Featured
-
-
Article |
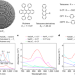 Lanthanide-doped inorganic nanoparticles turn molecular triplet excitons bright
Lanthanide-doped inorganic nanoparticles turn molecular triplet excitons bright
Optically dark (non-emitting) triplet excitons on organic molecules may be rendered bright by coupling the molecules to lanthanide-doped nanoparticles, providing a way to control such excitons in optoelectronic systems.
- Sanyang Han
- , Renren Deng
- & Akshay Rao
-
News & Views |
 Fresh evidence challenges the consensus view of active sites in an industrial catalyst
Fresh evidence challenges the consensus view of active sites in an industrial catalyst
A study of the industrial catalyst titanium silicalite-1 suggests that the conventional view of the structure of its active sites is wrong. The findings might enable further optimization of related industrial catalysts.
- Bert M. Weckhuysen
-
Article |
 Sub-cycle atomic-scale forces coherently control a single-molecule switch
Sub-cycle atomic-scale forces coherently control a single-molecule switch
The near field of a terahertz wave confined to a scanning probe tip provides femtosecond atomic-scale forces that coherently modulate the switching probability of a molecule between two stable adsorption geometries.
- Dominik Peller
- , Lukas Z. Kastner
- & Jascha Repp
-
Article |
 Coherent control of a surface structural phase transition
Coherent control of a surface structural phase transition
A structural phase transition from metal to insulator on a solid surface is controlled by an ultrafast sequence of optical pulses.
- Jan Gerrit Horstmann
- , Hannes Böckmann
- & Claus Ropers
-
Article |
 Mapping the emergence of molecular vibrations mediating bond formation
Mapping the emergence of molecular vibrations mediating bond formation
Femtosecond X-ray liquidography is used to track the vibrational wavepacket trajectories of gold atoms in solution, enabling time-resolved observations of the emergence of vibrations and the evolution of the formation of covalent bonds.
- Jong Goo Kim
- , Shunsuke Nozawa
- & Hyotcherl Ihee
-
Article |
 Leveraging excited-state coherence for synthetic control of ultrafast dynamics
Leveraging excited-state coherence for synthetic control of ultrafast dynamics
Information from quantum coherence observations guides synthetic modifications of an iron-based chromophore, increasing the excited-state dynamics lifetime by a factor of 20, with implications for photo-induced electron-transfer applications.
- Bryan C. Paulus
- , Sara L. Adelman
- & James K. McCusker
-
News & Views |
 Strong chemical reducing agents produced by light
Strong chemical reducing agents produced by light
An electrically neutral radical has been found to be a potent chemical reducing agent when excited by light. Remarkably, it is produced from a positively charged precursor that has long been used as a strong excited-state oxidizing agent.
- Radek Cibulka
-
Article |
 Discovery and characterization of an acridine radical photoreductant
Discovery and characterization of an acridine radical photoreductant
Photoexcited acridine radical catalysts are found to have redox potentials more reducing than lithium, which is attributed to the population of higher-energy doublet excited states via a twisted intramolecular charge-transfer species.
- Ian A. MacKenzie
- , Leifeng Wang
- & David A. Nicewicz
-
Article |
 In situ NMR metrology reveals reaction mechanisms in redox flow batteries
In situ NMR metrology reveals reaction mechanisms in redox flow batteries
Real-time nuclear magnetic resonance studies of electrolyte decomposition and self-discharge in redox flow batteries provide insights into the underlying mechanisms of the reactions, such as radical formation and electron transfer.
- Evan Wenbo Zhao
- , Tao Liu
- & Clare P. Grey
-
News & Views |
 Infrared spectroscopy finally sees the light
Infrared spectroscopy finally sees the light
The reliance of infrared spectroscopy on light transmission limits the sensitivity of many analytical applications. An approach that depends on the emission of infrared radiation from molecules promises to solve this problem.
- Andreas Barth
-
Article |
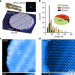 Atomic imaging of the edge structure and growth of a two-dimensional hexagonal ice
Atomic imaging of the edge structure and growth of a two-dimensional hexagonal ice
Real-space imaging of the edge structures and growth of a two-dimensional ice on a gold substrate is achieved using noncontact atomic-force microscopy with a carbon monoxide tip.
