Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access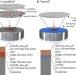 Mid-infrared supermirrors with finesse exceeding 400 000
Mid-infrared supermirrors with finesse exceeding 400 000
The researchers showcase all-crystalline and hybrid mid-infrared supermirrors with the lowest optical losses ever demonstrated in this wavelength range, representing an unprecedented improvement over any existing mirrors made with any production technology.
- Gar-Wing Truong
- , Lukas W. Perner
- & Garrett D. Cole
-
Article
| Open Access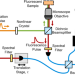 Fluorescence lifetime Hong-Ou-Mandel sensing
Fluorescence lifetime Hong-Ou-Mandel sensing
Standard techniques for Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy are limited by the electronics to 100’s of picoseconds time resolution. Here, the authors show how to use two-photon interference to perform fluorescence lifetime sensing with picosecond-scale resolution.
- Ashley Lyons
- , Vytautas Zickus
- & Daniele Faccio
-
Article
| Open Access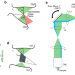 Blazed oblique plane microscopy reveals scale-invariant inference of brain-wide population activity
Blazed oblique plane microscopy reveals scale-invariant inference of brain-wide population activity
Recording neuronal activity at cellular resolution across an entire adult vertebrate brain is challenging. Here, the authors develop a blazed oblique plane microscope to perform brain-wide activity measurements in an adult vertebrate at high cellular resolution.
- Maximilian Hoffmann
- , Jörg Henninger
- & Benjamin Judkewitz
-
Article
| Open Access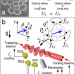 Nanoscale feedback control of six degrees of freedom of a near-sphere
Nanoscale feedback control of six degrees of freedom of a near-sphere
Levitated nanoparticles are a new platform for exploring quantum mechanics at macroscopic scales. The authors realize feedback controls of all external degrees of freedom of a nanoparticle, with one translational degree in the quantum ground state.
- Mitsuyoshi Kamba
- , Ryoga Shimizu
- & Kiyotaka Aikawa
-
Article
| Open Access Overlapping speckle correlation algorithm for high-resolution imaging and tracking of objects in unknown scattering media
Overlapping speckle correlation algorithm for high-resolution imaging and tracking of objects in unknown scattering media
Imaging moving objects within scattering media is important for a wide range of fields but remains challenging in many practical scenarios. Here, the authors present an overlapping speckle correlation algorithm for imaging and tracking particles in unknown media with limited prior sample knowledge.
- Yaoyao Shi
- , Wei Sheng
- & Youwen Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Autonomous nanorobots with powerful thrust under dry solid-contact conditions by photothermal shock
Autonomous nanorobots with powerful thrust under dry solid-contact conditions by photothermal shock
Optically trapping objects, marked by Nobel Prizes in 1997 and 2018 for applications in vacuum and liquids, remains challenging on solid surfaces. Here, the authors demonstrate a breakthrough by using photothermal-shock tweezers and explore nano-conventional robot applications
- Zhaoqi Gu
- , Runlin Zhu
- & Fuxing Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic construction of refractive index-dependent vibrations using surface plasmon-phonon polaritons
Dynamic construction of refractive index-dependent vibrations using surface plasmon-phonon polaritons
Molecular vibrations serve as valuable signatures for the constituent elements and bonding in compounds. Here, using Surface-Enhanced Infrared Absorption spectroscopy, the authors study refractive index dependent vibrations of surface phonon polaritons and surface plasmon platform, targeting dynamic biomonitoring.
- Hong Zhou
- , Zhihao Ren
- & Chengkuo Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Time-domain observation of interlayer exciton formation and thermalization in a MoSe2/WSe2 heterostructure
Time-domain observation of interlayer exciton formation and thermalization in a MoSe2/WSe2 heterostructure
Here, the authors use ultrafast transient absorption spectroscopy with a broadband white-light probe to simultaneously resolve interlayer charge transfer and interlayer exciton formation dynamics in a MoSe2/WSe2 heterostructure.
- Veronica R. Policht
- , Henry Mittenzwey
- & Stefano Dal Conte
-
Article
| Open Access Multipole engineering by displacement resonance: a new degree of freedom of Mie resonance
Multipole engineering by displacement resonance: a new degree of freedom of Mie resonance
Mie resonances are typically manipulated through varying nanostructure shape/size. Here, authors found that Gaussian beam displacement excites higher-order multipolar modes, not accessible by plane wave, featuring maximal linear and nonlinear scattering efficiency when the focus is misaligned.
