find that, after the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic, hand washing norms increased, but no evidence was observed for a robust change in most other norms.
- Giulia Andrighetto
- , Aron Szekely
- & Kimmo Eriksson
-
Article
| Open Access Effect of trade on global aquatic food consumption patterns
Effect of trade on global aquatic food consumption patterns
Xu and colleagues find that the average trophic level of aquatic food items in the human diet is declining (from 3.42 to 3.18) because of the considerable increase in low-trophic level aquaculture species output relative to that of capture fisheries since 1976. Additionally they find that trade has contributed to increasing the availability and trophic level of aquatic foods in >60% of the world’s countries.
- Kangshun Zhao
- , Steven D. Gaines
- & Jun Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Structured information extraction from scientific text with large language models
Structured information extraction from scientific text with large language models
Extracting scientific data from published research is a complex task required specialised tools. Here the authors present a scheme based on large language models to automatise the retrieval of information from text in a flexible and accessible manner.
- John Dagdelen
- , Alexander Dunn
- & Anubhav Jain
-
Article
| Open Access Global and regional ocean mass budget closure since 2003
Global and regional ocean mass budget closure since 2003
This study shows that ice loss and human water use models explain global and regional satellite-observed ocean mass changes since 2003 and thereby pinpoint the main cause of sea level rise, with a negligible role coming from natural variability.
- Carsten Bjerre Ludwigsen
- , Ole Baltazar Andersen
- & Matt A. King
-
Article
| Open Access Sequential stacking link prediction algorithms for temporal networks
Sequential stacking link prediction algorithms for temporal networks
Link prediction in temporal networks is relevant for many real-world systems, however, current approaches are usually characterized by high computational costs. The authors propose a temporal link prediction framework based on the sequential stacking of static network features, for improved computational speed, appropriate for temporal networks with completely unobserved or partially observed target layers.
- Xie He
- , Amir Ghasemian
- & Peter J. Mucha
-
Article
| Open Access Income determines the impact of cash transfers on HIV/AIDS: cohort study of 22.7 million Brazilians
Income determines the impact of cash transfers on HIV/AIDS: cohort study of 22.7 million Brazilians
Brazil has operated a conditional cash transfer program to support families living in precarious conditions since 2004. Here, the authors use linked administrative and health data to investigate the impacts of the program on HIV/AIDS-related outcomes, demonstrating strong positive associations.
- Andréa F. Silva
- , Inês Dourado
- & Davide Rasella
-
Article
| Open Access Delayed increase in stone tool cutting-edge productivity at the Middle-Upper Paleolithic transition in southern Jordan
Delayed increase in stone tool cutting-edge productivity at the Middle-Upper Paleolithic transition in southern Jordan
Lithic cutting-edge productivity is a way of quantifying prehistoric human technological evolution. Here, the authors examine the Middle-to-Upper Paleolithic transition across eight assemblages in the eastern Mediterranean, finding the transition to be later than expected and associated with bladelet technology development.
- Seiji Kadowaki
- , Joe Yuichiro Wakano
- & Sate Massadeh
-
Article
| Open Access Overlay databank unlocks data-driven analyses of biomolecules for all
Overlay databank unlocks data-driven analyses of biomolecules for all
In this work, the authors report NMR lipids Databank to promote decentralised sharing of biomolecular molecular dynamics (MD) simulation data with an overlay design. Programmatic access enables analyses of rare phenomena and advances the training of machine learning models.
- Anne M. Kiirikki
- , Hanne S. Antila
- & O. H. Samuli Ollila
-
Article
| Open Access Implicit racial biases are lower in more populous more diverse and less segregated US cities
Implicit racial biases are lower in more populous more diverse and less segregated US cities
Implicit biases are influenced by social contexts which, in cities, are shaped by the constraints of urban infrastructure networks. Here the authors show that more populous, more diverse, and less segregated cities are less biased and that this is predicted by a complex systems model.
- Andrew J. Stier
- , Sina Sajjadi
- & Marc G. Berman
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting the risk and speed of drug resistance emerging in soil-transmitted helminths during preventive chemotherapy
Predicting the risk and speed of drug resistance emerging in soil-transmitted helminths during preventive chemotherapy
Resistance to chemotherapy for soil-transmitted helminth infection has been detected in veterinary settings but not yet in human infections. Here, the authors investigate the risk of resistance in humans and how it may change as a result of scaling-up preventative deworming programs.
- Luc E. Coffeng
- , Wilma A. Stolk
- & Sake J. de Vlas
-
Article
| Open Access A triple increase in global river basins with water scarcity due to future pollution
A triple increase in global river basins with water scarcity due to future pollution
Here the authors find one third of global sub-basins will face severe clean water scarcity in 2050. Nitrogen pollution aggravates water scarcity in >2,000 sub-basins thus 3 billion more people will be posed with severe water scarcity in 2050.