- Runze Ma
- , Duanyun Cao
- & Ying Jiang
-
Article |
 Probing the critical nucleus size for ice formation with graphene oxide nanosheets
Probing the critical nucleus size for ice formation with graphene oxide nanosheets
Nucleation experiments with water droplets containing differently sized graphene oxide nanosheets provide an experimental indication of the temperature-dependent size of the critical ice nucleus.
- Guoying Bai
- , Dong Gao
- & Jianjun Wang
-
News & Views |
 The nano-revolution spawned by carbon
The nano-revolution spawned by carbon
In 1985, scientists reported the discovery of the cage-like carbon molecule C60. The finding paved the way for materials such as graphene and carbon nanotubes, and was a landmark in the emergence of nanotechnology.
- Pulickel M. Ajayan
-
Letter |
 Analogue quantum chemistry simulation
Analogue quantum chemistry simulation
An analogue quantum simulator based on ultracold atoms in optical lattices and cavity quantum electrodynamics is proposed for the solution of quantum chemistry problems and tested numerically for a simple molecule.
- Javier Argüello-Luengo
- , Alejandro González-Tudela
- & J. Ignacio Cirac
-
Article |
 Metal-free directed sp2-C–H borylation
Metal-free directed sp2-C–H borylation
A method for the site-selective C–H borylation of arenes and heteroarenes is described, in which BBr3 acts as both a reagent and a catalyst.
- Jiahang Lv
- , Xiangyang Chen
- & Zhuangzhi Shi
-
News & Views |
 A versatile cold-molecule collider
A versatile cold-molecule collider
Superconducting magnets have been used to trap cold oxygen molecules and study their collisions. This method could lead to a better understanding of low-temperature interactions for a broad range of molecules.
- Dajun Wang
-
News & Views |
 Crystallization tracked atom by atom
Crystallization tracked atom by atom
Atoms of a metal alloy have been tracked as they form crystal nuclei — the first ordered clusters of atoms or molecules produced during crystallization. The findings might help to develop a general nucleation theory.
- Peter G. Vekilov
-
Letter |
 Observing crystal nucleation in four dimensions using atomic electron tomography
Observing crystal nucleation in four dimensions using atomic electron tomography
Atomic electron tomography captures crystal nucleation in four dimensions in FePt nanoparticles, with the observed early-stage nucleation not consistent with classical nucleation theory.
- Jihan Zhou
- , Yongsoo Yang
- & Jianwei Miao
-
Letter |
 Selective triplet exciton formation in a single molecule
Selective triplet exciton formation in a single molecule
Recombination of excitons to produce molecular light emission is made more efficient by controlling electron spin within the molecule to produce spin-triplet excitons only, without the usual accompanying spin-singlet excitons.
- Kensuke Kimura
- , Kuniyuki Miwa
- & Yousoo Kim
-
News & Views |
 A twist in the tale of the structure of ice
A twist in the tale of the structure of ice
A classic study found that crystalline ice adopts an amorphous form when compressed. Experiments now find that alternative phase transitions can occur — with implications for theories about water’s structure.
- John S. Tse
-
Letter |
 Absence of amorphous forms when ice is compressed at low temperature
Absence of amorphous forms when ice is compressed at low temperature
Slow compression of ice at low temperature results in the sequential formation of a series of crystalline phases, challenging theories that connect amorphous ice to supercooled liquid water.
- Chris A. Tulk
- , Jamie J. Molaison
- & Dennis D. Klug
-
News & Views |
 Snapshots of vibrating molecules
Snapshots of vibrating molecules
A spectroscopic imaging method has reached a resolution 1,000 times better than the limits of standard optical imaging techniques — and reveals vibrational modes of molecules previously seen only in computational models.
- Eric C. Le Ru
-
Letter |
 Visualizing vibrational normal modes of a single molecule with atomically confined light
Visualizing vibrational normal modes of a single molecule with atomically confined light
The vibrational normal modes in a single molecule are imaged using tip-enhanced Raman spectromicroscopy performed in the atomistic near-field.
- Joonhee Lee
- , Kevin T. Crampton
- & V. Ara Apkarian
-
Letter |
 Molecular streaming and its voltage control in ångström-scale channels
Molecular streaming and its voltage control in ångström-scale channels
Pressure-driven transport of aqueous salts through ångström-scale channels created from two-dimensional materials shows a transistor-like effect in which applying a tiny bias voltage can increase transport by up to 20 times.
