Featured
-
-
Article |
 Ablation of TrkB signalling in CCK neurons results in hypercortisolism and obesity
Ablation of TrkB signalling in CCK neurons results in hypercortisolism and obesity
Glucocorticoid levels in the body are controlled by an intricate feedback system acting on the hypothalamus. Here the authors provide molecular insight into this process, identifying TrkB signalling in cholecystokinin-GABAergic neurons as a key component of hypothalamic glucocorticoid signalling.
- Mirjam Geibel
- , Sylvia Badurek
- & Liliana Minichiello
-
Article |
 3D multifunctional integumentary membranes for spatiotemporal cardiac measurements and stimulation across the entire epicardium
3D multifunctional integumentary membranes for spatiotemporal cardiac measurements and stimulation across the entire epicardium
Tools for cardiac physiological mapping are important for basic and clinical cardiac research. Here the authors use 3D printing to create a thin, elastic silicone sheath that fits tightly around the entire epicardium and contains sensors to measure a variety of physiological parameters of the beating heart ex vivo.
- Lizhi Xu
- , Sarah R. Gutbrod
- & John A. Rogers
-
Article
| Open Access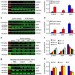 IRF8 suppresses pathological cardiac remodelling by inhibiting calcineurin signalling
IRF8 suppresses pathological cardiac remodelling by inhibiting calcineurin signalling
The transcription factor interferon regulatory factor 8 (IRF8) is known to regulate differentiation and function of immune cells. Here the authors show that IRF8 is upregulated in the hypertrophic heart in humans and mice, where it suppresses cardiac remodelling by inhibiting calcineurin signalling.
- Ding-Sheng Jiang
- , Xiang Wei
- & Hongliang Li
-
Article |
 Genome-wide RNAi ionomics screen reveals new genes and regulation of human trace element metabolism
Genome-wide RNAi ionomics screen reveals new genes and regulation of human trace element metabolism
The composition of trace elements in human cells (the ionome) is an important component of metabolism. Here, the authors carry out a high-throughput, genome-wide analysis of the human ionome and identify cellular regulators of important trace elements such as selenium, copper and iron.
- Mikalai Malinouski
- , Nesrin M. Hasan
- & Vadim N. Gladyshev
-
Article |
 Neonatal testosterone suppresses a neuroendocrine pulse generator required for reproduction
Neonatal testosterone suppresses a neuroendocrine pulse generator required for reproduction
The milk-ejection reflex in mammals requires the coordinated bursting of oxytocin neurons in the hypothalamus. Here, Israel et al.show that the rhythmic bursting behaviour displayed by these neurons is active in both male and female neonatal rats, but is inactivated in males after the first week of life.
- Jean-Marc Israel
- , Jean-Marie Cabelguen
- & Philippe Ciofi
-
Article
| Open Access Critical roles of nardilysin in the maintenance of body temperature homoeostasis
Critical roles of nardilysin in the maintenance of body temperature homoeostasis
The precise regulation of mammalian body temperature is important for survival. Here the authors show that the peptidase nardilysin represses the transcription factor PGC-1α, and identify nardilysin as a regulator of basal body temperature, cold-induced thermogenesis and body insulation.
- Yoshinori Hiraoka
- , Tatsuhiko Matsuoka
- & Eiichiro Nishi
-
Article |
 Global metabolic network reorganization by adaptive mutations allows fast growth of Escherichia coli on glycerol
Global metabolic network reorganization by adaptive mutations allows fast growth of Escherichia coli on glycerol
Organisms can adapt to environmental change but how this affects metabolism is unclear. Here, the authors provide a detailed analysis of the effects of individual adaptive mutations on the metabolic network in E. coli, and find evidence of metabolic reprogramming during laboratory evolution on glycerol.
- Kian-Kai Cheng
- , Baek-Seok Lee
- & Martin Robert
-
Article |
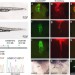 Kctd10 regulates heart morphogenesis by repressing the transcriptional activity of Tbx5a in zebrafish
Kctd10 regulates heart morphogenesis by repressing the transcriptional activity of Tbx5a in zebrafish
T-box transcription factors such as Tbx5 have essential roles during cardiac development. Here the authors show that a member of the potassium channel tetramerization domain-containing family, Kctd10 is required for zebrafish heart development and represses the transcriptional activity of Tbx5.
