Featured
-
-
Article |
 Normal muscle regeneration requires tight control of muscle cell fusion by tetraspanins CD9 and CD81
Normal muscle regeneration requires tight control of muscle cell fusion by tetraspanins CD9 and CD81
The skeletal muscle has a remarkable capacity to regenerate after injury. Here Charrin et al. reveal that restoration of muscle architecture after injury requires a tight control of muscle cell fusion by the tetraspanin proteins CD9 and CD81 through their interaction with the cell surface protein CD9P-1.
- Stéphanie Charrin
- , Mathilde Latil
- & Eric Rubinstein
-
Article |
 Titanium dioxide nanomaterials cause endothelial cell leakiness by disrupting the homophilic interaction of VE–cadherin
Titanium dioxide nanomaterials cause endothelial cell leakiness by disrupting the homophilic interaction of VE–cadherin
Nanoparticles can accumulate in tissues but how they interact with cells is poorly understood. Here Setyawati and colleagues report that titanium dioxide nanoparticles disrupt protein complexes of the tight junction protein VE-cadherin on endothelial cells to increase blood vessel permeability.
- M.I. Setyawati
- , C.Y. Tay
- & D.T. Leong
-
Article |
 Microbiota-derived lactate accelerates colon epithelial cell turnover in starvation-refed mice
Microbiota-derived lactate accelerates colon epithelial cell turnover in starvation-refed mice
Epithelial cells in the colon mainly use microbial fermentation products as energy sources. Here Okada et al. find that lactate produced by commensal Lactobacillus murinusregulates colonic epithelial cell proliferation and show that mice are more susceptible to carcinogens when refed after a period of starvation.
- Toshihiko Okada
- , Shinji Fukuda
- & Taeko Dohi
-
Article
| Open Access A chronic model of arthritis supported by a strain-specific periarticular lymph node in BALB/c mice
A chronic model of arthritis supported by a strain-specific periarticular lymph node in BALB/c mice
Mouse models of arthritis generally do not result in both chronic disease and autoantibody production—two key features of the human disease. Here the authors obtain both features by combining two common protocols, and find that disease severity is associated with the presence of a previously unidentified lymph node.
- Uta Baddack
- , Sven Hartmann
- & Gerd Müller
-
Article |
 Sulfhydration mediates neuroprotective actions of parkin
Sulfhydration mediates neuroprotective actions of parkin
The gasotransmitter hydrogen sulfide signals by sulfide modification of target proteins. Vandiver and colleagues study the sulfhydration of parkin by hydrogen sulfide and find that sulfhydration stimulates its activity, and that this activity is reduced in patients with Parkinson’s disease.
- M. Scott Vandiver
- , Bindu D. Paul
- & Solomon H. Snyder
-
Article |
 Expansion of host cellular niche can drive adaptation of a zoonotic malaria parasite to humans
Expansion of host cellular niche can drive adaptation of a zoonotic malaria parasite to humans
The number of human infections caused by the primate malaria parasite P. knowlesi is increasing. Lim et al. demonstrate that host specificity is due to the preference of the parasite for young blood cells, and that the parasite can adapt to proliferate in human blood containing a range of differently aged cells.
- Caeul Lim
- , Elsa Hansen
- & Manoj T. Duraisingh
-
Article |
 Interstitial cells of Cajal integrate excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission with intestinal slow-wave activity
Interstitial cells of Cajal integrate excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission with intestinal slow-wave activity
Interstitial cells of Cajal generate rhythmic pacemaker currents, which result in rhythmic bowel contractions. Klein and colleagues use knock-in mutations to inactivate these cells in mice and find that they modulate bowel contractions by integrating excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission in the gut.
- Sabine Klein
- , Barbara Seidler
- & Dieter Saur
-
Article
| Open Access Telomeres shorten at equivalent rates in somatic tissues of adults
Telomeres shorten at equivalent rates in somatic tissues of adults
Telomere shortening as a result of cell proliferation has been implicated in human ageing. Here, Daniali and colleagues show that telomere length and the rate of age-dependent shortening vary between adults but are similar within tissues of the same individual.
