Featured
-
-
Research Briefing |
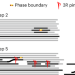 Mechanism of plastic deformation in metal monochalcogenides
Mechanism of plastic deformation in metal monochalcogenides
Metal monochalcogenides — a class of van der Waals layered semiconductors — can exhibit ultrahigh plasticity. Investigation of the deformation mechanism reveals that on mechanical loading, these materials undergo local phase transitions that, coupled with the concurrent generation of a microcrack network, give rise to the ultrahigh plasticity.
-
News & Views |
 Resistance to fatigue
Resistance to fatigue
An additively manufactured AlSi10Mg alloy shows high fatigue strength, even close to its tensile strength, for micro-sized samples. The fine cells in its inherent three-dimensional network are considered as cages to limit damage accumulation.
- Christopher Hutchinson
-
Article |
 Achieving ultrahigh fatigue resistance in AlSi10Mg alloy by additive manufacturing
Achieving ultrahigh fatigue resistance in AlSi10Mg alloy by additive manufacturing
An ultrahigh fatigue-resistant AlSi10Mg alloy is achieved by additive manufacturing, with its three-dimensional dual-phase cellular nanostructure acting as a strong volumetric nanocage to inhibit fatigue damage accumulation.
- Chengyi Dan
- , Yuchi Cui
- & Jian Lu
-
Article |
 Metamaterial adhesives for programmable adhesion through reverse crack propagation
Metamaterial adhesives for programmable adhesion through reverse crack propagation
Strong yet releasable metamaterial adhesives are fabricated using nonlinear cut architectures to achieve control of the crack propagation interface for programmable, directional and spatially selective adhesion.
- Dohgyu Hwang
- , Chanhong Lee
- & Michael D. Bartlett
-
Review Article |
 Hierarchically structured bioinspired nanocomposites
Hierarchically structured bioinspired nanocomposites
This Review discusses recent progress in bioinspired nanocomposite design, emphasizing the role of hierarchical structuring at distinct length scales to create multifunctional, lightweight and robust structural materials for diverse technological applications.
- Dhriti Nepal
- , Saewon Kang
- & Hendrik Heinz
-
News & Views |
 Move imperceptibly
Move imperceptibly
Pine cones deform ultraslowly as humidity changes, which is mostly driven by the spring-shaped and square microtubular heterostructure of the vascular bundles. This mechanism inspires the development of soft actuators with imperceptible but efficient motion under environmental stimuli.
- Cecilia Laschi
- & Barbara Mazzolai
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable gear-based mechanical metamaterials
Programmable gear-based mechanical metamaterials
A design paradigm to create robust robotic metamaterials using versatile gear clusters is demonstrated. It enables intriguing programmability of elastic properties and shape while preserving stability for intelligent machines.
- Xin Fang
- , Jihong Wen
- & Peter Gumbsch
-
Article |
 The toughness of mechanical metamaterials
The toughness of mechanical metamaterials
Microscale architecting enables metamaterials to achieve mechanical properties not accessible to bulk materials. Here the authors show that established design protocols for the fracture of materials need to be revised to predict the failure of these materials.
- Angkur Jyoti Dipanka Shaikeea
- , Huachen Cui
- & Vikram Sudhir Deshpande
-
News & Views |
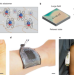 Energy supply from magnetoelastic composites
Energy supply from magnetoelastic composites
The giant magnetoelastic effect measured in magnetic elastomers enables new energy generators for wearable and implantable electronics.
- Denys Makarov
-
News & Views |
 Popping, locking robots
Popping, locking robots
An interplay between deswelling and buckling in a polymer gel is harnessed to achieve sequential snap events for repeatable jumping motion, opening the door to autonomously moving soft robots.
- Johannes T. B. Overvelde
-
News & Views |
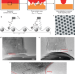 Visualized atom by atom
Visualized atom by atom
The processes of metallic asperities moving across each other, which are decisive in most machinery, have been visualized at the atomic scale, revealing unexpected behaviour especially when under tensile stress.
- Udo D. Schwarz
-
Article |
 Centimetre-scale crack-free self-assembly for ultra-high tensile strength metallic nanolattices
Centimetre-scale crack-free self-assembly for ultra-high tensile strength metallic nanolattices
Metal nanolattices are fabricated at an unprecedented scale by using a crack-free self-assembly method. The dense nanostructures enable tensile strengths that approach the theoretical limit.