- Yu-Lung Tang
- , Te-Hsin Yen
- & Shi-Wei Chu
-
Article
| Open Access Accessible hotspots for single-protein SERS in DNA-origami assembled gold nanorod dimers with tip-to-tip alignment
Accessible hotspots for single-protein SERS in DNA-origami assembled gold nanorod dimers with tip-to-tip alignment
The identification of individual proteins is highly desirable in diagnostics. Here, the authors report on DNA-origami assembled dimers of gold nanorod with accessible hotspots to capture and identify single proteins from solution by SERS.
- Francis Schuknecht
- , Karol Kołątaj
- & Theobald Lohmueller
-
Article
| Open Access Disordered metasurface enabled single-shot full-Stokes polarization imaging leveraging weak dichroism
Disordered metasurface enabled single-shot full-Stokes polarization imaging leveraging weak dichroism
Polarization imaging can capture information from the scene that cannot directly be recorded by traditional intensity cameras. Here, authors demonstrate a single-shot full Stokes polarization camera incorporating a disordered metasurface array with weak dichroism.
- Qingbin Fan
- , Weizhu Xu
- & Ting Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Training large-scale optoelectronic neural networks with dual-neuron optical-artificial learning
Training large-scale optoelectronic neural networks with dual-neuron optical-artificial learning
Optoelectronic neural networks are a promising avenue in AI computing for parallelization, power efficiency, and speed. Here, the authors present a dual-neuron optical-artificial learning approach for training large-scale diffractive neural networks, achieving VGG-level performance on ImageNet in simulation with a network that is 10 times larger than existing ones.
- Xiaoyun Yuan
- , Yong Wang
- & Lu Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient optical plasmonic tweezer-controlled single-molecule SERS characterization of pH-dependent amylin species in aqueous milieus
Efficient optical plasmonic tweezer-controlled single-molecule SERS characterization of pH-dependent amylin species in aqueous milieus
Studying rare species in mixtures is challenging. Here, authors utilize on-and-off optical plasmonic trapping to control SERS-active nanocavity to analyse pH-dependent amylin species at single-molecule level, unveiling amyloid aggregation mechanisms.
- Wenhao Fu
- , Huanyu Chi
- & Jinqing Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Metasurface-empowered snapshot hyperspectral imaging with convex/deep (CODE) small-data learning theory
Metasurface-empowered snapshot hyperspectral imaging with convex/deep (CODE) small-data learning theory
Hyperspectral imagers play a vital role in material identification, but traditionally, they have been bulky. Here, the authors introduce a compact hyperspectral imaging system that combines metasurface optics with small-data deep learning.
- Chia-Hsiang Lin
- , Shih-Hsiu Huang
- & Pin Chieh Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Tracing multiple scattering trajectories for deep optical imaging in scattering media
Tracing multiple scattering trajectories for deep optical imaging in scattering media
Deep imaging in complex scattering media is hindered by multiple light scattering. Here, the authors proposed a method to trace multiple scattering trajectories in situ using a recorded reflection matrix and achieved enhanced imaging depth by converting these multiple scattering to signal waves.
- Sungsam Kang
- , Yongwoo Kwon
- & Wonshik Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Polarization structured light 3D depth image sensor for scenes with reflective surfaces
Polarization structured light 3D depth image sensor for scenes with reflective surfaces
Highly reflective surfaces are notorious in 3D sensing because they can cause errors in depth perception. Here, the authors devise a polarization structured light 3D sensor for this problem, in which high-contrast-grating VCSELs are used. Experiments are reported to demonstrate the sensor can be used to see and see through the highly reflective surfaces.
- Xuanlun Huang
- , Chenyang Wu
- & Connie J. Chang-Hasnain
-
Article
| Open Access Rheological engineering of perovskite suspension toward high-resolution X-ray flat-panel detector
Rheological engineering of perovskite suspension toward high-resolution X-ray flat-panel detector
The film uniformity is essential to the fixed pattern noise (FPN) and resolution of X-ray detectors. Here the authors demonstrate the rheological engineering of the perovskite suspension to achieve low FPN of 1.39% and high resolution of 0.51 lp/pix.
