Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Phonon slowdown
Phonon slowdown
A detailed understanding of phonon transport is crucial for engineering the thermal properties of materials. A particular doping strategy is now shown to lead to good thermoelectric performance with low thermal conductivity.
- Zhilun Lu
-
-
Research Briefing |
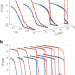 A multilayer superconductor acts as an interdependent network
A multilayer superconductor acts as an interdependent network
An experimental platform comprising two disordered superconductors separated by a thermally conducting electrical insulator represents a controllable physical system of interdependent networks. This system is modelled by thermally coupled networks of Josephson junctions. This platform could provide insights into theoretical multiscale phenomena, such as cascading tipping points or self-organized branching processes.
-
Article
| Open Access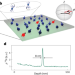 Probing many-body dynamics in a two-dimensional dipolar spin ensemble
Probing many-body dynamics in a two-dimensional dipolar spin ensemble
Solid-state systems are established candidates to study models of many-body physics but have limited control and readout capabilities. Ensembles of defects in diamond may provide a solution for studying dipolar systems.
- E. J. Davis
- , B. Ye
- & N. Y. Yao
-
Article |
 Visualization of bulk and edge photocurrent flow in anisotropic Weyl semimetals
Visualization of bulk and edge photocurrent flow in anisotropic Weyl semimetals
Understanding the fundamental mechanisms of photocurrent generation is important for photodetector design. Now, the anisotropy of the thermal properties of Weyl semimetals is shown to generate circulating photocurrents.
- Yu-Xuan Wang
- , Xin-Yue Zhang
- & Brian B. Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast X-ray imaging of the light-induced phase transition in VO2
Ultrafast X-ray imaging of the light-induced phase transition in VO2
The intermediate states in photo-excited phase transitions are expected to be inhomogeneous. However, ultrafast X-ray imaging shows the early part of the metal–insulator transition in VO2 is homogeneous but then becomes heterogeneous.
- Allan S. Johnson
- , Daniel Perez-Salinas
- & Simon E. Wall
-
Article |
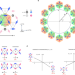 Piezomagnetic switching of the anomalous Hall effect in an antiferromagnet at room temperature
Piezomagnetic switching of the anomalous Hall effect in an antiferromagnet at room temperature
Control of magnetization is important for applications in spintronics. Now, the piezomagnetic effect allows strain to control the anomalous Hall effect in a metal at room temperature by rotating its antiferromagnetic order.
- M. Ikhlas
- , S. Dasgupta
- & S. Nakatsuji
-
Article |
 Strained crystalline nanomechanical resonators with quality factors above 10 billion
Strained crystalline nanomechanical resonators with quality factors above 10 billion
Soft clamping reduces the dissipation of nanomechanical resonators, but this method has been limited to amorphous materials. When applied in crystalline silicon, it enables resonators with quality factors beyond ten billion.
- A. Beccari
- , D. A. Visani
- & T. J. Kippenberg
-
Article
| Open Access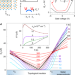 Evidence for equilibrium exciton condensation in monolayer WTe2
Evidence for equilibrium exciton condensation in monolayer WTe2
Exciton condensation has been observed in various three-dimensional (3D) materials. Now, monolayer WTe2—a 2D topological insulator—also shows the phenomenon. Strong electronic interactions allow the excitons to form and condense at high temperature.
- Bosong Sun
- , Wenjin Zhao
- & David H. Cobden
-
Article |
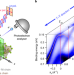 Detecting photoelectrons from spontaneously formed excitons
Detecting photoelectrons from spontaneously formed excitons
Excitons have been predicted to form spontaneously—without external excitation—in some materials. Low-temperature ARPES measurements on Ta2NiSe5 now provide evidence for such an excitonic insulator and for so-called preformed excitons.
- Keisuke Fukutani
- , Roland Stania
- & Han Woong Yeom
-
Article |
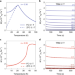 Exchange bias due to coupling between coexisting antiferromagnetic and spin-glass orders
Exchange bias due to coupling between coexisting antiferromagnetic and spin-glass orders
Coexistence of a spin-glass phase with antiferromagnetism in an intercalated crystal produces a large exchange bias effect. This is due to the interplay of disorder and frustration.
