News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Nonlinearity-induced topological phase transition characterized by the nonlinear Chern number
Nonlinearity-induced topological phase transition characterized by the nonlinear Chern number
Linear topological systems can be characterized using invariants such as the Chern number. This concept can be extended to the nonlinear regime, giving rise to nonlinearity-induced topological phase transitions.
- Kazuki Sone
- , Motohiko Ezawa
- & Takahiro Sagawa
-
News & Views |
 Multiphoton quantum statistics from scattered classical light
Multiphoton quantum statistics from scattered classical light
Even by shining classical light on a single opening, one can perform a double-slit experiment and discover a surprising variety of quantum mechanical multi-photon correlations — thanks to surface plasmon polaritons and photon-number-resolving detectors.
- Martijn Wubs
-
-
Article |
 Non-Hermitian topological phase transitions controlled by nonlinearity
Non-Hermitian topological phase transitions controlled by nonlinearity
The phase transition from a topologically trivial state to non-Hermitian conducting edge modes can be controlled by optical nonlinearities, achieving picosecond switching speeds.
- Tianxiang Dai
- , Yutian Ao
- & Jianwei Wang
-
Editorial |
 Strive towards sustainability
Strive towards sustainability
Exacerbated by the impacts of climate change and the recent energy crisis, concentrated efforts towards more sustainable research have become matters of urgency, in particular for large-scale accelerator complexes and light sources.
-
Article
| Open Access Coupling of terahertz light with nanometre-wavelength magnon modes via spin–orbit torque
Coupling of terahertz light with nanometre-wavelength magnon modes via spin–orbit torque
Engineering of the spin–orbit interactions in a magnetic multilayered structure makes it possible to coherently generate coherent spin waves using terahertz radiation, which could benefit the development of spintronic devices.
- Ruslan Salikhov
- , Igor Ilyakov
- & Sergey Kovalev
-
News & Views |
 Light in the darkness
Light in the darkness
Laser light is usually limited to the same wavelength range as the spontaneous emission of the active material. A judicious choice of dielectric coatings on the cavity has now enabled laser emission far beyond the spectral range of the gain medium.
- Alessandra Toncelli
-
Letter |
 Multiphonon-assisted lasing beyond the fluorescence spectrum
Multiphonon-assisted lasing beyond the fluorescence spectrum
As laser action emerges from fluorescence, its emission wavelength lies within the fluorescence spectrum. Exploiting multiphonon processes can take the laser emission far beyond the spectral limits defined by a material’s intrinsic fluorescence.
- Fei Liang
- , Cheng He
- & Yan-Feng Chen
-
Article |
 Self-organized lasers from reconfigurable colloidal assemblies
Self-organized lasers from reconfigurable colloidal assemblies
Experiments inspired by the behaviour of active matter show that an external optical stimulus can spatially reconfigure colloidal random lasers and continuously tune their lasing threshold.
- Manish Trivedi
- , Dhruv Saxena
- & Giorgio Volpe
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Letter |
 High-harmonic generation from an epsilon-near-zero material
High-harmonic generation from an epsilon-near-zero material
High harmonics are generated from a thin film by leveraging the epsilon-near-zero effect. These kinds of harmonic are found to exhibit a pronounced spectral redshift as well as linewidth broadening caused by the time-dependency of this effect.
- Yuanmu Yang
- , Jian Lu
- & Igal Brener
-
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Better than Brillouin
Better than Brillouin
Light can be coupled to sound via Brillouin scattering, but realizing an efficient interaction isn’t trivial. A new type of resonator succeeds in doing so in a macroscopic device — boasting features that better its nanoscale counterparts.
- Jeremy Bourhill
- & Michael E. Tobar
-
-
Article |
 Coherence time of over a second in a telecom-compatible quantum memory storage material
Coherence time of over a second in a telecom-compatible quantum memory storage material
A candidate for efficient broadband quantum memory at telecommunication wavelengths is identified. The long coherence time and the efficient optical spin pumping demonstrated in the experiment make it practical for spin-wave storage.
- Miloš Rančić
- , Morgan P. Hedges
- & Matthew J. Sellars
-
Letter |
 Giant anisotropic nonlinear optical response in transition metal monopnictide Weyl semimetals
Giant anisotropic nonlinear optical response in transition metal monopnictide Weyl semimetals
An optical second-harmonic generation study of a series of transition metal monopnictide Weyl semimetals reveals a giant, anisotropic nonlinear optical response in these systems.
- Liang Wu
- , S. Patankar
- & J. Orenstein
-
Letter |
 High-harmonic generation from an atomically thin semiconductor
High-harmonic generation from an atomically thin semiconductor
Observations of high-harmonic generation from a single layer of a transition metal dichalcogenide opens the door to studying strong-field and attosecond phenomena in two-dimensional materials.
- Hanzhe Liu
- , Yilei Li
- & David A. Reis
-
Letter |
 Ultrastrong coupling of a single artificial atom to an electromagnetic continuum in the nonperturbative regime
Ultrastrong coupling of a single artificial atom to an electromagnetic continuum in the nonperturbative regime
A superconducting artificial atom coupled to a 1D waveguide tests the limits of light–matter interaction in an unexplored coupling regime, which may enable new perspectives for quantum technologies.
- P. Forn-Díaz
- , J. J. García-Ripoll
- & A. Lupascu
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Entering an acoustic phase
Entering an acoustic phase
Electrons moving in a one-dimensional crystal can acquire a geometrical phase. Sound waves in phononic crystals are now shown to display the same effect — underlining the similarity between conventional solids and acoustic metamaterials.
- Julio T. Barreiro
-
Letter |
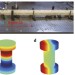 Geometric phase and band inversion in periodic acoustic systems
Geometric phase and band inversion in periodic acoustic systems
The behaviour of sound waves in phononic crystals—metamaterials with spatially varying acoustic characteristics—is similar to that of electrons in solids. Now, phononic band inversion and Zak phases have been measured for a 1D phononic system.
- Meng Xiao
- , Guancong Ma
- & C. T. Chan
-
-
-
Article |
 Wave propagation control at the deep subwavelength scale in metamaterials
Wave propagation control at the deep subwavelength scale in metamaterials
Photonic crystals efficiently control wave propagation on a wavelength scale, but this means they can become very large when long wavelengths are involved. Metamaterials made of resonant unit cells can confine and guide waves even at scales far below their wavelength.
- Fabrice Lemoult
- , Nadège Kaina
- & Geoffroy Lerosey
-
-
Article |
 Giant superfluorescent bursts from a semiconductor magneto-plasma
Giant superfluorescent bursts from a semiconductor magneto-plasma
Superfluorescence—the emission of coherent light from an initially incoherent collection of excited dipoles—is now identified in a semiconductor. Laser-excited electron–hole pairs spontaneously polarize and then abruptly decay to produce intense pulses of light.
- G. Timothy Noe II
- , Ji-Hee Kim
- & Junichiro Kono

 Single molecule ready to couple
Single molecule ready to couple Radiation for cooler cities
Radiation for cooler cities All the colours of the rainbow
All the colours of the rainbow The measure of a cell
The measure of a cell One mode at a time
One mode at a time Hot emission by design
Hot emission by design Bigger is better
Bigger is better Photonic crystal maze
Photonic crystal maze Wings of a butterfly
Wings of a butterfly Sound cans
Sound cans Symphony of lights
Symphony of lights