- Xiangjun Tong
- , Yao Zu
- & Bo Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access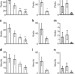 Hypothalamic inhibition of socio-sexual behaviour by increasing neuroestrogen synthesis
Hypothalamic inhibition of socio-sexual behaviour by increasing neuroestrogen synthesis
The conversion of testosterone into oestrogen in the brain is implicated in male aggressive behaviour. Ubuka et al.show that gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone inhibits male aggression by increasing oestrogen synthesis in the brain beyond its optimum concentration for the expression of aggressive behaviour.
- Takayoshi Ubuka
- , Shogo Haraguchi
- & Kazuyoshi Tsutsui
-
Article
| Open Access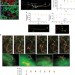 A paracrine network regulates the cross-talk between human lung stem cells and the stroma
A paracrine network regulates the cross-talk between human lung stem cells and the stroma
The human lung contains Lgr6-positive progenitor cells, which have the potential to generate multiple epithelial lineages in cell explant studies. Here, the authors present a role of p38a MAPK signalling in regulating the cross-talk between this lung progenitor cell population and the stromal and endothelial cells comprising their niche microenvironment.
- E. Josue Ruiz
- , Feride Oeztuerk-Winder
- & Juan-Jose Ventura
-
Article |
 Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species regulate the strength of inhibitory GABA-mediated synaptic transmission
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species regulate the strength of inhibitory GABA-mediated synaptic transmission
Cellular energy metabolism is essential for sustaining neuronal signalling in the brain. Acardi et al.show that mitochondrial reactive oxygen species, which are by-products of cellular metabolism, selectively strengthen inhibitory transmission by recruiting a subpopulation of GABAA receptors.
- Michael V. Accardi
- , Bryan A. Daniels
- & Derek Bowie
-
Article |
 Genome-scale metabolic modelling of hepatocytes reveals serine deficiency in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Genome-scale metabolic modelling of hepatocytes reveals serine deficiency in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Alterations in hepatocyte metabolism can lead to disorders such as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Here the authors create a comprehensive model of hepatocyte metabolism and use it to identify metabolic pathways altered in disease, revealing that serine levels are reduced in patients with NASH.
- Adil Mardinoglu
- , Rasmus Agren
- & Jens Nielsen
-
Article |
 Predicting network functions with nested patterns
Predicting network functions with nested patterns
Identifying functionally important features of complex biological networks is computationally challenging. Ganter et al.develop a probabilistic framework that uses recurrent metabolite patterns to predict the properties and existence of reactions within a genome-scale metabolic network.
- Mathias Ganter
- , Hans-Michael Kaltenbach
- & Jörg Stelling
-
Article |
 Gap junction signalling is a stress-regulated component of adrenal neuroendocrine stimulus-secretion coupling in vivo
Gap junction signalling is a stress-regulated component of adrenal neuroendocrine stimulus-secretion coupling in vivo
Findings from ex vivo studies suggest that gap junctional coupling contributes to hormone release in neuroendocrine/endocrine tissues. Here, the authors provide in vivo evidence that direct communication between adrenal chromaffin cells viagap junctions contributes to catecholamine secretion.
- Michel G. Desarménien
- , Carole Jourdan
- & Nathalie C. Guérineau
-
Article
| Open Access A failure in energy metabolism and antioxidant uptake precede symptoms of Huntington’s disease in mice
A failure in energy metabolism and antioxidant uptake precede symptoms of Huntington’s disease in mice
Defective ascorbic acid flux is a sign of metabolic failure associated with Huntington’s disease. Here, Acuña et al.show that reduction in ascorbic acid flux from astrocytes precedes the symptoms of Huntington’s disease in mice and impairs ascorbic acid uptake in neurons.
- Aníbal I. Acuña
- , Magdalena Esparza
- & Maite A. Castro
-
Article |
 Essential regulation of cell bioenergetics in Trypanosoma brucei by the mitochondrial calcium uniporter
Essential regulation of cell bioenergetics in Trypanosoma brucei by the mitochondrial calcium uniporter
The mitochondrial calcium uniporter supports oxidative phosphorylation in mammals; however, it is also present in blood-stage trypanosomes, which lack a functional respiratory chain. Huang et al. show that the mitochondrial calcium uniporter is essential for blood-stage survival and metabolism in Trypanosoma brucei.