- Eran Maniv
- , Ryan A. Murphy
- & James G. Analytis
-
Letter |
 Observation of flat bands in twisted bilayer graphene
Observation of flat bands in twisted bilayer graphene
Spectroscopic measurements using nano-ARPES on twisted bilayer graphene directly highlight the presence of the flat bands.
- Simone Lisi
- , Xiaobo Lu
- & Felix Baumberger
-
Letter |
 Long-range ballistic propagation of carriers in methylammonium lead iodide perovskite thin films
Long-range ballistic propagation of carriers in methylammonium lead iodide perovskite thin films
Charge-carrier dynamics are fundamental to the operation and performance of semiconductor devices. In methylammonium lead iodide perovskites, carriers in the non-equilibrium regime after excitation propagate ballistically over 150 nm within 20 fs.
- Jooyoung Sung
- , Christoph Schnedermann
- & Akshay Rao
-
Letter |
 Giant gate-controlled proximity magnetoresistance in semiconductor-based ferromagnetic–non-magnetic bilayers
Giant gate-controlled proximity magnetoresistance in semiconductor-based ferromagnetic–non-magnetic bilayers
The authors demonstrate magnetoresistance of 80% from a two-dimensional electron gas proximity coupled to a ferromagnetic layer. This extends spintronics functionality to semiconductor devices.
- Kosuke Takiguchi
- , Le Duc Anh
- & Masaaki Tanaka
-
Letter |
 Giant anomalous Nernst effect and quantum-critical scaling in a ferromagnetic semimetal
Giant anomalous Nernst effect and quantum-critical scaling in a ferromagnetic semimetal
A magnetic field and temperature gradient produce a large electric potential in a ferromagnet, indicating the possible presence of Weyl points. The specific structure of Weyl points gives the electrons quantum-critical properties.
- Akito Sakai
- , Yo Pierre Mizuta
- & Satoru Nakatsuji
-
Review Article |
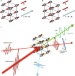 Antiferromagnetic opto-spintronics
Antiferromagnetic opto-spintronics
An overview of how electromagnetic radiation can be used for probing and modification of the magnetic order in antiferromagnets, and possible future research directions.
- P. Němec
- , M. Fiebig
- & A. V. Kimel
-
-
Review Article |
 Emergent functions of quantum materials
Emergent functions of quantum materials
Topology and collective phenomena give quantum materials emergent functions that provide a platform for developing next-generation quantum technologies, as surveyed in this Review.
- Yoshinori Tokura
- , Masashi Kawasaki
- & Naoto Nagaosa
-
Article |
 Coexistence of ultra-long spin relaxation time and coherent charge transport in organic single-crystal semiconductors
Coexistence of ultra-long spin relaxation time and coherent charge transport in organic single-crystal semiconductors
A linear relationship between spin and momentum relaxation shows that the spin relaxation in an organic semiconductor crystal that has ultra-long spin lifetimes and coherent band-like transport is governed by the Elliott–Yafet mechanism.
- Junto Tsurumi
- , Hiroyuki Matsui
- & Jun Takeya
-
News & Views |
 The anharmonicity blacksmith
The anharmonicity blacksmith
Anharmonicity is a property of lattice vibrations governing how they interact and how well they conduct heat. Experiments on tin selenide, the most efficient thermoelectric material known, now provide a link between anharmonicity and electronic orbitals.
- Joseph P. Heremans
-
Article |
 Orbitally driven giant phonon anharmonicity in SnSe
Orbitally driven giant phonon anharmonicity in SnSe
Tin selenide is at present the best thermoelectric conversion material. Neutron scattering results and ab initio simulations show that the large phonon scattering is due to the development of a lattice instability driven by orbital interactions.