- Zihao Song
- , Xinyuan Du
- & Jiang Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Learning diffractive optical communication around arbitrary opaque occlusions
Learning diffractive optical communication around arbitrary opaque occlusions
Researchers demonstrate robust optical communication around fully opaque occlusions, partially or entirely blocking the light path, using a pair of electronic encoder and passive diffractive decoder that are jointly optimized using deep learning.
- Md Sadman Sakib Rahman
- , Tianyi Gan
- & Aydogan Ozcan
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid sensing of hidden objects and defects using a single-pixel diffractive terahertz sensor
Rapid sensing of hidden objects and defects using a single-pixel diffractive terahertz sensor
Researchers showcase a deep learning-designed diffractive terahertz sensor that rapidly detects hidden defects within 3D samples based on the output spectrum measured by a single-pixel detector, eliminating sample scanning or image formation/processing.
- Jingxi Li
- , Xurong Li
- & Aydogan Ozcan
-
Article
| Open Access Single virus fingerprinting by widefield interferometric defocus-enhanced mid-infrared photothermal microscopy
Single virus fingerprinting by widefield interferometric defocus-enhanced mid-infrared photothermal microscopy
The study of viruses relies on the detection of viral proteins or viral nucleic acids. Here, the authors present a widefield interferometric defocus-enhanced mid-infrared photothermal (WIDE-MIP) microscope for high-throughput fingerprinting of single viruses.
- Qing Xia
- , Zhongyue Guo
- & Ji-Xin Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Subwavelength terahertz imaging via virtual superlensing in the radiating near field
Subwavelength terahertz imaging via virtual superlensing in the radiating near field
The authors develop a method for sub-diffraction near-field imaging using measurements taken relatively far from an object, amplifying evanescent waves that encode the highest resolution. The increased distance greatly reduces the perturbation of the fields by the imaging device itself.
- Alessandro Tuniz
- & Boris T. Kuhlmey
-
Article
| Open Access Creating tunable lateral optical forces through multipolar interplay in single nanowires
Creating tunable lateral optical forces through multipolar interplay in single nanowires
It is a significant challenge to create an interface-free lateral optical force under the illumination of a single polarized plane wave. Here, the authors provide a minimalist paradigm to address this challenge by exploiting multipolar interplay in a single elongated particle.
- Fan Nan
- , Francisco J. Rodríguez-Fortuño
- & Xiaohao Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated reconstructive spectrometer with programmable photonic circuits
Integrated reconstructive spectrometer with programmable photonic circuits
Recent years have seen a growing need for miniaturized spectroscopic tools. Here, authors present a novel integrated spectrometer with programmable photonic circuits, achieving record-high resolution and bandwidth via only a few filtering components.
- Chunhui Yao
- , Kangning Xu
- & Richard Penty
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo noninvasive systemic myography of acute systemic vasoactivity in female pregnant mice
In vivo noninvasive systemic myography of acute systemic vasoactivity in female pregnant mice
The assessment of selective therapeutics targeted to treat altered vasoactivity, a major characteristic of cardiovascular and oncological diseases, is still challenging due to unknown whole-body selectivity. Here the authors demonstrate that photoacoustic tomography has the potential to capture significant acute vasodilation of major arteries and vasculature selectivity.
- Kristie Huda
- , Dylan J. Lawrence
- & Carolyn L. Bayer
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing moiré ferroelectricity via plasmons and nano-photocurrent in graphene/twisted-WSe2 structures
Visualizing moiré ferroelectricity via plasmons and nano-photocurrent in graphene/twisted-WSe2 structures
Recent experiments have shown the formation of ferroelectric domains in twisted van der Waals bilayers. Here, the authors report near-field infrared nano-imaging and nano-photocurrent measurements to investigate ferroelectricity in minimally twisted WSe2 by visualizing the plasmonic and photo-thermoelectric response of an adjacent graphene monolayer.