- Zhimin Jiang
- & James H. Pikul
-
Letter |
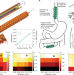 Kirigami-inspired stents for sustained local delivery of therapeutics
Kirigami-inspired stents for sustained local delivery of therapeutics
A kirigami-inspired stent-based system has been developed for extended local drug delivery to the gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts as well as the vascular system.
- Sahab Babaee
- , Yichao Shi
- & Giovanni Traverso
-
Article |
 High-rate nanofluidic energy absorption in porous zeolitic frameworks
High-rate nanofluidic energy absorption in porous zeolitic frameworks
Porous materials can absorb energy by water infiltration, but studies at industrially relevant high-rate intrusions are rare. Here, high-rate experiments are performed on ZIFs showing high energy storage capacity, while molecular simulations allow design rules to be formulated for absorption materials.
- Yueting Sun
- , Sven M. J. Rogge
- & Jin-Chong Tan
-
Article |
 Electrical bioadhesive interface for bioelectronics
Electrical bioadhesive interface for bioelectronics
A graphene nanocomposite hydrogel showing anisotropic swelling is used to realize an electrically conducting and removable bioadhesive that improves the mechanical and electrical integration of bioelectronics devices with wet dynamic tissues.
- Jue Deng
- , Hyunwoo Yuk
- & Xuanhe Zhao
-
Article |
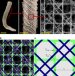 Mechanically robust lattices inspired by deep-sea glass sponges
Mechanically robust lattices inspired by deep-sea glass sponges
Computational analysis and mechanical testing demonstrate that the skeletal system of a marine sponge has, through the course of evolution, achieved a near-optimal resistance to buckling.
- Matheus C. Fernandes
- , Joanna Aizenberg
- & Katia Bertoldi
-
Article |
 A natural impact-resistant bicontinuous composite nanoparticle coating
A natural impact-resistant bicontinuous composite nanoparticle coating
A coating made from densely packed hydroxyapatite particles in an organic matrix endows the dactyl club of mantis shrimps with high stiffness and energy damping.
- Wei Huang
- , Mehdi Shishehbor
- & David Kisailus
-
Article |
 Monolithic digital patterning of polydimethylsiloxane with successive laser pyrolysis
Monolithic digital patterning of polydimethylsiloxane with successive laser pyrolysis
A laser-based patterning method enables the fast fabrication of high-quality two- and three-dimensional features in polydimethylsiloxane for microfluidics and biomedical applications.
- Jaeho Shin
- , Jihoon Ko
- & Seung Hwan Ko
-
Letter |
 Unprecedented non-hysteretic superelasticity of [001]-oriented NiCoFeGa single crystals
Unprecedented non-hysteretic superelasticity of [001]-oriented NiCoFeGa single crystals
NiCoFeGa single crystals exhibit large non-hysteretic superelasticity over broad temperature and composition ranges. It is attributed to the continuous phase transition with applied stress, which is related to the fluctuation of entangled ordered and disordered crystal structures.
- Haiyang Chen
- , Yan-Dong Wang
- & Yang Ren
-
News & Views |
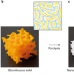 Divide and print
Divide and print
A three-dimensional printing approach based on the photopolymerization-induced phase separation of resins is used to fabricate complex glass structures with distinct chemical composition and porosity.
- Dorothea Helmer
- & Bastian E. Rapp
-
Article |
 Programming shape using kirigami tessellations
Programming shape using kirigami tessellations
Geometric analysis and constrained optimization algorithms allow for the design of kirigami patterns that can be deployed into any two- or three-dimensional shape.
- Gary P. T. Choi
- , Levi H. Dudte
- & L. Mahadevan
-
Letter |
 Surface charge printing for programmed droplet transport
Surface charge printing for programmed droplet transport
Rewritable surface charge density gradients enable the direct, high-speed and long-distance transport of droplets on distinct surfaces without the need of additional energy input.
- Qiangqiang Sun
- , Dehui Wang
- & Xu Deng
-
Comment |
 Scientific, technological and economic issues in metal printing and their solutions
Scientific, technological and economic issues in metal printing and their solutions
3D printing is now widely used in aerospace, healthcare, energy, automotive and other industries. Metal printing, in particular, is the fastest growing sector, yet its development presents scientific, technological and economic challenges that must be understood and addressed.