- Lily Daniali
- , Athanase Benetos
- & Abraham Aviv
-
Article
| Open Access A model of parity-dependent immunity to placental malaria
A model of parity-dependent immunity to placental malaria
Exposure to malaria during pregnancy can result in its spread to the placenta; however, the risk of placental infection decreases with subsequent pregnancies. By constructing a mathematical model, the authors find that this is likely due to a reduction in the duration of infection rather than a reduced risk of transfer.
- Patrick G. T. Walker
- , Jamie T. Griffin
- & Azra C. Ghani
-
Article |
 Engineering the type III secretion system in non-replicating bacterial minicells for antigen delivery
Engineering the type III secretion system in non-replicating bacterial minicells for antigen delivery
Bacterial type III secretion systems (T3SS) improve the delivery of vaccine antigens and antigen-specific immune responses but require the use of live vaccines. Carleton et al. report the assembly of a functional T3SS in replication-incompetent bacterial minicells that can deliver vaccine antigens in vitro and in vivo.
- Heather A. Carleton
- , María Lara-Tejero
- & Jorge E. Galán
-
Article |
 An ex vivo gene therapy approach to treat muscular dystrophy using inducible pluripotent stem cells
An ex vivo gene therapy approach to treat muscular dystrophy using inducible pluripotent stem cells
Patient-specific induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells hold great potential for regenerative cell therapies. Here Filareto et al. genetically correct iPS cells from mice with muscular dystrophy and use these cells to treat the same animals, providing a proof-of-principle for autologous iPS cell therapy.
- Antonio Filareto
- , Sarah Parker
- & Rita C. R. Perlingeiro
-
Article |
 Human hypocretin and melanin-concentrating hormone levels are linked to emotion and social interaction
Human hypocretin and melanin-concentrating hormone levels are linked to emotion and social interaction
The emotional state of humans depends on the temporal concentration of neurochemicals. Blouin et al. measure temporal changes in two neuropeptides, hypocretin and melanin-concentrating hormone, and find that hypocretin but not melanin-concentrating hormone is linked to positive emotions and social interaction.
- Ashley M. Blouin
- , Itzhak Fried
- & Jerome M. Siegel
-
Article
| Open Access Phantom pain is associated with preserved structure and function in the former hand area
Phantom pain is associated with preserved structure and function in the former hand area
Reorganization of the sensorimotor cortex due to loss of sensory input is implicated in phantom pain. Makin and colleagues use functional MRI to show that phantom pain experience is instead associated with maintained local functional and structural cortical representations but disrupted inter-regional connectivity.
- Tamar R. Makin
- , Jan Scholz
- & Heidi Johansen-Berg
-
Article |
 Aldara activates TLR7-independent immune defence
Aldara activates TLR7-independent immune defence
The skin cancer treatment Aldara generates psoriasis-like symptoms in mice, which are thought to be due to stimulation of TLR7 by the active ingredient imiquimod. The authors show that some of these inflammatory effects are independent of both imiquimod and TLR7, implicating an unexpected role for the vehicle.
- Anne Walter
- , Matthias Schäfer
- & Maries van den Broek
-
Article |
 Loss of TRPM2 function protects against irradiation-induced salivary gland dysfunction
Loss of TRPM2 function protects against irradiation-induced salivary gland dysfunction
A debilitating side effect of radiotherapy in patients with head and neck cancers is xerostomia as a result of salivary gland dysfunction. Here Liu et al. show that activation of the calcium channel TRPM2 in salivary gland cells contributes to irradiation-induced loss of salivary fluid secretion.
- Xibao Liu
- , Ana Cotrim
- & Indu Ambudkar
-
Article |
 Holographic optogenetic stimulation of patterned neuronal activity for vision restoration
Holographic optogenetic stimulation of patterned neuronal activity for vision restoration
Photo-stimulation can be used to control neuronal circuits, but current strategies lack optimal precision and resolution. Reutsky-Gefen et al. demonstrate a potential approach for vision restoration via holographically patterned, optogenetic stimulation of retinal ganglion cells, with temporal precision.
- Inna Reutsky-Gefen
- , Lior Golan
- & Shy Shoham
-
Article |
 De novo lipogenesis in human fat and liver is linked to ChREBP-β and metabolic health
De novo lipogenesis in human fat and liver is linked to ChREBP-β and metabolic health
Changes in the biosynthesis of fatty acids can influence tissue insulin sensitivity and the development of metabolic diseases. Eissing and colleagues show that de novolipogenesis in liver and adipose tissue is linked to metabolic health in humans and can be modulated by bariatric surgery.