- Shuai Zhang
- , Yang Liu
- & D. N. Basov
-
Article
| Open Access Orientation distributions of vacuum-deposited organic emitters revealed by single-molecule microscopy
Orientation distributions of vacuum-deposited organic emitters revealed by single-molecule microscopy
The understanding of the orientation of luminescent molecules is currently limited by the ensemble-averaging nature of state-of-the-art measurements. Here, the authors apply single-molecule imaging to obtain complete orientation distributions of the transition dipole of individual emitter molecules.
- Francisco Tenopala-Carmona
- , Dirk Hertel
- & Malte C. Gather
-
Article
| Open Access High-resolution single-photon imaging with physics-informed deep learning
High-resolution single-photon imaging with physics-informed deep learning
High-resolution single-photon imaging is challenging due to complex hardware and noise disturbances. Here, the authors realise simultaneous single-photon denoising and super-resolution enhancement by physics-informed deep learning, with a physical multi-source noise model, two single-photon image datasets, and a deep transformer network.
- Liheng Bian
- , Haoze Song
- & Jun Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Intrinsic 1\({T}^{{\prime} }\) phase induced in atomically thin 2H-MoTe2 by a single terahertz pulse
Intrinsic 1\({T}^{{\prime} }\) phase induced in atomically thin 2H-MoTe2 by a single terahertz pulse
A single field-enhanced terahertz pulse was used to create 1\({T}^{{\prime} }\)-MoTe2 out of few-layer H-MoTe2 crystals, providing insights into the ultrafast polymorphic transition dynamics and resolving a long-standing debate over the realization of this transition by high-energy photon irradiation.
- Jiaojian Shi
- , Ya-Qing Bie
- & Keith A. Nelson
-
Article
| Open Access An entropy-controlled objective chip for reflective confocal microscopy with subdiffraction-limit resolution
An entropy-controlled objective chip for reflective confocal microscopy with subdiffraction-limit resolution
The optimized and disordered structures of planar diffractive lenses enable sub-diffraction limit focusing but destroy wide-field imaging. Here, the authors introduce the information entropy to evaluate the disorder of PDL and achieve good balance between super-focusing and imaging.
- Jun He
- , Dong Zhao
- & Kun Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Light-enhanced molecular polarity enabling multispectral color-cognitive memristor for neuromorphic visual system
Light-enhanced molecular polarity enabling multispectral color-cognitive memristor for neuromorphic visual system
Designing optoelectronic synapses having a multispectral color-discriminating ability is crucial for neuromorphic visual system. Here, the authors propose an strategy to introduce RGB color-discriminating synaptic functionality into a 2-terminals memristor regardless of switching medium and design a color image-recognizing CNN and light-programmable reservoir computing.
- Jongmin Lee
- , Bum Ho Jeong
- & Hui Joon Park
-
Article
| Open Access Robotic-OCT guided inspection and microsurgery of monolithic storage devices
Robotic-OCT guided inspection and microsurgery of monolithic storage devices
Demand for data recovery from monolithic storage devices is high but current methods are inefficient. Here, authors develop a robotic OCT-guided inspection and microsurgery method, minimizing damage to device and enhancing data recovery efficiency.
- Bin He
- , Yuxin Zhang
- & Ning Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Optimized virtual optical waveguides enhance light throughput in scattering media
Optimized virtual optical waveguides enhance light throughput in scattering media
Virtual optical waveguide can be potentially utilised in variety of applications that require in situ light steering yet the efficacy is still unclear. Here, the authors show that ultrasonically-sculpted virtual gradient-index waveguides are effective in guiding and confining light inside tissue and other scattering media, and significantly outperform external lenses at this task.
- Adithya Pediredla
- , Matteo Giuseppe Scopelliti
- & Ioannis Gkioulekas
-
Article
| Open Access Demonstration of an AI-driven workflow for autonomous high-resolution scanning microscopy
Demonstration of an AI-driven workflow for autonomous high-resolution scanning microscopy
Modern microscopes can image a sample with sub-Angstrom and sub-picosecond resolutions, but this often requires analysis of tremendously large datasets. Here, the authors demonstrate that an autonomous experiment can yield over a 70% reduction in dataset size while still producing high-fidelity images of the sample.