- T. DebRoy
- , T. Mukherjee
- & W. Zhang
-
News & Views |
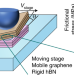 Slippery in every direction
Slippery in every direction
A graphite and hexagonal boron nitride heterojunction enables superlubric sliding, almost independent of alignment orientation, in micrometre-sized contacts under ‘real-life’ working conditions.
- J. G. Vilhena
- & Rubén Pérez
-
Article |
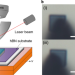 Robust microscale superlubricity in graphite/hexagonal boron nitride layered heterojunctions
Robust microscale superlubricity in graphite/hexagonal boron nitride layered heterojunctions
Robust structural superlubricity is experimentally realized in microscale monocrystalline graphite/hBN heterojunctions. The friction anisotropy upon crystal reorientation is orders of magnitude smaller than that of homogeneous graphite contacts.
- Yiming Song
- , Davide Mandelli
- & Quanshui Zheng
-
Article |
 Designing perturbative metamaterials from discrete models
Designing perturbative metamaterials from discrete models
A perturbative method is proposed for the systematic design of mechanical metamaterials, where each element of the discrete model is associated with individual geometric features of the metamaterial, through the weak interaction between the unit cells.
- Kathryn H. Matlack
- , Marc Serra-Garcia
- & Chiara Daraio
-
Article |
 Additively manufactured hierarchical stainless steels with high strength and ductility
Additively manufactured hierarchical stainless steels with high strength and ductility
3D-printed steels with hierarchically heterogeneous microstructures demonstrate high strength and ductility.
- Y. Morris Wang
- , Thomas Voisin
- & Ting Zhu
-
Letter |
 Modulation of thermal and thermoelectric transport in individual carbon nanotubes by fullerene encapsulation
Modulation of thermal and thermoelectric transport in individual carbon nanotubes by fullerene encapsulation
Encapsulation of single- and double-wall carbon nanotubes in carbon nanocages, which may contain gadolinium or erbium, leads to a reduction of the thermal conductivity and an improved Seebeck coefficient.
- Takashi Kodama
- , Masato Ohnishi
- & Kenneth E. Goodson
-
Article |
 Antifogging abilities of model nanotextures
Antifogging abilities of model nanotextures
The antifogging properties of a structured surface can be considerably enhanced if the feature size is small enough and if the feature shapes are cones rather than cylinders.
- Timothée Mouterde
- , Gaëlle Lehoucq
- & David Quéré
-
Letter |
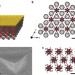 Orientational order controls crystalline and amorphous thermal transport in superatomic crystals
Orientational order controls crystalline and amorphous thermal transport in superatomic crystals
Room-temperature thermal conductivities in superatomic crystals are found to be proportional to the sound speed, while their behaviour can switch between amorphous- or crystalline-like, depending on temperature and the nature of superatoms used.
- Wee-Liat Ong
- , Evan S. O’Brien
- & Xavier Roy
-
Article |
 Intrusion rheology in grains and other flowable materials
Intrusion rheology in grains and other flowable materials
Experiments and simulations show that resistive forces on surfaces moving through granular matter or cohesive media arise as a consequence of local frictional yielding.
- Hesam Askari
- & Ken Kamrin
-
Article |
 Electrochemical stiffness in lithium-ion batteries
Electrochemical stiffness in lithium-ion batteries
Electrochemically induced stresses in battery electrodes leading to performance degradation are still poorly understood. In situ measurements show that stress scales proportionally with lithium intercalation rate and strain with capacity.
- Hadi Tavassol
- , Elizabeth M. C. Jones
- & Andrew A. Gewirth
-
Article |
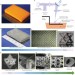 Multiscale metallic metamaterials
Multiscale metallic metamaterials
A large-area fabrication approach to achieve three-dimensional architectured metamaterials, with structural features spanning seven orders of magnitude, results in advanced mechanical properties, including high elasticity.
- Xiaoyu Zheng
- , William Smith
- & Christopher M. Spadaccini
-
News & Views |
 Smaller and stronger
Smaller and stronger
Fabrication of an ultra-strong glassy carbon nanolattice with a strut diameter of around 200 nm could stimulate the realization of advanced nanoscale architected materials.
