News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access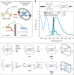 Suppression of Dexter transfer by covalent encapsulation for efficient matrix-free narrowband deep blue hyperfluorescent OLEDs
Suppression of Dexter transfer by covalent encapsulation for efficient matrix-free narrowband deep blue hyperfluorescent OLEDs
Suppressed Dexter transfer is needed to achieve efficient and stable hyperfluorescence, but complex matrices must be involved. A molecular design strategy has been proposed where Dexter transfer can be substantially reduced by an encapsulated terminal emitter, leading to ‘matrix-free’ hyperfluorescence.
- Hwan-Hee Cho
- , Daniel G. Congrave
- & Hugo Bronstein
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast vibrational control of organohalide perovskite optoelectronic devices using vibrationally promoted electronic resonance
Ultrafast vibrational control of organohalide perovskite optoelectronic devices using vibrationally promoted electronic resonance
Optically stimulated vibrational control for materials has the potential to improve the performance of optoelectronic devices. The vibrational control of FAPbBr3 perovskite solar cells has been demonstrated, where the fast dynamics of coupling between cations and inorganic sublattice may suppress non-radiative recombinations in perovskites, leading to reduced voltage losses.
- Nathaniel. P. Gallop
- , Dmitry R. Maslennikov
- & Artem A. Bakulin
-
Research Briefing |
 A spin-optical monolayer laser based on a photonic spin lattice
A spin-optical monolayer laser based on a photonic spin lattice
Inspired by valley pseudospins in two-dimensional materials, high-quality-factor (high-Q) spin–valley states were created through the photonic Rashba-type spin splitting of a bound state in the continuum. This approach enabled the construction of a coherent and controllable spin-optical laser using monolayer-integrated spin–valley microcavities without requiring magnetic fields or cryogenic temperatures.
-
Research Briefing |
 Large-bandgap organic semiconductors with trap-free charge transport
Large-bandgap organic semiconductors with trap-free charge transport
By optimizing the molecular organization of blue-emitting organic semiconductors, the vulnerability of the materials to extrinsic impurities that cause charge trapping, such as oxygen and water, is strongly reduced. Steric shielding of the electron-transporting core is shown to increase the electron transport by several orders of magnitude.
-
Article |
 Spin-valley Rashba monolayer laser
Spin-valley Rashba monolayer laser
The authors introduce a spin-optical laser based on a monolayer transition metal dichalcogenide coupled to a heterostructure microcavity supporting high-Q spin-valley resonances originating from photonic Rashba-type spin splitting of a bound state in the continuum.
- Kexiu Rong
- , Xiaoyang Duan
- & Erez Hasman
-
Research Briefing |
 A strategy for obtaining AlN heteroepitaxial films with high crystalline quality
A strategy for obtaining AlN heteroepitaxial films with high crystalline quality
High-quality aluminium nitride (AlN) heteroepitaxial films are obtained by the controlled discretization and coalescence of columns using nanopatterned AlN/sapphire templates with regular hexagonal holes. The density of dislocation etch pits in the AlN heteroepitaxial films is reduced to approximately 104 cm–2, approaching the value of that in AlN bulk single crystals.
-
Article |
 Group-III nitride heteroepitaxial films approaching bulk-class quality
Group-III nitride heteroepitaxial films approaching bulk-class quality
High-quality AlN heteroepitaxial films are obtained by controllable discretization and coalescence of columns on nano-patterned AlN/sapphire templates with hexagonal holes, where the density of dislocation etch pits is greatly reduced to ~10 × 104 cm−2.
- Jiaming Wang
- , Nan Xie
- & Bo Shen
-
Letter |
 Compact spin-valley-locked perovskite emission
Compact spin-valley-locked perovskite emission
We report compact spin-valley-locked perovskite emitting metasurfaces where spin-dependent geometric phases are imparted into bound states in the continuum via Brillouin zone folding, simultaneously enabling chiral purity, directionality and large emission angles.
- Yang Chen
- , Jiangang Feng
- & Cheng-Wei Qiu
-
Article |
 High-efficiency stretchable light-emitting polymers from thermally activated delayed fluorescence
High-efficiency stretchable light-emitting polymers from thermally activated delayed fluorescence
We synthesized stretchable electroluminescent polymers capable of reaching a near-unity theoretical quantum yield through thermally activated delayed fluorescence. Their polymers show 125% stretchability with 10% external quantum efficiency and demonstrate a fully stretchable organic light-emitting diode.