- Leah Eissing
- , Thomas Scherer
- & Ludger Scheja
-
Article
| Open Access GRK6 deficiency in mice causes autoimmune disease due to impaired apoptotic cell clearance
GRK6 deficiency in mice causes autoimmune disease due to impaired apoptotic cell clearance
The clearance of apoptotic cells by macrophages is important for tissue homoeostasis. Here Nakaya et al. reveal a role for GRK6 in the regulation of apoptotic engulfment and show that GRK6 deficiency in mice leads to autoimmune disease and iron accumulation in the spleen.
- Michio Nakaya
- , Mitsuru Tajima
- & Hitoshi Kurose
-
Article |
 Parasympathetic stimulation improves epithelial organ regeneration
Parasympathetic stimulation improves epithelial organ regeneration
Irradiation treatment for cancer therapy often causes irreparable damage to adult organs. Knox and colleagues study irradiated mouse submandibular salivary glands and find that restoring parasympathetic nerve function with the neurotrophic factor neurturin improves regeneration.
- Sarah M. Knox
- , Isabelle M. A. Lombaert
- & Matthew P. Hoffman
-
Article |
 Smoking exacerbates amyloid pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Smoking exacerbates amyloid pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
A link between smoking and the incidence of Alzheimer’s disease has been implicated in humans. In this study, transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease exposed to cigarette smoke display increased disease abnormalities in the brain, such as amyloidogenesis, neuroinflammation and tau phosphorylation.
- Ines Moreno-Gonzalez
- , Lisbell D. Estrada
- & Claudio Soto
-
Article |
 High-throughput hyperdimensional vertebrate phenotyping
High-throughput hyperdimensional vertebrate phenotyping
Large-scale screening of animal phenotypes requires automated detection and analysis of complex morphological information. Here, Yanik and colleagues present an imaging system based on optical projection tomography that generates micrometre-resolution 3D images of zebrafish larvae with within tens of seconds per animal.
- Carlos Pardo-Martin
- , Amin Allalou
- & Mehmet Fatih Yanik
-
Article
| Open Access Genome of the Chinese tree shrew
Genome of the Chinese tree shrew
The Chinese tree shrew, Tupaia belangeri chinensis, has been proposed as a potential animal model in biomedical research and drug safety testing. This study presents the full genome of the Chinese tree shrew, identifying common features between the tree shrew and primates.
- Yu Fan
- , Zhi-Yong Huang
- & Yong-Gang Yao
-
Article
| Open Access Interferon-induced transmembrane protein-3 genetic variant rs12252-C is associated with severe influenza in Chinese individuals
Interferon-induced transmembrane protein-3 genetic variant rs12252-C is associated with severe influenza in Chinese individuals
A variant in the IFITM3gene increases the risk of severe influenza, but homozygosity is rare in Caucasians. The authors show that the variant gene is homozygous in 25% of healthy Chinese people, and 69% of those with severe pandemic influenza, suggesting that this gene influences the epidemiology of influenza in South-East Asia.
- Yong-Hong Zhang
- , Yan Zhao
- & Tao Dong
-
Article |
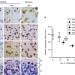 Heat shock factor-1 influences pathological lesion distribution of polyglutamine-induced neurodegeneration
Heat shock factor-1 influences pathological lesion distribution of polyglutamine-induced neurodegeneration
Heat shock factor-1 is a transcriptional regulator of heat shock proteins that is implicated in neurodegeneration. Kondo and colleagues study the effects of deleting heat shock factor-1 in a mouse model of muscular dystrophy and find that this augments the condition via the accumulation of androgen receptors.
- Naohide Kondo
- , Masahisa Katsuno
- & Gen Sobue
-
Article
| Open Access In vitro fabrication of functional three-dimensional tissues with perfusable blood vessels
In vitro fabrication of functional three-dimensional tissues with perfusable blood vessels
Artificially engineered tissues may have many therapeutic applications but complex tissues are hard to create in vitro. Here, Okano and colleagues report the production of functional cardiac tissue sheets with perfusable blood vessels, which increase the thickness and survival of transplanted tissue.