- Saugat Kandel
- , Tao Zhou
- & Mathew J. Cherukara
-
Article
| Open Access Compact all-fiber quantum-inspired LiDAR with over 100 dB noise rejection and single photon sensitivity
Compact all-fiber quantum-inspired LiDAR with over 100 dB noise rejection and single photon sensitivity
LiDARs exploiting quantum correlations provide enhancement in noise resilience and sensitivity, but high-power classical sources offer much higher operating distances. Here, the authors show how to exploit high power classical time-frequency correlations to keep the best of both worlds.
- Han Liu
- , Changhao Qin
- & Amr S. Helmy
-
Article
| Open Access Operando monitoring of thermal runaway in commercial lithium-ion cells via advanced lab-on-fiber technologies
Operando monitoring of thermal runaway in commercial lithium-ion cells via advanced lab-on-fiber technologies
Operando monitoring of thermal runaway in Li-ion batteries is critical. Here, authors develop an optical fiber sensor capable of insertion into 18650 batteries to monitor internal temperature and pressure during thermal runaway, facilitating battery safety assessment and early warning capability.
- Wenxin Mei
- , Zhi Liu
- & Tuan Guo
-
Article
| Open Access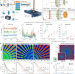 Infrared spectroscopic laser scanning confocal microscopy for whole-slide chemical imaging
Infrared spectroscopic laser scanning confocal microscopy for whole-slide chemical imaging
Chemical imaging, including infrared spectroscopic microscopy with molecular sensitivity, is useful for label-free biomedical analyses, but is limited by slow speed and poor image quality. Here, the authors design a fast mid-infrared microscope with low noise and high spatial resolution for high-throughput imaging of whole slides.
- Kevin Yeh
- , Ishaan Sharma
- & Rohit Bhargava
-
Article
| Open Access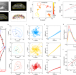 Switch of cell migration modes orchestrated by changes of three-dimensional lamellipodium structure and intracellular diffusion
Switch of cell migration modes orchestrated by changes of three-dimensional lamellipodium structure and intracellular diffusion
How do cells regulate their migration speed and direction? Here, authors discover that keratocyte cells can reversibly switch between different migration modes, by changing the 3D lamellipodium shape and intracellular diffusion.
- Chao Jiang
- , Hong-Yu Luo
- & Hui Li
-
Article
| Open Access A universal metasurface antenna to manipulate all fundamental characteristics of electromagnetic waves
A universal metasurface antenna to manipulate all fundamental characteristics of electromagnetic waves
The authors show a universal metasurface antenna capable of simultaneously and independently controlling all five fundamental properties of electromagnetic waves, including amplitude, phase, frequency, polarization, and momentum.
- Geng-Bo Wu
- , Jun Yan Dai
- & Chi Hou Chan
-
Article
| Open Access Hypothermal opto-thermophoretic tweezers
Hypothermal opto-thermophoretic tweezers
Traditional optical tweezers require high laser powers risking photothermal damage of the trapped objects. Here, the authors present hypothermal opto-thermophoretic tweezers (HOTTs), which use environmental cooling to simultaneously enhance thermophoretic trapping force at low laser powers and suppress the thermal damage to trapped objects.
- Pavana Siddhartha Kollipara
- , Xiuying Li
- & Yuebing Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Super-resolution multicolor fluorescence microscopy enabled by an apochromatic super-oscillatory lens with extended depth-of-focus
Super-resolution multicolor fluorescence microscopy enabled by an apochromatic super-oscillatory lens with extended depth-of-focus
Conventional super-oscillatory devices suffer from numerical-aperture related issue including depth of focus, chromatic dispersion, and focusing, Here, the authors utilised multi-objective genetic algorithm to optimise the design and experimentally demonstrated lens with an extended depth of focus, ultra-large working distance and suppressed side-lobes.
- Wenli Li
- , Pei He
- & Yiting Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Carrier-envelope phase on-chip scanner and control of laser beams
Carrier-envelope phase on-chip scanner and control of laser beams
Measurement and control of the carrier-envelope phase (CEP) is essential for applications of few-cycle laser beams. The authors present a compact on-chip, ambient-air, CEP scanning probe and show a 3D map of spatial changes of CEP and demonstrate CEP control in the focal volume with a spatial light modulator.