- Wei Liu
- , Cheng Zhang
- & Sihong Wang
-
Article |
 Dielectric control of reverse intersystem crossing in thermally activated delayed fluorescence emitters
Dielectric control of reverse intersystem crossing in thermally activated delayed fluorescence emitters
The role of the dielectric environment in thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) is not yet fully understood. Here the authors reveal the relevance of environment–emitter interactions in gating the reverse intersystem crossing and its particular relevance in dipolar TADF emitters.
- Alexander J. Gillett
- , Anton Pershin
- & David Beljonne
-
Article |
 Thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) organic molecules for efficient X-ray scintillation and imaging
Thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) organic molecules for efficient X-ray scintillation and imaging
Triplet exciton harvesting through thermally activated delayed fluorescence is shown to be effective also under X-ray excitation, increasing the efficiency and imaging quality of X-ray detectors based on organic scintillation.
- Wenbo Ma
- , Yirong Su
- & Yang Michael Yang
-
Perspective |
 Perovskite semiconductors for room-temperature exciton-polaritonics
Perovskite semiconductors for room-temperature exciton-polaritonics
An outlook on the potential of lead-halide perovskites as a playground for exciton-polariton studies and for the development of polaritonic devices operating at room temperature is provided.
- Rui Su
- , Antonio Fieramosca
- & Qihua Xiong
-
Review Article |
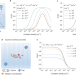 Metal halide perovskites for light-emitting diodes
Metal halide perovskites for light-emitting diodes
The development of perovskite emitters, their use in light-emitting devices, and the challenges in enhancing the efficiency and stability, as well as reducing the potential toxicity of this technology are discussed in this Review.
- Xiao-Ke Liu
- , Weidong Xu
- & Feng Gao
-
Article |
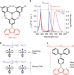 Understanding the luminescent nature of organic radicals for efficient doublet emitters and pure-red light-emitting diodes
Understanding the luminescent nature of organic radicals for efficient doublet emitters and pure-red light-emitting diodes
An investigation on the electronic transitions of organic radicals allows us to identify design rules to increase the oscillator strength of these emitters and obtain efficient radical-based light-emitting diodes operating in the visible range.
- Alim Abdurahman
- , Timothy J. H. Hele
- & Emrys W. Evans
-
Article |
 Highly efficient luminescence from space-confined charge-transfer emitters
Highly efficient luminescence from space-confined charge-transfer emitters
The use of rigid linkers to control the relative position and interaction of donor and acceptor units in exciplex emitters leads to the realization of organic light-emitting devices with enhanced external quantum efficiency.
- Xun Tang
- , Lin-Song Cui
- & Liang-Sheng Liao
-
News & Views |
 Lasing under ultralow pumping
Lasing under ultralow pumping
Ultralow-threshold plasmonic lasers under continuous-wave pumping at room temperature have been created using lattice plasmonic cavities integrated with gain material consisting of upconverting nanoparticles.
- Ren-Min Ma
-
Letter |
 A window to trap-free charge transport in organic semiconducting thin films
A window to trap-free charge transport in organic semiconducting thin films
Water clusters induce hole traps in organic semiconductor thin films. Detrimental effects of hole and electron traps on charge transport can be avoided by using materials with ionization energy and electron affinity within an energy window of 2.4 eV.
- Naresh B. Kotadiya
- , Anirban Mondal
- & Gert-Jan A. H. Wetzelaer
-
Article |
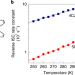 Critical role of intermediate electronic states for spin-flip processes in charge-transfer-type organic molecules with multiple donors and acceptors
Critical role of intermediate electronic states for spin-flip processes in charge-transfer-type organic molecules with multiple donors and acceptors
Triplet excited states related to partial molecular structures are shown to mediate spin-flip between lowest singlet and triplet excited states in multiple donor–acceptor charge-transfer-type organic molecules.
- Hiroki Noda
- , Xian-Kai Chen
- & Chihaya Adachi
-
News & Views |
 Radically more stable
Radically more stable
Violating the Aufbau principle is shown to be a successful strategy to improve the stability of neutral organic radicals used in organic light-emitting diodes.
- Sebastian Reineke
-
News & Views |
 Organic LEDs and solar cells united
Organic LEDs and solar cells united
Organic donor–acceptor heterojunctions can show efficient electroluminescence and at the same time generate charges under photovoltaic operation.