- T. Mouterde
- , A. Keerthi
- & B. Radha
-
News Feature |
 Beyond the periodic table
Beyond the periodic table
150 years after Mendeleev organized the elements by their characteristics, a special issue explores the enduring influence of this scientific masterpiece.
-
Letter |
 Atomically dispersed iron hydroxide anchored on Pt for preferential oxidation of CO in H2
Atomically dispersed iron hydroxide anchored on Pt for preferential oxidation of CO in H2
Atomically dispersed iron hydroxide deposited on silica-supported platinum nanoparticles enables complete and selective carbon monoxide removal through preferential oxidation in hydrogen in the temperature range from 198 to 380 kelvin.
- Lina Cao
- , Wei Liu
- & Junling Lu
-
News |
 First hint of near-room-temperature superconductor tantalizes physicists
First hint of near-room-temperature superconductor tantalizes physicists
High-pressure hydrogen materials could be a step towards a new era of superconductivity.
- Davide Castelvecchi
-
News & Views |
 Tiny crystals have big potential for determining structures of small molecules
Tiny crystals have big potential for determining structures of small molecules
A method called microcrystal electron diffraction can rapidly image the structures of small molecules, including those found in mixtures. Will it usurp X-ray crystallography for determining small-molecule structures?
- Alan Brown
- & Jon Clardy
-
Letter |
 Electronic noise due to temperature differences in atomic-scale junctions
Electronic noise due to temperature differences in atomic-scale junctions
A fundamental electronic noise—beyond electronic thermal noise and voltage-activated shot noise—that is generated by temperature differences across nanoscale conductors is demonstrated, with possible implications for thermometry and electronics.
- Ofir Shein Lumbroso
- , Lena Simine
- & Oren Tal
-
Research Highlight |
 The bonds that set a sugar’s sweetness
The bonds that set a sugar’s sweetness
Hydrogen bonds between sugar and nearby molecules help to determine the level of sweetness.
-
Nature Podcast |
 Podcast: Pancreatic cancer, silica cages, and AI bias
Podcast: Pancreatic cancer, silica cages, and AI bias
Listen to the latest science news, brought to you by Shamini Bundell and Benjamin Thompson.
-
Letter |
 Heterointerface effects in the electrointercalation of van der Waals heterostructures
Heterointerface effects in the electrointercalation of van der Waals heterostructures
The electrointercalation of lithium into van der Waals heterostructures of graphene, hexagonal boron nitride and molybdenum dichalcogenides is studied at the level of individual atomic interfaces.
- D. Kwabena Bediako
- , Mehdi Rezaee
- & Philip Kim
-
Letter |
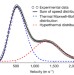 Velocity-resolved kinetics of site-specific carbon monoxide oxidation on platinum surfaces
Velocity-resolved kinetics of site-specific carbon monoxide oxidation on platinum surfaces
The catalytic oxidation of carbon monoxide over platinum proceeds through two distinct channels: it is dominated at low temperatures by the more active step sites and at high temperatures by the more abundant terrace sites of the platinum surface.
- Jannis Neugebohren
- , Dmitriy Borodin
- & Theofanis N. Kitsopoulos
-
Letter |
 Comprehensive suppression of single-molecule conductance using destructive σ-interference
Comprehensive suppression of single-molecule conductance using destructive σ-interference
Highly insulating silicon-based molecules, engineered so that conduction is fully suppressed by σ quantum interference even for molecules less than a nanometre long, could prove useful in molecular-scale electronic circuitry.
- Marc H. Garner
- , Haixing Li
- & Gemma C. Solomon
-
Letter |
 Potential enthalpic energy of water in oils exploited to control supramolecular structure
Potential enthalpic energy of water in oils exploited to control supramolecular structure
Less than 0.01 per cent by weight of water in an alkane solvent is sufficient to interact with co-dissolved supramolecular polymeric chains by hydrogen bonding and modulate the structure of the assembly.
- Nathan J. Van Zee
- , Beatrice Adelizzi
- & E. W. Meijer
-
Article |
 Simulating the vibrational quantum dynamics of molecules using photonics
Simulating the vibrational quantum dynamics of molecules using photonics
By mapping vibrations in molecules to photons in waveguides, the vibrational quantum dynamics of various molecules are simulated using a photonic chip.