- Guozhong Huang
- , Anibal E. Vercesi
- & Roberto Docampo
-
Article |
 Highly efficient methane biocatalysis revealed in a methanotrophic bacterium
Highly efficient methane biocatalysis revealed in a methanotrophic bacterium
Methane is a promising renewable carbon source for chemical synthesis, yet methane bio-gas is currently underutilised as a feedstock. Here the authors examine the metabolic processes of methanotrophic bacteria to assess their use for conversion of methane to value-added chemical products.
- M. G. Kalyuzhnaya
- , S. Yang
- & M. E. Lidstrom
-
Article
| Open Access A truncated Wnt7a retains full biological activity in skeletal muscle
A truncated Wnt7a retains full biological activity in skeletal muscle
Wnt7a regulates various aspects of skeletal muscle function. Here, the authors show that a truncated Wnt7a protein lacking the palmitoylation domain retains its biological activity in skeletal muscle, suggesting that simplified Wnt7a proteins may be viable as Wnt-based therapeutics.
- Julia von Maltzahn
- , Radoslav Zinoviev
- & Michael A. Rudnicki
-
Article |
 Orai1-dependent calcium entry promotes skeletal muscle growth and limits fatigue
Orai1-dependent calcium entry promotes skeletal muscle growth and limits fatigue
The calcium-selective Orai1 channel regulates cytosolic calcium levels in a variety of cells. Here the authors use transgenic mice with muscle-specific expression of dysfunctional Orai1 to show that Orai1-mediated store-operated calcium entry promotes growth and limits fatigue of adult skeletal muscle.
- Lan Wei-LaPierre
- , Ellie M. Carrell
- & Robert T. Dirksen
-
Article |
 A Nodal-independent and tissue-intrinsic mechanism controls heart-looping chirality
A Nodal-independent and tissue-intrinsic mechanism controls heart-looping chirality
Nodal signalling has been implicated in the asymmetric positioning of various organs. Here, Noël et al.show that the asymmetry of the embryonic zebrafish heart is also established in the absence of Nodal signalling, suggesting a Nodal-independent mechanism that relies on actomyosin activity.
- Emily S. Noël
- , Manon Verhoeven
- & Jeroen Bakkers
-
Article |
 Model-based identification of drug targets that revert disrupted metabolism and its application to ageing
Model-based identification of drug targets that revert disrupted metabolism and its application to ageing
Systems biology is considered a promising tool for the identification of new drug targets. Here Yizhak and colleagues present an algorithm to analyse gene expression data and identify potential drug targets that would shift cellular metabolism from a given disease state to that of a healthier state.
- Keren Yizhak
- , Orshay Gabay
- & Eytan Ruppin
-
Article
| Open Access Sox17 is indispensable for acquisition and maintenance of arterial identity
Sox17 is indispensable for acquisition and maintenance of arterial identity
The transcription factor Sox17 is required for the development of the vasculature in vertebrates. Here Corada et al. show that Sox17 acts downstream of Wnt signalling and upstream of Notch signalling in the regulation of artery and vein differentiation in mice.
- Monica Corada
- , Fabrizio Orsenigo
- & Elisabetta Dejana
-
Article |
 Switch of glycolysis to gluconeogenesis by dexamethasone for treatment of hepatocarcinoma
Switch of glycolysis to gluconeogenesis by dexamethasone for treatment of hepatocarcinoma
Hepatocytes use gluconeogenesis to produce glucose, but whether this process is altered in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is unclear. Here, the loss of gluconeogenesis in HCC and altered glucocorticoid regulation is demonstrated and glucocorticoid treatment is shown to reduce tumour burden.
- Ruihua Ma
- , Wanguang Zhang
- & Bo Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Connexin40 regulates platelet function
Connexin40 regulates platelet function
Hemichannels and gap junctions containing the connexin Cx37 are required for platelet functions such as aggregation and granule secretion through poorly defined mechanisms. Vaiyapuri et al. show that Cx40 is also required and can act independently of Cx37 in mouse platelets.
- Sakthivel Vaiyapuri
- , Leonardo A. Moraes
- & Jonathan M. Gibbins
-
Article |
 Dependence of fertility on kisspeptin–Gpr54 signaling at the GnRH neuron
Dependence of fertility on kisspeptin–Gpr54 signaling at the GnRH neuron
The kisspeptin receptor GPR54 is implicated in the maintenance of mammalian fertility. Kirilov et al.study GPR54 mutant mice and identify a subset of neurons in the brain expressing gonadotropin-releasing hormone as the critical site for kisspeptin action.