- Wolfgang Brütting
-
News & Views |
 Lasers that shine brighter
Lasers that shine brighter
A photonic crystal design, consisting of two separated lattices arranged in a specific way, forms the base of high-brightness semiconductor lasers, with a very narrow beam divergence angle.
- L. Kuipers
-
Article |
 Double-lattice photonic-crystal resonators enabling high-brightness semiconductor lasers with symmetric narrow-divergence beams
Double-lattice photonic-crystal resonators enabling high-brightness semiconductor lasers with symmetric narrow-divergence beams
An optimized design for a broad-area surface-emitting photonic-crystal laser leads to high brightness of over 300 MW cm–2 sr–1 and an output power of 10 W under pulsed excitation.
- Masahiro Yoshida
- , Menaka De Zoysa
- & Susumu Noda
-
Article |
 Electron–phonon interaction in efficient perovskite blue emitters
Electron–phonon interaction in efficient perovskite blue emitters
Films of exfoliated crystals of two-dimensional hybrid metal halide perovskites with phenyl groups as organic cations show increased molecular rigidity, reduced electron–phonon interactions and blue emission with photoluminescence quantum yield approaching 80%.
- Xiwen Gong
- , Oleksandr Voznyy
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Article |
 Hole trap formation in polymer light-emitting diodes under current stress
Hole trap formation in polymer light-emitting diodes under current stress
Quantitative analysis of polymer LED degradation under current stress provides insight on the role of hole traps and their formation. Blending of the emitting material with large-bandgap semiconductors leads to trap dilution and improved stability.
- Quan Niu
- , Roland Rohloff
- & N. Irina Crăciun
-
News & Views |
 Electrifying quantum dots for lasers
Electrifying quantum dots for lasers
Compositional grading of colloidal quantum dots enables electrically driven amplification of light, bringing electrically driven lasers from these materials very close.
- Ifor Samuel
-
Article |
 Optical gain in colloidal quantum dots achieved with direct-current electrical pumping
Optical gain in colloidal quantum dots achieved with direct-current electrical pumping
Core/shell type-I semiconductor nanocrystals with compositionally graded shell and embedded in a current-focusing device architecture reach population inversion, a condition required for lasing, when excited with direct current.
- Jaehoon Lim
- , Young-Shin Park
- & Victor I. Klimov
-
Article |
 Beating the thermodynamic limit with photo-activation of n-doping in organic semiconductors
Beating the thermodynamic limit with photo-activation of n-doping in organic semiconductors
The activation of cleavable organometallic dimers upon exposure to ultraviolet radiation allows air-stable n-type doping of organic materials with electron affinity lower than the expected thermodynamic reducing strength of the dimers.
- Xin Lin
- , Berthold Wegner
- & Antoine Kahn
-
News & Views |
 Stabilizing colour and intensity
Stabilizing colour and intensity
Thermally activated defects in a blue-emitting phosphor can enhance energy transfer to the activator, and compensate for thermal quenching.
- Philippe F. Smet
- & Jonas J. Joos
-
Article |
 A zero-thermal-quenching phosphor
A zero-thermal-quenching phosphor
A blue-emitting phosphor without thermal quenching is reported. The emission losses at high temperatures are compensated by a counter mechanism, originating in energy transfer between electron–hole pairs and thermally activated defect levels.
- Yoon Hwa Kim
- , Paulraj Arunkumar
- & Won Bin Im
-
Editorial |
 Shiny condensates
Shiny condensates
Commercialization of exciton–polariton research as well as investigation of exciting physical phenomena in exciton–polariton condensates relies on improving material properties.
-
News & Views |
 High-throughput virtual screening
High-throughput virtual screening
Computer networks, trained with data from delayed-fluorescence materials that have been successfully used in organic light-emitting diodes, facilitate the high-speed prediction of good emitters for display and lighting applications.
- Shuzo Hirata
- & Katsuyuki Shizu
-
Commentary |
 Physics and applications of exciton–polariton lasers
Physics and applications of exciton–polariton lasers
Although exciton–polariton lasers have been experimentally demonstrated in a variety of material systems, robust practical implementations are still challenging. Similarities with atomic Bose–Einstein condensates make the system suitable for chip-based quantum simulators for non-trivial many-body physics.
- Michael D. Fraser
- , Sven Höfling
- & Yoshihisa Yamamoto
-
Article |
 Design of efficient molecular organic light-emitting diodes by a high-throughput virtual screening and experimental approach
Design of efficient molecular organic light-emitting diodes by a high-throughput virtual screening and experimental approach
A high-throughput virtual screening approach is used to select molecules with efficient, thermally activated delayed fluorescence. The good performance of several selected emitters in organic LED applications has also been confirmed experimentally.