- C. W. Li
- , J. Hong
- & O. Delaire
-
Letter |
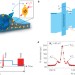 Three-stage decoherence dynamics of an electron spin qubit in an optically active quantum dot
Three-stage decoherence dynamics of an electron spin qubit in an optically active quantum dot
The mechanisms of decoherence in solid-state spin qubits subject to low magnetic fields turn out to be more complex than previously expected as an additional fast relaxation stage has now been identified.
- Alexander Bechtold
- , Dominik Rauch
- & Jonathan J. Finley
-
News & Views |
 The birth of an exciton
The birth of an exciton
The photons that make up visible light are indivisible. But certain organic materials can use singlet fission to divide the energy from one photon equally between two molecules. Experiments now reveal the molecular dynamics behind this phenomenon.
- Troy Van Voorhis
-
Letter |
 Orbital textures and charge density waves in transition metal dichalcogenides
Orbital textures and charge density waves in transition metal dichalcogenides
A theoretical and experimental study reveals the relation between charge density waves and orbital textures for different stackings in a two-dimensional layered material.
- T. Ritschel
- , J. Trinckauf
- & J. Geck
-
Article |
 Evidence for conical intersection dynamics mediating ultrafast singlet exciton fission
Evidence for conical intersection dynamics mediating ultrafast singlet exciton fission
A vibrational wavepacket generated in a spin singlet is shown to be transferable to spin triplets during singlet fission in organic semiconductors, providing a link between multi-molecular singlet fission and single-molecular internal conversion.
- Andrew J. Musser
- , Matz Liebel
- & Philipp Kukura
-
Letter |
 Dynamics and inertia of skyrmionic spin structures
Dynamics and inertia of skyrmionic spin structures
Understanding the motion of magnetic skyrmions is essential if they are to be used as information carriers in devices. It is now shown that topological confinement endows the skyrmions with an unexpectedly large mass, which plays a key role in their dynamics.
- Felix Büttner
- , C. Moutafis
- & S. Eisebitt
-
News & Views |
 Power inequality
Power inequality
Non-reciprocal components are useful in microwave engineering and photonics, but they are not without their drawbacks. A compact design now provides non-reciprocity without resorting to magnets or nonlinearity.
- Ari Sihvola
-
Letter |
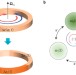 Magnetic-free non-reciprocity and isolation based on parametrically modulated coupled-resonator loops
Magnetic-free non-reciprocity and isolation based on parametrically modulated coupled-resonator loops
Communication systems require non-reciprocal electromagnetic propagation, which is difficult to realize in circuits. An alternative is demonstrated by modulating the phase of strongly coupled resonators in a circular configuration.
- Nicholas A. Estep
- , Dimitrios L. Sounas
- & Andrea Alù
-
-
News & Views |
 Orbital control
Orbital control
On cooling, transition metal oxides often undergo a phase change from an electrically conducting to an insulating state. Now it is shown that the metal–insulator transition temperature of vanadium dioxide thin films can be controlled by applying strain.
- Takashi Mizokawa
-
News & Views |
 To see a SAW
To see a SAW
Mechanical oscillations of microscopic resonators have recently been observed in the quantum regime. This idea could soon be extended from localized vibrations to travelling waves thanks to a sensitive probe of so-called surface acoustic waves.
- Aashish Clerk
-
Article |
 Local probing of propagating acoustic waves in a gigahertz echo chamber
Local probing of propagating acoustic waves in a gigahertz echo chamber
Mechanical oscillations of microscopic resonators have recently been observed in the quantum regime. This idea could soon be extended from localized vibrations to travelling waves thanks to a sensitive probe of so-called surface acoustic waves.
- Martin V. Gustafsson
- , Paulo V. Santos
- & Per Delsing

 Coupling to octahedral tilts in halide perovskite nanocrystals induces phonon-mediated attractive interactions between excitons
Coupling to octahedral tilts in halide perovskite nanocrystals induces phonon-mediated attractive interactions between excitons Physics in a cocktail glass
Physics in a cocktail glass