- Milen Kirilov
- , Jenny Clarkson
- & Allan E. Herbison
-
Article |
 Human copper chaperone for superoxide dismutase 1 mediates its own oxidation-dependent import into mitochondria
Human copper chaperone for superoxide dismutase 1 mediates its own oxidation-dependent import into mitochondria
The accumulation of superoxide in mitochondria is counteracted by superoxide dismutase 1 and its activating chaperone CCS1. Suzuki et al.show that in human cells, mature CCS1 itself mediates CCS1 import and helps to oxidize CCS1 and SOD1 in the mitochondrial intermembrane space.
- Yutaka Suzuki
- , Muna Ali
- & Jan Riemer
-
Article |
 The carotid body as a putative therapeutic target for the treatment of neurogenic hypertension
The carotid body as a putative therapeutic target for the treatment of neurogenic hypertension
Enhanced sympathetic drive from chemoreceptors in the carotid body contributes to hypertension. Here McBryde et al. show that carotid sinus denervation is an effective antihypertensive treatment in rats with neurogenic hypertension even if performed in addition to renal denervation.
- Fiona D. McBryde
- , Ana P. Abdala
- & Julian F. R. Paton
-
Article
| Open Access Genome analysis reveals insights into physiology and longevity of the Brandt’s bat Myotis brandtii
Genome analysis reveals insights into physiology and longevity of the Brandt’s bat Myotis brandtii
Bats account for 20 per cent of all mammals, these are the only mammals with powered flight, and are among the few animals that echolocate. Here, Seim et al. sequence the genome of the long-lived (>40 years) Brandt’s bat, Myotis brandtiiand provide clues to its evolution, longevity and other traits.
- Inge Seim
- , Xiaodong Fang
- & Vadim N. Gladyshev
-
Article
| Open Access Glycogen shortage during fasting triggers liver–brain–adipose neurocircuitry to facilitate fat utilization
Glycogen shortage during fasting triggers liver–brain–adipose neurocircuitry to facilitate fat utilization
During fasting, animals shift their energy source from carbohydrates to triglycerides. Here, Izumida et al. report that glycogen shortage in the liver activates a liver–brain–adipose-tissue neurocircuit that signals the switch in fuel source from liver glycogen to triglycerides in fat cells.
- Yoshihiko Izumida
- , Naoya Yahagi
- & Hitoshi Shimano
-
Article
| Open Access Orbitofrontal and striatal circuits dynamically encode the shift between goal-directed and habitual actions
Orbitofrontal and striatal circuits dynamically encode the shift between goal-directed and habitual actions
Interactions between corticostriatal circuits are implicated in the shifts between habit- and goal-directed actions. Gremel and Costa show that the orbital frontal cortex and the dorsal medial striatum are necessary for goal-directed actions, whereas the dorsal lateral striatum is necessary for habitual actions.
- Christina M. Gremel
- & Rui M. Costa
-
Article
| Open Access Prelamin A causes progeria through cell-extrinsic mechanisms and prevents cancer invasion
Prelamin A causes progeria through cell-extrinsic mechanisms and prevents cancer invasion
Mutations in the metalloproteinase Zmpste24 preclude prelamin A processing and cause premature ageing. Here, de la Rosaet al.create mosaic Zmpste24 mice, revealing that cell-extrinsic effects are essential for accelerated ageing caused by prelamin A accumulation and that prelamin A reduces invasiveness of cancer cells.
- Jorge de la Rosa
- , José M.P. Freije
- & Carlos López-Otín
-
Article |
 Reductive glutamine metabolism is a function of the α-ketoglutarate to citrate ratio in cells
Reductive glutamine metabolism is a function of the α-ketoglutarate to citrate ratio in cells
Reductive glutamine metabolism supports cell proliferation under stress conditions such as hypoxia. Here Fendtet al.report that the ratio between the two metabolites α-ketoglutarate and citrate determines whether glutamine is metabolized oxidatively or reductively.
- Sarah-Maria Fendt
- , Eric L. Bell
- & Gregory Stephanopoulos
-
Article
| Open Access Brown fat in a protoendothermic mammal fuels eutherian evolution
Brown fat in a protoendothermic mammal fuels eutherian evolution
Endothermy facilitated mammalian species radiation, but the events leading to sustained thermogenesis are not clear. Here, the authors report functional brown adipose tissue in a protoendothermic mammal, linking nonshivering thermogenesis directly to the roots of eutherian endothermic evolution.
