Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Parental histone transfer caught at the replication fork
Parental histone transfer caught at the replication fork
Structures of the yeast replisome associated with the FACT complex and an evicted histone hexamer offer insights into the mechanism of replication-coupled histone recycling for maintaining epigenetic inheritance.
- Ningning Li
- , Yuan Gao
- & Yuanliang Zhai
-
Article
| Open Access Cooperation between bHLH transcription factors and histones for DNA access
Cooperation between bHLH transcription factors and histones for DNA access
Cryo-EM structures and analysis provide insight into the mechanisms by which basic helix–loop–helix transcription factors access E-box DNA sequences that are embedded within nucleosomes, and cooperate with other transcription factors.
- Alicia K. Michael
- , Lisa Stoos
- & Nicolas H. Thomä
-
Article
| Open Access Histone modifications regulate pioneer transcription factor cooperativity
Histone modifications regulate pioneer transcription factor cooperativity
Binding of the human pioneer transcription factor OCT4 to nucleosomes containing endogenous DNA sequences causes changes to the nucleosome structure and facilitates the cooperative assembly of multiple pioneer transcription factors, a property that can be affected by histone modifications.
- Kalyan K. Sinha
- , Silvija Bilokapic
- & Mario Halic
-
Article |
 Mechanisms of BRCA1–BARD1 nucleosome recognition and ubiquitylation
Mechanisms of BRCA1–BARD1 nucleosome recognition and ubiquitylation
The authors elucidate the mechanisms for the ubiquitylation specificity and recruitment of the ubiquitin ligase complex BRCA1–BARD1 to damaged DNA within chromatin to facilitate homologous recombination.
- Qi Hu
- , Maria Victoria Botuyan
- & Georges Mer
-
Article |
 Molecular basis of nucleosomal H3K36 methylation by NSD methyltransferases
Molecular basis of nucleosomal H3K36 methylation by NSD methyltransferases
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the nucleosome-bound NSD2 and NSD3 histone methyltransferases reveal the molecular basis of their histone modification activity, and show how mutations in these proteins can lead to oncogenesis.
- Wanqiu Li
- , Wei Tian
- & Zhanxin Wang
-
Article |
 Measuring DNA mechanics on the genome scale
Measuring DNA mechanics on the genome scale
A high-throughput, chromosome-wide analysis of DNA looping reveals its contribution to the organization of chromatin, and provides insight into how nucleosomes are deposited and organised de novo.
- Aakash Basu
- , Dmitriy G. Bobrovnikov
- & Taekjip Ha
-
Article |
 Nucleosome-bound SOX2 and SOX11 structures elucidate pioneer factor function
Nucleosome-bound SOX2 and SOX11 structures elucidate pioneer factor function
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the DNA-binding domains of the pioneer transcription factor SOX2 and its close homologue SOX11 elucidate the role of these factors in initiating chromatin opening and nucleosome remodelling.
- Svetlana O. Dodonova
- , Fangjie Zhu
- & Patrick Cramer
-
Article |
 Structure of the transcription coactivator SAGA
Structure of the transcription coactivator SAGA
Structural studies on the yeast transcription coactivator complex SAGA (Spt–Ada–Gcn5–acetyltransferase) provide insights into the mechanism of initiation of regulated transcription by this multiprotein complex, which is conserved among eukaryotes.
- Haibo Wang
- , Christian Dienemann
- & Patrick Cramer
-
Article |
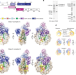 FACT caught in the act of manipulating the nucleosome
FACT caught in the act of manipulating the nucleosome
Two cryo-electron-microscopy images of the histone chaperone FACT interacting with components of nucleosomes shed light on how FACT manipulates nucleosomes to promote transcription, DNA repair and DNA replication.
- Yang Liu
- , Keda Zhou
- & Karolin Luger
-
Article |
 HP1 reshapes nucleosome core to promote phase separation of heterochromatin
HP1 reshapes nucleosome core to promote phase separation of heterochromatin
The S. pombe HP1 protein Swi6 couples chromatin compaction to phase separation by dynamically exposing buried histone residues within nucleosomes.