- Chris Sparrow
- , Enrique Martín-López
- & Anthony Laing
-
Research Highlight |
 Why your feet slip and slide on ice
Why your feet slip and slide on ice
Experiments and simulations disprove an old theory.
-
Letter |
 The effect of hydration number on the interfacial transport of sodium ions
The effect of hydration number on the interfacial transport of sodium ions
A sodium ion hydrated with three (rather than one, two, four or five) water molecules diffuses orders of magnitude more quickly than the other ion hydrates owing to the interfacial symmetry mismatch.
- Jinbo Peng
- , Duanyun Cao
- & Ying Jiang
-
News & Views |
 Observations of the birth of crystals
Observations of the birth of crystals
Different forms of molecular crystals often have distinct properties, which can greatly influence their potential applications. A way of controlling the crystal form of a protein has now been reported.
- Robert G. Alberstein
- & F. Akif Tezcan
-
Letter |
 Maximizing and stabilizing luminescence from halide perovskites with potassium passivation
Maximizing and stabilizing luminescence from halide perovskites with potassium passivation
Modifying the surfaces and grain boundaries of perovskites with passivating potassium halide layers can mitigate non-radiative losses and photoinduced ion migration, increasing luminescence yields and improving charge transport and interfaces with device electrodes.
- Mojtaba Abdi-Jalebi
- , Zahra Andaji-Garmaroudi
- & Samuel D. Stranks
-
Letter |
 Sterically controlled mechanochemistry under hydrostatic pressure
Sterically controlled mechanochemistry under hydrostatic pressure
‘Molecular anvil’ molecules consisting of a compressible mechanophore and incompressible ligands react under hydrostatic pressure to produce elemental metal via an unexplored mechanism.
- Hao Yan
- , Fan Yang
- & Nicholas A. Melosh
-
News & Views |
 Tight complexes from disordered proteins
Tight complexes from disordered proteins
Charged groups on protein surfaces often take part in molecular interactions. Two unstructured proteins have been found to use charge complementarity to form a tight complex that has biologically useful kinetic properties.
- Rebecca B. Berlow
- & Peter E. Wright
-
Article |
 Extreme disorder in an ultrahigh-affinity protein complex
Extreme disorder in an ultrahigh-affinity protein complex
A high-affinity complex of histone H1 and prothymosin-α reveals an unexpected interaction mechanism, where the large opposite net charge enables the two proteins to remain highly disordered even in the complex.
- Alessandro Borgia
- , Madeleine B. Borgia
- & Benjamin Schuler
-
-
Letter |
 Role of stacking disorder in ice nucleation
Role of stacking disorder in ice nucleation
Stacking-disordered ice crystallites are shown to have an ice nucleation rate much higher than predicted by classical nucleation theory, which needs to be taken into account in cloud modelling.
- Laura Lupi
- , Arpa Hudait
- & Valeria Molinero
-
News & Views |
 Twenty years of drying droplets
Twenty years of drying droplets
When a particle-laden droplet evaporates on a solid surface, the particles form a ring-like deposit. The explanation for this phenomenon, provided in 1997, has led to advances in many areas of science and engineering.
- Ronald G. Larson
-
News |
 New definitions of scientific units are on the horizon
New definitions of scientific units are on the horizon
Metrologists are poised to change how scientists measure the Universe.
- Elizabeth Gibney
-
Letter |
 Organic long persistent luminescence
Organic long persistent luminescence
A blend of two organic molecules excited by a simple LED light source can release the stored excitation energy slowly as ‘long persistent luminescence’ over periods of up to an hour.
- Ryota Kabe
- & Chihaya Adachi
-
News & Views |
 Catalytic hotspots get noisy
Catalytic hotspots get noisy
Identifying and imaging catalytically active sites on solid surfaces is a grand challenge for science. A microscopy technique has been developed that images 'noise' to detect active sites with nanometre-scale resolution. See Letter p.74
- Christian Dette
- & Shannon W. Boettcher

 Transporting and concentrating vibrational energy to promote isomerization
Transporting and concentrating vibrational energy to promote isomerization Ice niceties
Ice niceties