- Rebecca Oelkrug
- , Nadja Goetze
- & Carola W. Meyer
-
Article |
 A stabilizing factor for mitochondrial respiratory supercomplex assembly regulates energy metabolism in muscle
A stabilizing factor for mitochondrial respiratory supercomplex assembly regulates energy metabolism in muscle
Interactions between mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes control electron transfer and oxidative phosphorylation. Here, the authors find that COX7RP regulates supercomplex assembly, and show that decreasing or increasing COX7RP expression, respectively, reduces and enhances muscular performance in mice.
- Kazuhiro Ikeda
- , Sachiko Shiba
- & Satoshi Inoue
-
Article |
 Large fibre size in skeletal muscle is metabolically advantageous
Large fibre size in skeletal muscle is metabolically advantageous
Energy demand in muscle is largely due to maintaining the membrane potential of muscle fibres. Jimenez et al.study the metabolic cost of maintaining the membrane potential of muscle fibres across different species of crustaceans and fishes, and find that larger fibres are metabolically cheaper to maintain.
- Ana Gabriela Jimenez
- , Richard M. Dillaman
- & Stephen T. Kinsey
-
Article |
 Fibroblast growth factor 21 protects against cardiac hypertrophy in mice
Fibroblast growth factor 21 protects against cardiac hypertrophy in mice
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) regulates energy metabolism in peripheral tissues. Here Planavila and colleagues show that FGF21 also acts directly on cardiomyocytes, thereby protecting mice against cardiac hypertrophy.
- A. Planavila
- , I. Redondo
- & F. Villarroya
-
Article |
 A common functional promoter variant links CNR1 gene expression to HDL cholesterol level
A common functional promoter variant links CNR1 gene expression to HDL cholesterol level
Haplotypes in CNR1, the gene encoding the cannabinoid receptor CB1, are known to influence HDL cholesterol levels. Here Feng and colleagues identify rs806371 as a novel regulatory element reducing CNR1 gene expression and as the causal allele driving the association between CNR1 and HDL cholesterol levels in humans.
- Q. Feng
- , K.C. Vickers
- & R.A. Wilke
-
Article
| Open Access Haemodynamically dependent valvulogenesis of zebrafish heart is mediated by flow-dependent expression of miR-21
Haemodynamically dependent valvulogenesis of zebrafish heart is mediated by flow-dependent expression of miR-21
microRNAs rapidly regulate gene expression and are implicated in cardiogenesis and angiogenesis. Banjo and colleagues show that the microRNA mir-21 is activated by the physical forces generated by blood flow, and that this regulates the development of heart valves in zebrafish.
- Toshihiro Banjo
- , Janin Grajcarek
- & Toshihiko Ogura
-
Article
| Open Access The orphan receptor Gpr83 regulates systemic energy metabolism via ghrelin-dependent and ghrelin-independent mechanisms
The orphan receptor Gpr83 regulates systemic energy metabolism via ghrelin-dependent and ghrelin-independent mechanisms
The murine G protein-coupled receptor 83 (Gpr83) is expressed widely in the brain, but its physiological role is largely unknown. Here Müller et al.show that Gpr83 regulates systemic energy metabolism in part by modulating ghrelin signalling in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus.
- Timo D. Müller
- , Anne Müller
- & Matthias H. Tschöp
-
Article |
 Constitutively active Foxo3 in oocytes preserves ovarian reserve in mice
Constitutively active Foxo3 in oocytes preserves ovarian reserve in mice
The number of primordial follicles, which constitute the ovarian reserve, decreases with age. By overexpressing a constitutively active version of the transcription factor FOXO3, the authors increase the ovarian reserve and fertility in aging female mice.
- Emanuele Pelosi
- , Shakib Omari
- & Chris Ottolenghi
-
Article
| Open Access The gut microbiota suppresses insulin-mediated fat accumulation via the short-chain fatty acid receptor GPR43
The gut microbiota suppresses insulin-mediated fat accumulation via the short-chain fatty acid receptor GPR43
The gut microbiota produces metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which can influence the development of obesity. Here Kimura et al.show that SCFAs act via the receptor GPR43, which acts as a sensor for excessive dietary energy and controls body energy utilization as well as metabolic homoeostasis.
- Ikuo Kimura
- , Kentaro Ozawa
- & Gozoh Tsujimoto
-
Article
| Open Access Select interneuron clusters determine female sexual receptivity in Drosophila
Select interneuron clusters determine female sexual receptivity in Drosophila
The protein spinster is implicated in Drosophilacourtship behaviour. Sakurai and colleagues identify two clusters of spinster-expressing interneurons, and show that these cells are required for female receptivity to male advances.