- S. Sanulli
- , M. J. Trnka
- & G. J. Narlikar
-
Article |
 DNA damage detection in nucleosomes involves DNA register shifting
DNA damage detection in nucleosomes involves DNA register shifting
Cryo-electron microscopy structures reveal that the DNA-repair factor UV-DDB exposes inaccessible nucleosome lesions for binding by inducing a translational shift in the nucleosome position.
- Syota Matsumoto
- , Simone Cavadini
- & Nicolas H. Thomä
-
Letter |
 Principles of nucleosome organization revealed by single-cell micrococcal nuclease sequencing
Principles of nucleosome organization revealed by single-cell micrococcal nuclease sequencing
Single-cell micrococcal nuclease sequencing simultaneously measures chromatin accessibility and genome-wide nucleosome positioning in single cells to reveal principles of nucleosome organization.
- Binbin Lai
- , Weiwu Gao
- & Keji Zhao
-
Letter |
 Insights from biochemical reconstitution into the architecture of human kinetochores
Insights from biochemical reconstitution into the architecture of human kinetochores
Biochemical reconstitution of a synthetic human kinetochore with 21 protein subunits and centromeric nucleosomal DNA unveils fundamental principles of kinetochore organization and function.
- John R. Weir
- , Alex C. Faesen
- & Andrea Musacchio
-
Letter |
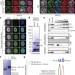 A core viral protein binds host nucleosomes to sequester immune danger signals
A core viral protein binds host nucleosomes to sequester immune danger signals
Here, a small core protein of human adenoviruses is shown to associate with histones, sequestering proteins on host chromatin and preventing inflammatory proteins from being released and triggering inflammation.
- Daphne C. Avgousti
- , Christin Herrmann
- & Matthew D. Weitzman
-
Letter |
 Structural basis for retroviral integration into nucleosomes
Structural basis for retroviral integration into nucleosomes
Retroviruses such as HIV rely on the intasome, a tetramer of integrase protein bound to the viral DNA ends interacting with host chromatin, for integration into the host genome; the structure of the intasome as it interacts with a nucleosome is now solved, giving insight into the integration process.
- Daniel P. Maskell
- , Ludovic Renault
- & Peter Cherepanov
-
Letter |
 Histone H2A.Z subunit exchange controls consolidation of recent and remote memory
Histone H2A.Z subunit exchange controls consolidation of recent and remote memory
The authors identify a specific histone variant as a memory-suppressor that is initially reduced in expression within the hippocampus during memory formation; as a memory is consolidated to the cortex, reduced histone association with specific plasticity genes is observed, promoting stabilization of the memory.
- Iva B. Zovkic
- , Brynna S. Paulukaitis
- & J. David Sweatt
-
Letter |
 Two independent transcription initiation codes overlap on vertebrate core promoters
Two independent transcription initiation codes overlap on vertebrate core promoters
The transcription start sites used during the maternal to zygotic transition in zebrafish are mapped, revealing that the transition is characterized by a switch between two different sequence signs to guide transcription initiation, which often co-exist in core promoters.
- Vanja Haberle
- , Nan Li
- & Boris Lenhard
-
Letter |
 Structural basis of histone H2A–H2B recognition by the essential chaperone FACT
Structural basis of histone H2A–H2B recognition by the essential chaperone FACT
The crystal structure of the FACT histone chaperone domain Spt16M in complex with the H2A–H2B heterodimer is solved; Spt16M makes several interactions with histones and seems to block the interaction of H2B with DNA, which could explain how FACT destabilizes nucleosomes to promote transcription.