- Hidekazu Sekine
- , Tatsuya Shimizu
- & Teruo Okano
-
Article |
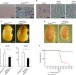 The phosphatase Dullard negatively regulates BMP signalling and is essential for nephron maintenance after birth
The phosphatase Dullard negatively regulates BMP signalling and is essential for nephron maintenance after birth
Kidney maintenance and function are essential for a healthy organism. Here Nishinakamura and colleagues show that the phosphatase Dullard suppresses BMP signalling and apoptosis in the mouse kidney and that Dullard is required for the maintenance of functional nephrons after birth.
- Masaji Sakaguchi
- , Sazia Sharmin
- & Ryuichi Nishinakamura
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial association with PTEX complexes defines regions for effector export into Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes
Spatial association with PTEX complexes defines regions for effector export into Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes
During red blood cell infection, malaria parasites export hundreds of proteins that remodel the host cell surface. Cowman and colleagues identify a putative protein translocator complex spatially associated with exported proteins, revealing the cellular domains involved in protein export.
- David T. Riglar
- , Kelly L. Rogers
- & Alan F. Cowman
-
Article
| Open Access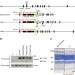 A point mutation in Semaphorin 4A associates with defective endosomal sorting and causes retinal degeneration
A point mutation in Semaphorin 4A associates with defective endosomal sorting and causes retinal degeneration
Semaphorin 4A is implicated in photoreceptor survival. Nojima and colleagues generate transgenic mice with different mutations in the Sema4A gene and find that point mutation of F350 causes severe degeneration in photoreceptor cells, which can be rescued by virus-mediated gene therapy.
- Satoshi Nojima
- , Toshihiko Toyofuku
- & Atsushi Kumanogoh
-
Article
| Open Access Computational identification of a transiently open L1/S3 pocket for reactivation of mutant p53
Computational identification of a transiently open L1/S3 pocket for reactivation of mutant p53
About 40% of human cancers carry missense mutations in the tumour suppressor protein p53. Here the authors identify a transiently open pocket in the protein, and by targeting a small molecule to it, partially restore mutant p53 tumour suppressor activity.
- Christopher D. Wassman
- , Roberta Baronio
- & Rommie E. Amaro
-
Article |
 A novel pathway for the production of hydrogen sulfide from D-cysteine in mammalian cells
A novel pathway for the production of hydrogen sulfide from D-cysteine in mammalian cells
Hydrogen sulphide is a signalling molecule with cytoprotective activity in mammals. Here, Kimura and colleagues identify a new biosynthetic pathway for the production of hydrogen sulphide from D-cysteine, which is shown to protect mouse kidneys from oxidative stress after ischaemia/reperfusion injury.
- Norihiro Shibuya
- , Shin Koike
- & Hideo Kimura
-
Article
| Open Access On-demand optogenetic control of spontaneous seizures in temporal lobe epilepsy
On-demand optogenetic control of spontaneous seizures in temporal lobe epilepsy
Temporal lobe epilepsy in adults does not always respond to treatment. Krook-Magnuson and colleagues use optogenetics to inhibit and activate excitatory and inhibitory neurons, respectively, in a mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy, and find that they can stop seizures on a moment-to-moment basis.
- Esther Krook-Magnuson
- , Caren Armstrong
- & Ivan Soltesz
-
Article |
 MicroRNA-30c inhibits human breast tumour chemotherapy resistance by regulating TWF1 and IL-11
MicroRNA-30c inhibits human breast tumour chemotherapy resistance by regulating TWF1 and IL-11
The role of microRNAs in chemotherapy resistance remains to be elucidated. Bockhorn et al.report that microRNA-30c, a human breast tumour prognostic marker, has a key role by targeting the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition promoter twinfilin 1 and downstream interleukin-11 expression.
- Jessica Bockhorn
- , Rachel Dalton
- & Huiping Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Proteome-wide selected reaction monitoring assays for the human pathogen Streptococcus pyogenes
Proteome-wide selected reaction monitoring assays for the human pathogen Streptococcus pyogenes
Selected reaction monitoring mass spectrometry (SRM-MS) can quantify dynamic changes in protein expression with high sensitivity. Karlsson et al. define optimal detection parameters for 10,412 distinct group A Streptococcus pyogenespeptides, which facilitates proteome-wide SRM-MS studies in this bacterium.