- Mengru Wang
- , Benjamin Leon Bodirsky
- & Maryna Strokal
-
Article
| Open Access Stringent sustainability regulations for global supply chains are supported across middle-income democracies
Stringent sustainability regulations for global supply chains are supported across middle-income democracies
Citizens in middle-income countries (Brazil, India, Indonesia) support aligning local sustainability rules with new laws originating in OECD nations. People favor stricter regulations, driven by optimistic expectations of the benefits outweighing potential costs.
- E. Keith Smith
- , Dennis Kolcava
- & Thomas Bernauer
-
Article
| Open Access Sustainability benefits of transitioning from current diets to plant-based alternatives or whole-food diets in Sweden
Sustainability benefits of transitioning from current diets to plant-based alternatives or whole-food diets in Sweden
The authors found that replacing animal source foods with plant-based alternatives would lead to substantial reductions in environmental impacts, while meeting most nutrition recommendations and being cost-competitive with the current average Swedish diet.
- Anne Charlotte Bunge
- , Rachel Mazac
- & Line Gordon
-
Comment
| Open Access Implementing community-engaged pharmacogenomics in Indigenous communities
Implementing community-engaged pharmacogenomics in Indigenous communities
Innovative pharmacogenomic approaches (genetic variation related to medication response) are needed to reduce disease and disparities in Indigenous communities. We support community-based pharmacogenomics research, inclusive of Indigenous values and priorities, to improve the health and well-being of Indigenous peoples.
- Katrina G. Claw
- , Casey R. Dorr
- & Erica L. Woodahl
-
Comment
| Open AccessAfrican leadership is critical in responding to public health threats
The African continent demonstrated decisive leadership throughout its response to the COVID-19 pandemic, leveraging lessons learned from previous outbreaks and acting quickly to limit the impact of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. We propose a framework to build on these successes that calls for greater collaboration between African leaders, and greater inclusion of African voices in the global health ecosystem.
- Nicaise Ndembi
- , Aggrey Aluso
- & Jean Kaseya
-
Article
| Open Access Intensifying rice production to reduce imports and land conversion in Africa
Intensifying rice production to reduce imports and land conversion in Africa
Here the authors demonstrate that cropland expansion following the historical trend together with closing the current exploitable yield gap by half or more across Africa reduces the continent’s reliance on land conversions and imports by 2050.
- Shen Yuan
- , Kazuki Saito
- & Patricio Grassini
-
Article
| Open Access Global surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in food animals using priority drugs maps
Global surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in food animals using priority drugs maps
Monitoring antimicrobial resistance in food animals is challenging due to limited surveillance systems. Here, the authors combine data from point prevalence surveys in lower- and middle-income settings to map resistance to seven antimicrobials and predict which are likely to exceed key resistance thresholds.
- Cheng Zhao
- , Yu Wang
- & Thomas P. Van Boeckel
-
Article
| Open Access Greenhouse gas emissions from US irrigation pumping and implications for climate-smart irrigation policy
Greenhouse gas emissions from US irrigation pumping and implications for climate-smart irrigation policy
This study demonstrates the energy use of US pump irrigation produced 12.6 million tonnes CO2e in 2018, with spatial variability modulated by water source and fuel choice. These county-level estimates can inform strategic irrigation expansion and emissions reduction efforts.
- Avery W. Driscoll
- , Richard T. Conant
- & Nathaniel D. Mueller
-
Article
| Open Access Acoustic and language-specific sources for phonemic abstraction from speech
Acoustic and language-specific sources for phonemic abstraction from speech
How speech sounds come to be understood as language remains unclear. Here, the authors find that brain responses to speech in part reflect abstraction of phonological units specific to the language being spoken, mediated through relationships between acoustic features.
- Anna Mai
- , Stephanie Riès
- & Timothy Q. Gentner
-
Comment
| Open Access A bumpy road ahead for genetic biocontainment
A bumpy road ahead for genetic biocontainment
While the research community continues to develop novel proposals for intrinsic biocontainment of genetically engineered organisms, translation to real-world deployment faces several challenges.
- Dalton R. George
- , Mark Danciu
- & Emma K. Frow
-
Article
| Open Access Modelling six sustainable development transformations in Australia and their accelerators, impediments, enablers, and interlinkages
Modelling six sustainable development transformations in Australia and their accelerators, impediments, enablers, and interlinkages
Global research has identified six critical transformations to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals by 2030. Here, Allen et al model all six transformations in a national context and discuss implications for accelerating progress on the goals.
- Cameron Allen
- , Annabel Biddulph
- & Shirin Malekpour
-
Article
| Open Access An artificial intelligence-based model for optimal conjunctive operation of surface and groundwater resources
An artificial intelligence-based model for optimal conjunctive operation of surface and groundwater resources
Towards optimizing the conjunctive operation of surface and groundwater resources in arid and semi-arid regions, here the authors propose a hybrid method involving moth-swarm and symbiotic organism search algorithms and artificial neural networks and demonstrate it for the HalīlRood basin.
- Saeid Akbarifard
- , Mohamad Reza Madadi
- & Mohammad Zounemat-Kermani

 An analysis of the accuracy of retrospective birth location recall using sibling data
An analysis of the accuracy of retrospective birth location recall using sibling data