- Maria Hondele
- , Tobias Stuwe
- & Andreas G. Ladurner
-
Letter |
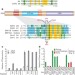 Regulation of ISWI involves inhibitory modules antagonized by nucleosomal epitopes
Regulation of ISWI involves inhibitory modules antagonized by nucleosomal epitopes
Two separate regulatory regions on the Drosophila chromatin remodeller ISWI are defined, AutoN and NegC, which negatively regulate ATP hydrolysis and the coupling of ATP hydrolysis to productive DNA translocation, respectively; epitopes on nucleosomes activate ISWI by inhibiting these negative regulatory domains, ensuring that remodelling occurs only in the appropriate chromatin context.
- Cedric R. Clapier
- & Bradley R. Cairns
-
Letter |
 The Fun30 nucleosome remodeller promotes resection of DNA double-strand break ends
The Fun30 nucleosome remodeller promotes resection of DNA double-strand break ends
Nucleolytic degradation of 5′ strands at DNA double-strand breaks in yeast is shown to be facilitated by the nucleosome remodeller Fun30, particularly within chromatin bound by the checkpoint adaptor protein known to inhibit resection, Rad9.
- Xuefeng Chen
- , Dandan Cui
- & Grzegorz Ira
-
Article |
 A map of nucleosome positions in yeast at base-pair resolution
A map of nucleosome positions in yeast at base-pair resolution
A new technique for mapping nucleosomes genome-wide with single-base-pair accuracy, by chemical modification of engineered histones.
- Kristin Brogaard
- , Liqun Xi
- & Jonathan Widom
-
News & Views |
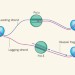 How to duplicate a DNA package
How to duplicate a DNA package
Cells replicate half of their genome as short fragments that are put together later on. The way in which this process is linked to the formation of DNA–protein complexes called nucleosomes is now becoming clearer. See Article p.434
- Alysia Vandenberg
- & Geneviève Almouzni
-
Letter |
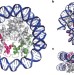 Crystal structure of the human centromeric nucleosome containing CENP-A
Crystal structure of the human centromeric nucleosome containing CENP-A
- Hiroaki Tachiwana
- , Wataru Kagawa
- & Hitoshi Kurumizaka
-
Letter |
 Determinants of nucleosome organization in primary human cells
Determinants of nucleosome organization in primary human cells
- Anton Valouev
- , Steven M. Johnson
- & Arend Sidow
-
Article |
 Structure and mechanism of the chromatin remodelling factor ISW1a
Structure and mechanism of the chromatin remodelling factor ISW1a
- Kazuhiro Yamada
- , Timothy D. Frouws
- & Timothy J. Richmond
-
Article |
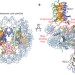 Structure of RCC1 chromatin factor bound to the nucleosome core particle
Structure of RCC1 chromatin factor bound to the nucleosome core particle
The small GTPase Ran regulates nuclear transport and cell division by creating a gradient of RanGTP around chromosomes. The RCC1 protein recruits Ran to nucleosomes and activates Ran's nucleotide exchange activity. Here, the crystal structure of the complex between RCC1 and the nucleosome core particle is revealed. It provides an atomic view of how a chromatin protein interacts with the histone and DNA components of the nucleosome.
- Ravindra D. Makde
- , Joseph R. England
- & Song Tan
-
Letter |
 Relationship between nucleosome positioning and DNA methylation
Relationship between nucleosome positioning and DNA methylation
Nucleosomes are composed of around 147 bases of DNA wrapped around an octamer of histone proteins. Here, a genome-wide analysis of nucleosome positioning in Arabidopsis thaliana has been combined with profiles of DNA methylation at single base resolution, revealing 10-base periodicities in the DNA methylation status of nucleosome-bound DNA. The results indicate that nucleosome positioning influences the pattern of DNA methylation throughout the genome.
- Ramakrishna K. Chodavarapu
- , Suhua Feng
- & Matteo Pellegrini

 Cryo-EM structures of RAD51 assembled on nucleosomes containing a DSB site
Cryo-EM structures of RAD51 assembled on nucleosomes containing a DSB site