- Christofer Karlsson
- , Lars Malmström
- & Johan Malmström
-
Article |
 Elevated oncofoetal miR-17-5p expression regulates colorectal cancer progression by repressing its target gene P130
Elevated oncofoetal miR-17-5p expression regulates colorectal cancer progression by repressing its target gene P130
Tumorigenesis has been likened to a form of cellular reversion to the embryonic state. Ma et al.identify a foetal miRNA as an oncogenic activator of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in colorectal cancer, whose expression is negatively correlated with survival but is positively correlated with response to adjuvant chemotherapy.
- Yanlei Ma
- , Peng Zhang
- & Huanlong Qin
-
Article
| Open Access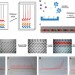 Multiplexed volumetric bar-chart chip for point-of-care diagnostics
Multiplexed volumetric bar-chart chip for point-of-care diagnostics
Diagnostic microfluidic devices often require complicated optical systems and computers to quantify results. Here, Qin and colleagues link enzymatic biomarker detection with the displacement of ink, resulting in a device that displays quantitative results as bar graphs directly on the device.
- Yujun Song
- , Yuanqing Zhang
- & Lidong Qin
-
Article |
 A role for calpain-dependent cleavage of TDP-43 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis pathology
A role for calpain-dependent cleavage of TDP-43 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis pathology
The mislocalization and downregulation of the proteins TDP-43 and ADAR2, respectively, are implicated in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis pathology. Yamashita et al. find that downregulation of ADAR2 results in calcium-permeable AMPA receptor-mediated calpain activation and subsequent aberrant cleavage of TDP-43.
- Takenari Yamashita
- , Takuto Hideyama
- & Shin Kwak
-
Article
| Open Access Exhaustion of nucleus pulposus progenitor cells with ageing and degeneration of the intervertebral disc
Exhaustion of nucleus pulposus progenitor cells with ageing and degeneration of the intervertebral disc
Back pain and sciatica are often caused by intervertebral disc degeneration. Sakai and colleagues identify a subset of nucleus pulposus progenitor cells from the intervertebral disc and show that loss of these progenitor cells correlates with ageing and intervertebral disc degeneration.
- Daisuke Sakai
- , Yoshihiko Nakamura
- & Joji Mochida
-
Article
| Open Access Symptomatic atherosclerosis is associated with an altered gut metagenome
Symptomatic atherosclerosis is associated with an altered gut metagenome
The gut microbiota has emerged as an environmental factor that can influence the development of obesity and diabetes. Here, Karlsson et al. report compositional and functional alterations of the gut metagenome in patients with symptomatic atherosclerosis.
- Fredrik H. Karlsson
- , Frida Fåk
- & Jens Nielsen
-
Article
| Open Access Factors determining the occurrence of submicroscopic malaria infections and their relevance for control
Factors determining the occurrence of submicroscopic malaria infections and their relevance for control
Malaria can persist at levels that escape detection by standard microscopy, but can be detected by PCR. Okell et al.now show that rates of submicroscopic infection can be predicted using more widely available microscopy data, and are most epidemiologically significant in areas with low malaria transmission.
- Lucy C. Okell
- , Teun Bousema
- & Chris J. Drakeley
-
Article |
 Molecular mechanism of the assembly of an acid-sensing receptor ion channel complex
Molecular mechanism of the assembly of an acid-sensing receptor ion channel complex
Polycystic kidney disease family proteins form heteromeric complexes with transient receptor potential channel subunits of the TRPP subfamily. Yu and colleagues find that the polycystic kidney disease protein, PKD1L3, is an ion channel pore-forming subunit in the acid-sensing PKD1L3/TRPP3 complex.
- Yong Yu
- , Maximilian H. Ulbrich
- & Jian Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Fibrinogen-induced perivascular microglial clustering is required for the development of axonal damage in neuroinflammation
Fibrinogen-induced perivascular microglial clustering is required for the development of axonal damage in neuroinflammation
Multiple sclerosis is characterized by the activation of microglia cells. Davalos et al. investigate the early stages of neuroinflammation in mice and reveal that the plasma protein fibrinogen induces microglial clustering around the brain vasculature, which facilitates lesion formation and focal axonal damage.
- Dimitrios Davalos
- , Jae Kyu Ryu
- & Katerina Akassoglou
-
Article |
 Chimpanzees and humans harbour compositionally similar gut enterotypes
Chimpanzees and humans harbour compositionally similar gut enterotypes
Humans tend to adopt one of a limited number of different bacterial community structures in the gut, known as enterotypes. Moeller et al.now show that these microbial fingerprints are conserved in chimpanzees, and that individuals can switch between enterotypes over periods of several years.