- Xiaoyan Li
- & Huajian Gao
-
-
Article |
 Hydrogels with tunable stress relaxation regulate stem cell fate and activity
Hydrogels with tunable stress relaxation regulate stem cell fate and activity
Hydrogels with faster stress relaxation enhance the spreading, proliferation, and osteogenic differentiation of embedded mesenchymal stem cells.
- Ovijit Chaudhuri
- , Luo Gu
- & David J. Mooney
-
Letter |
 Tough bonding of hydrogels to diverse non-porous surfaces
Tough bonding of hydrogels to diverse non-porous surfaces
A hydrogel-design strategy achieves transparent and conductive bonding of synthetic hydrogels to a variety of non-porous surfaces, with interfacial toughness values over 1,000 J m−2.
- Hyunwoo Yuk
- , Teng Zhang
- & Xuanhe Zhao
-
Review Article |
 Programmable and adaptive mechanics with liquid crystal polymer networks and elastomers
Programmable and adaptive mechanics with liquid crystal polymer networks and elastomers
This Review discusses stimuli-responsive liquid crystalline polymer networks and elastomers as materials with programmable mechanics for use in functional devices.
- Timothy J. White
- & Dirk J. Broer
-
Article |
 Reversible dilatancy in entangled single-wire materials
Reversible dilatancy in entangled single-wire materials
A single, self-coiled wire is shown to exhibit a Poisson function ranging from above 1 in compression to below 0 in tension. Such material architectures may offer new functionalities in mechanical devices.
- David Rodney
- , Benjamin Gadot
- & Laurent Orgéas
-
Letter |
 Optimal wrapping of liquid droplets with ultrathin sheets
Optimal wrapping of liquid droplets with ultrathin sheets
Highly bendable yet unstretchable ultrathin sheets can wrap a liquid droplet to form an optimal non-spherical shape that minimizes the unwrapped interfacial area, regardless of interfacial energies and the sheet’s mechanical properties.
- Joseph D. Paulsen
- , Vincent Démery
- & Narayanan Menon
-
-
Article |
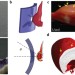 The role of quasi-plasticity in the extreme contact damage tolerance of the stomatopod dactyl club
The role of quasi-plasticity in the extreme contact damage tolerance of the stomatopod dactyl club
Nanoindentation and spectroscopy measurements show that the impact surface of the dactyl club—a hammer-like device that stomatopods use to shatter hard seashells—has a quasi-plastic response that enhances the damage tolerance of the clubs.
- Shahrouz Amini
- , Maryam Tadayon
- & Ali Miserez
-
Article |
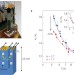 Phonon-induced diamagnetic force and its effect on the lattice thermal conductivity
Phonon-induced diamagnetic force and its effect on the lattice thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of diamagnetic InSb decreases as a magnetic field is increased at low temperatures and is attributed to local dynamic diamagnetism, bringing forth evidence of the magnetic response of phonons.
- Hyungyu Jin
- , Oscar D. Restrepo
- & Joseph P. Heremans
-
Article |
 Extracellular matrix stiffness and composition jointly regulate the induction of malignant phenotypes in mammary epithelium
Extracellular matrix stiffness and composition jointly regulate the induction of malignant phenotypes in mammary epithelium
Malignant phenotypes in the mammary epithelium have been correlated to increases in extracellular matrix stiffness. It is now shown that the effect of matrix stiffness in normal mammary epithelial cells can be offset by an increase in basement-membrane ligands and that both the stiffness and composition of the matrix are sensed by the β4 integrin. The results suggest that the relationship between matrix stiffness and composition is a more relevant predictor of breast-cancer progression.
- Ovijit Chaudhuri
- , Sandeep T. Koshy
- & David J. Mooney
-
-
News & Views |
 Diamonds are forever — or are they?
Diamonds are forever — or are they?
The friction and wear of materials is part of our everyday experience, and yet these processes are not well understood. The example of diamond highlights wear processes that result from bumping atoms, showing that the devil is indeed in the details.
- Jay Fineberg

 Prediction of DNA origami shape using graph neural network
Prediction of DNA origami shape using graph neural network Spinning top-ology
Spinning top-ology Square strength
Square strength