- Akira Sakurai
- , Masayuki Koganezawa
- & Daisuke Yamamoto
-
Article |
 Control of lung vascular permeability and endotoxin-induced pulmonary oedema by changes in extracellular matrix mechanics
Control of lung vascular permeability and endotoxin-induced pulmonary oedema by changes in extracellular matrix mechanics
Vascular permeability is increased by inflammation and in disorders such as acute respiratory distress syndrome. Mammoto et al. show that lung vascular permeability is controlled by the stiffness of the extracellular matrix and identify lysyl oxidase as a regulator of vascular leakage in pulmonary oedema in mice.
- Akiko Mammoto
- , Tadanori Mammoto
- & Donald E. Ingber
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular mechanics of mineralized collagen fibrils in bone
Molecular mechanics of mineralized collagen fibrils in bone
Bone is a natural composite of collagen and hydroxyapatite but, surprising, little is known about its characteristics at the molecular scale. Nair et al. conduct molecular-scale simulations of mineralized collagen networks to better understand how bone achieves superior mechanical properties to its constituents.
- Arun K. Nair
- , Alfonso Gautieri
- & Markus J. Buehler
-
Article
| Open Access VE-PTP regulates VEGFR2 activity in stalk cells to establish endothelial cell polarity and lumen formation
VE-PTP regulates VEGFR2 activity in stalk cells to establish endothelial cell polarity and lumen formation
Vascular endothelial growth factor is implicated in blood vessel development. In zebrafish, Hayashi et al. find that blood vessel development is dependent on the suppression of vascular endothelial growth factor by the phosphatase VE-PTP, which is recruited by activation of the angiopoietin receptor Tie2.
- Makoto Hayashi
- , Arindam Majumdar
- & Lena Claesson-Welsh
-
Article |
 α-SNAP inhibits AMPK signaling to reduce mitochondrial biogenesis and dephosphorylates Thr172 in AMPKα in vitro
α-SNAP inhibits AMPK signaling to reduce mitochondrial biogenesis and dephosphorylates Thr172 in AMPKα in vitro
The energy-sensing kinase AMPK is regulated by phosphorylation, however, the identity of AMPK phosphatases remains uncertain. Here the authors show that α-SNAP, a protein previously known for its role in membrane fusion, can dephosphorylate AMPK despite lacking a recognizable phosphatase domain.
- Lifu Wang
- & David L. Brautigan
-
Article |
 Human hypocretin and melanin-concentrating hormone levels are linked to emotion and social interaction
Human hypocretin and melanin-concentrating hormone levels are linked to emotion and social interaction
The emotional state of humans depends on the temporal concentration of neurochemicals. Blouin et al. measure temporal changes in two neuropeptides, hypocretin and melanin-concentrating hormone, and find that hypocretin but not melanin-concentrating hormone is linked to positive emotions and social interaction.
- Ashley M. Blouin
- , Itzhak Fried
- & Jerome M. Siegel
-
Article |
 Haemogenic endocardium contributes to transient definitive haematopoiesis
Haemogenic endocardium contributes to transient definitive haematopoiesis
Cardiac and endocardial/endothelial cells arise from progenitor cells expressing multiple haematopoietic transcription factors. Nakano and colleagues find that Nkx2–5-positive endocardial cells serve as a de novosource for definitive haematopoietic progenitors during mammalian embryogenesis.
- Haruko Nakano
- , Xiaoqian Liu
- & Atsushi Nakano
-
Article |
 De novo lipogenesis in human fat and liver is linked to ChREBP-β and metabolic health
De novo lipogenesis in human fat and liver is linked to ChREBP-β and metabolic health
Changes in the biosynthesis of fatty acids can influence tissue insulin sensitivity and the development of metabolic diseases. Eissing and colleagues show that de novolipogenesis in liver and adipose tissue is linked to metabolic health in humans and can be modulated by bariatric surgery.
- Leah Eissing
- , Thomas Scherer
- & Ludger Scheja

 Hepatic IRE1α regulates fasting-induced metabolic adaptive programs through the XBP1s–PPARα axis signalling
Hepatic IRE1α regulates fasting-induced metabolic adaptive programs through the XBP1s–PPARα axis signalling