- Andrew H. Moeller
- , Patrick H. Degnan
- & Howard Ochman
-
Article |
 Detection and differential diagnosis of colon cancer by a cumulative analysis of promoter methylation
Detection and differential diagnosis of colon cancer by a cumulative analysis of promoter methylation
Changes in the methylation pattern of gene promoters are hallmarks of certain cancers, such as colon cancer. Here Yang et al.identify and validate a set of genes and measure the cumulative methylation of promoters, which allows them to distinguish between two stages of colon cancer.
- Qiong Yang
- , Ying Dong
- & Shu Wang
-
Article |
 The metastasis-promoting S100A4 protein confers neuroprotection in brain injury
The metastasis-promoting S100A4 protein confers neuroprotection in brain injury
Multifunctional S100 proteins are upregulated in brain injury, but their role in neurodegeneration is not clear. Dmytriyeva and colleagues study in vivomodels of brain trauma and find that the S100A4 protein and its peptide mimetics protect neurons via the interleukin-10 receptor and the Janus kinase (JAK)/STAT pathway.
- Oksana Dmytriyeva
- , Stanislava Pankratova
- & Darya Kiryushko
-
Article |
 A peptide derived from laminin-γ3 reversibly impairs spermatogenesis in rats
A peptide derived from laminin-γ3 reversibly impairs spermatogenesis in rats
The temporal opening and closing of cell–cell junctions at the blood–testis barrier allows the passage of immature germ cells during spermatogenesis. Su and colleagues identify a peptide fragment of the laminin-γ3 chain that disrupts the blood–testis barrier and reversibly impairs spermatogenesis in rats.
- Linlin Su
- , Dolores D. Mruk
- & C. Yan Cheng
-
Article |
 Sos-mediated cross-activation of wild-type Ras by oncogenic Ras is essential for tumorigenesis
Sos-mediated cross-activation of wild-type Ras by oncogenic Ras is essential for tumorigenesis
The ras family of oncogenes consists of H-ras, K-ras and N-ras, and usually only one of these genes is mutated in a given tumour type. In this study, K-ras is found to promote the activation of wild-type H-ras and N-ras in a manner dependent on the Ras guanine nucleotide exchange factor Son of sevenless.
- Hao-Hsuan Jeng
- , Laura J Taylor
- & Dafna Bar-Sagi
-
Article |
 CaV1.3-selective L-type calcium channel antagonists as potential new therapeutics for Parkinson's disease
CaV1.3-selective L-type calcium channel antagonists as potential new therapeutics for Parkinson's disease
L-type calcium channels comprising the CaV1.3 subunit have been linked to the generation of mitochondrial oxidant stress in Parkinson’s disease. Kang et al. identify pyrimidine-2,4,6-triones as a potential molecular scaffold, which they modify to develop a potent and highly selective CaV1.3 antagonist.
- Soosung Kang
- , Garry Cooper
- & Richard B. Silverman
-
Article |
 Direct isolation and RNA-seq reveal environment-dependent properties of engrafted neural stem/progenitor cells
Direct isolation and RNA-seq reveal environment-dependent properties of engrafted neural stem/progenitor cells
Studies on neural stem and progenitor cells have shown they may be useful in treating spinal cord injuries, but the results are variable. Kumamaruet al.transplant these cells in injured spinal cords of mice, and find that their therapeutic properties are dynamically altered depending on their environment.
- Hiromi Kumamaru
- , Yasuyuki Ohkawa
- & Seiji Okada
-
Article
| Open Access Prion protein facilitates uptake of zinc into neuronal cells
Prion protein facilitates uptake of zinc into neuronal cells
Prion proteins are implicated in a range of neurodegenerative diseases, which are, in part, due to a disruption of metal homeostasis. Wattet al.use selective antagonists to show that prion proteins mediate zinc uptake by interacting with GluA2-lacking, GluA1-containing AMPA receptors.
- Nicole T. Watt
- , David R. Taylor
- & Nigel M. Hooper

 Externally controlled on-demand release of anti-HIV drug using magneto-electric nanoparticles as carriers
Externally controlled on-demand release of anti-HIV drug using magneto-electric nanoparticles as carriers