- Rafael Gómez-Bombarelli
- , Jorge Aguilera-Iparraguirre
- & Alán Aspuru-Guzik
-
-
Review Article |
 The road towards polaritonic devices
The road towards polaritonic devices
This review discusses exciton–polaritons in microcavities and their emerging technological applications, with emphasis on the materials challenges for operation at room temperature.
- Daniele Sanvitto
- & Stéphane Kéna-Cohen
-
Feature |
 China's first pulsed neutron source
China's first pulsed neutron source
The China Spallation Neutron Source is expected to produce its first beam in 2017. Hesheng Chen and Xun-Li Wang provide an overview of this user facility and what it means for science in China and elsewhere.
- Hesheng Chen
- & Xun-Li Wang
-
Editorial |
 Extreme light
Extreme light
The Extreme Light Infrastructure (ELI) project is dedicated to the investigation of light–matter interactions at high laser intensities and on short timescales.
-
-
News & Views |
 Lower threshold for nanowire lasers
Lower threshold for nanowire lasers
Hybrid perovskite is introduced as a new material for nanowire lasers. One-dimensional nanostructures of these perovskites can be optically pumped to lase with tunable wavelength at relatively low threshold, which marks a step towards their use in integrated photonics.
- Anthony Fu
- & Peidong Yang
-
Editorial |
 Let there be light
Let there be light
Inorganic semiconductors, organic emitters and colloidal quantum dots are pushing the LED revolution in lighting and displays.
-
Commentary |
 Complementary LED technologies
Complementary LED technologies
Organic semiconducting molecules and colloidal quantum dots both make for excellent luminescent materials. Compared with the more established solid-state light-emitting technologies, organic LEDs and quantum-dot LEDs are in their infancy, yet they offer unique properties.
- Sebastian Reineke
-
Commentary |
 A revolution in lighting
A revolution in lighting
Key materials discoveries have prompted the rise of inorganic light-emitting diodes in the lighting industry. Remaining challenges are being addressed to further extend the impact of this technology in lighting, displays and other applications.
- Philipp Pust
- , Peter J. Schmidt
- & Wolfgang Schnick
-
Article |
 Lead halide perovskite nanowire lasers with low lasing thresholds and high quality factors
Lead halide perovskite nanowire lasers with low lasing thresholds and high quality factors
A surface-initiated solution growth method is used to synthesize single-crystal nanowires of organic–inorganic perovskite that show very low lasing threshold. Coating the nanowires with metallic films marginally affects the lasing performance.
- Haiming Zhu
- , Yongping Fu
- & X-Y. Zhu
-
-
News & Views |
 Lasing from 2D atomic crystals
Lasing from 2D atomic crystals
The coupling of monolayer tungsten diselenide and a photonic-crystal cavity leads to ultralow-threshold lasing.
- Vinod Menon
-
News & Views |
 Stacked 2D materials shed light
Stacked 2D materials shed light
A powerful strategy to leverage and combine the optoelectronic characteristics of different 2D materials is to stack them into vertical van der Waals heterostructures. This approach is now used to realize efficient light-emitting devices.
- Xiaomu Wang
- & Fengnian Xia
-
-
Editorial |
 Perovskite fever
Perovskite fever
Staggering increases in the performance of organic–inorganic perovskite solar cells have renewed the interest in these materials. However, further developments and the support from academic and industrial partners will hinge on the reporting of accurate efficiency values.
-
Article |
 Narrow-band red-emitting Sr[LiAl3N4]:Eu2+ as a next-generation LED-phosphor material
Narrow-band red-emitting Sr[LiAl3N4]:Eu2+ as a next-generation LED-phosphor material
For high-power white-light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to become a technological reality there is a need to find more efficient red-emitting phosphor materials. Eu2+-doped Sr[LiAl3N4], a member of the nitridoaluminates compound class, is now proved to be a high-performance narrow-band red-emitting phosphor material that can be easily coupled with existing GaN-based blue-LED technology for use in white LEDs.
- Philipp Pust
- , Volker Weiler
- & Wolfgang Schnick

 Efficient blue emitter with a hoop
Efficient blue emitter with a hoop A new twist for OLEDs
A new twist for OLEDs A 2D barrier to defects
A 2D barrier to defects