- Václav Hanus
- , Beatrix Fehér
- & Péter Dombi
-
Article
| Open Access Exciton Superposition across Moiré States in a Semiconducting Moiré Superlattice
Exciton Superposition across Moiré States in a Semiconducting Moiré Superlattice
The moiré lattice of trilayer WSe2 and monolayer WS2 host interlayer excitons localized at different moiré sites. Using an electric field, the authors tune the superposition between two moiré sites via hybridization with intralayer excitons in WSe2.
- Zhen Lian
- , Dongxue Chen
- & Su-Fei Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Handheld snapshot multi-spectral camera at tens-of-megapixel resolution
Handheld snapshot multi-spectral camera at tens-of-megapixel resolution
Current multispectral video cameras can hardly scale up beyond megapixel resolution and do not apply to large-scale scenes. The authors design a tens-ofmegapixel handheld multi-spectral imaging scheme, build a setup achieving 65-megapixel videography of 12 wavebands, and show its wide applications.
- Weihang Zhang
- , Jinli Suo
- & Qionghai Dai
-
Article
| Open Access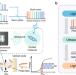 Dual-comb optomechanical spectroscopy
Dual-comb optomechanical spectroscopy
Spectroscopic gas sensing with high sensitivity and selectivity finds an increasing number of applications. Here, the authors report an approach to ultrasensitive multiplexed gas sensing by integrating dual-comb spectroscopy with cavity optomechanics.
- Xinyi Ren
- , Jin Pan
- & Heping Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Multicolor lifetime imaging and its application to HIV-1 uptake
Multicolor lifetime imaging and its application to HIV-1 uptake
Multicolor imaging employing genetically-encodable fluorescent proteins permits spatiotemporal live cell imaging of multiple cues. Here, authors use multicolor lifetime imaging to visualize quadruple-labelled human immunodeficiency viruses within cellular contexts.
- Tobias Starling
- , Irene Carlon-Andres
- & Sergi Padilla-Parra
-
Article
| Open Access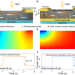 Enabling low-drift flexible perovskite photodetectors by electrical modulation for wearable health monitoring and weak light imaging
Enabling low-drift flexible perovskite photodetectors by electrical modulation for wearable health monitoring and weak light imaging
Defects and ion migration in perovskites hinder their potential as active material for flexible photodetectors. Here, the authors provide an electrical field modulation strategy to enhance the operational stability and the signal-to-noise ratio of flexible perovskite photodetectors.
- Yingjie Tang
- , Peng Jin
- & Bowen Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-wideband optical coherence elastography from acoustic to ultrasonic frequencies
Ultra-wideband optical coherence elastography from acoustic to ultrasonic frequencies
Understanding the mechanical properties of materials is critical in many fields, from soft hydrogels to biological tissues, yet current measurement methods lack the spatial and time resolution to characterize samples with complex structures. Here, the authors show non-invasive elastography technique offering advancements in resolution, sensitivity, and measurement frequencies.
- Xu Feng
- , Guo-Yang Li
- & Seok-Hyun Yun
-
Article
| Open Access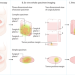 EGFR-targeted fluorescence molecular imaging for intraoperative margin assessment in oral cancer patients: a phase II trial
EGFR-targeted fluorescence molecular imaging for intraoperative margin assessment in oral cancer patients: a phase II trial
By using tumor-specific fluorescent tracers, fluorescence molecular imaging (FMI) can be used to visualize tumor tissues with high specificity. Here the authors report the results of a phase II trial to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of an EGFR-targeted FMI for intraoperative margin assessment in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma.
- Jaron G. de Wit
- , Jasper Vonk
- & Max J. H. Witjes
-
Article
| Open Access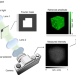 Non-interferometric stand-alone single-shot holographic camera using reciprocal diffractive imaging
Non-interferometric stand-alone single-shot holographic camera using reciprocal diffractive imaging
An ideal holographic camera acquires depth information about an object by measuring the light field. Here, the authors present a reference-free single-shot holographic image sensor that freely focuses the image of real-world objects via reciprocal diffractive imaging.
- Jeonghun Oh
- , Herve Hugonnet
- & YongKeun Park

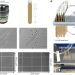 ComplexEye: a multi-lens array microscope for high-throughput embedded immune cell migration analysis
ComplexEye: a multi-lens array microscope for high-throughput embedded immune cell migration analysis